
Testking_640-802_V13
.pdf
VLANs establish broadcast domains in switched networks, so by virtue of having the option to create many efficient broadcast domains, congestion is reduced and network throughput is greatly enhanced. VLANs allow networks to be divided by department or resource needs, rather then by physical location. When people move departments, leave a department, or join a department, administration is easy and convenient with a few keystrokes.
Incorrect Answers:
B, D. These would be router functions at layer 3. Switches and VLANs operate at layer 2 of the OSI model.
C. The use of VLANs may actually increase the latency in some cases, as traffic from one VLAN to the other will need to be routed.
QUESTION NO: 6
Two VLANs are connected to a switch as follows:
In this TestKing network segment, hosts on the same VLAN can communicate with each other but are unable to communicate with hosts on different VLANs. What is needed to allow communication between these two TestKing VLANs?
A.A router with subinterfaces configured on the physical interface that is connected to the switch
B.A router with an IP address on the physical interface that is connected to the switch
C.A switch with a trunk link that is configured between the switches
D.A switch with an access link that is configured between the switches
E.None of the above
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 191 -

Answer: A
QUESTION NO: 7
You are working as a network technician at TestKing University, when you get a call from the Engineering Faculty. They're complaining that they're receiving obsolete information from the Business Faculty's network traffic broadcasts. What can you do to contain the Business Faculty's broadcast while still keeping it connected to the internet and the enterprise services of the University? (Select all valid answer choices)
A.Use half and full-duplex Ethernet on the Engineering Department LAN
B.Establish a VTP domain to minimize the obsolete traffic
C.Change the switch IP address of the switch
D.Create separate VLANs and subnets for the two departments and route between the two
E.Provide greater bandwidth to the Engineering Department LAN
F.Place the business department on a separate subnet and route between networks
Answer: D, F
Explanation:
In order to prevent the broadcast and link level multicast traffic separated between the departments, they need to be isolated at layer two. This can be accomplished in two ways. The first is to create separate VLANs and place each department into a different one. The second method would be to separate the two departments into two completely different networks, and route between them.
Incorrect Answers:
A.Mixing the use of half and full duplex will make no difference to the number of broadcasts sent.
B.Trunking is only useful in networks that already contain VLANs.
C.This will make no difference, as all users will still be contained within the same IP subnet.
E.The amount of bandwidth involved will not have any impact on the amount of broadcasts that are sent and received.
QUESTION NO: 8
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 192 -
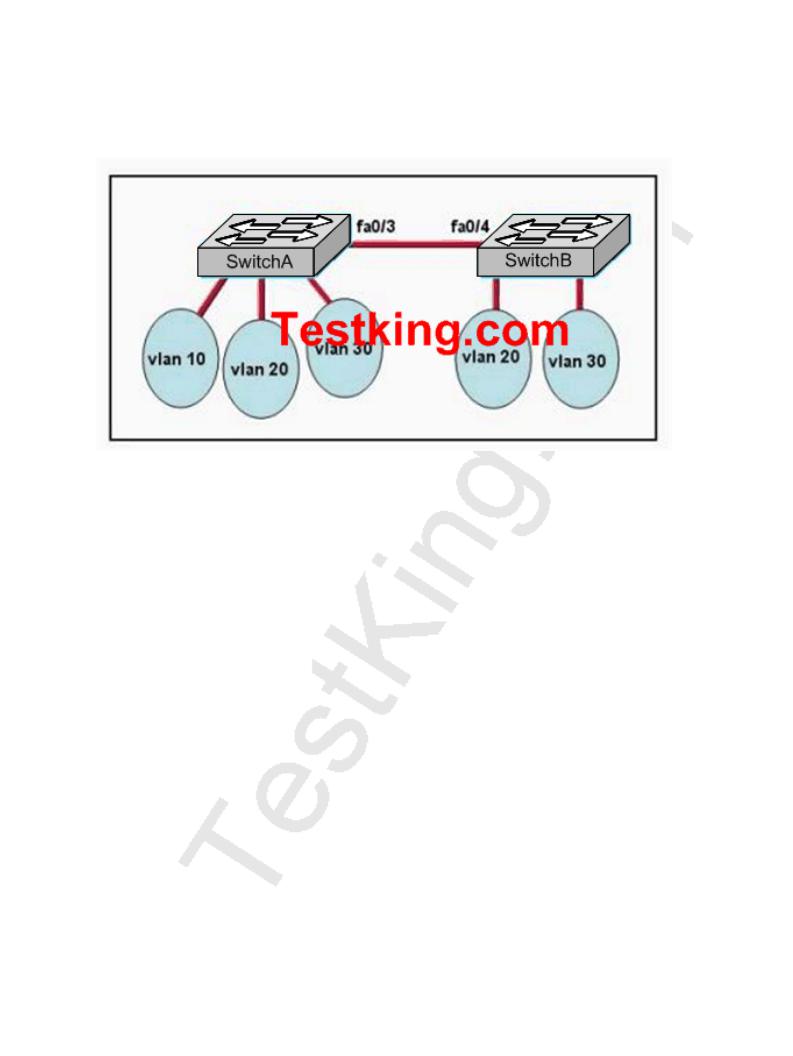
Two TestKing switches are shown below:
The switches have been configured with static VLANs as shown. During testing, the network administrator notices that VLAN 20 on SwitchA has no connectivity with VLAN 30 on SwitchB. What should the network administrator do?
A.Configure the interconnected ports on SwitchA and SwitchB into access mode.
B.Connect the two switches with a straight-through cable.
C.Add a Layer 3 device to connect VLAN 20 and VLAN 30.
D.Configure the management VLAN with IP address.
E.Ensure that the VIP passwords match on both switches.
Answer: C Explanation:
Network devices in different VLANs cannot communicate with one another without a router to route traffic between the VLANs. In most network environments, VLANs are associated with individual networks or subnetworks.
For example, in an IP network, each subnetwork is mapped to an individual VLAN.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 193 -
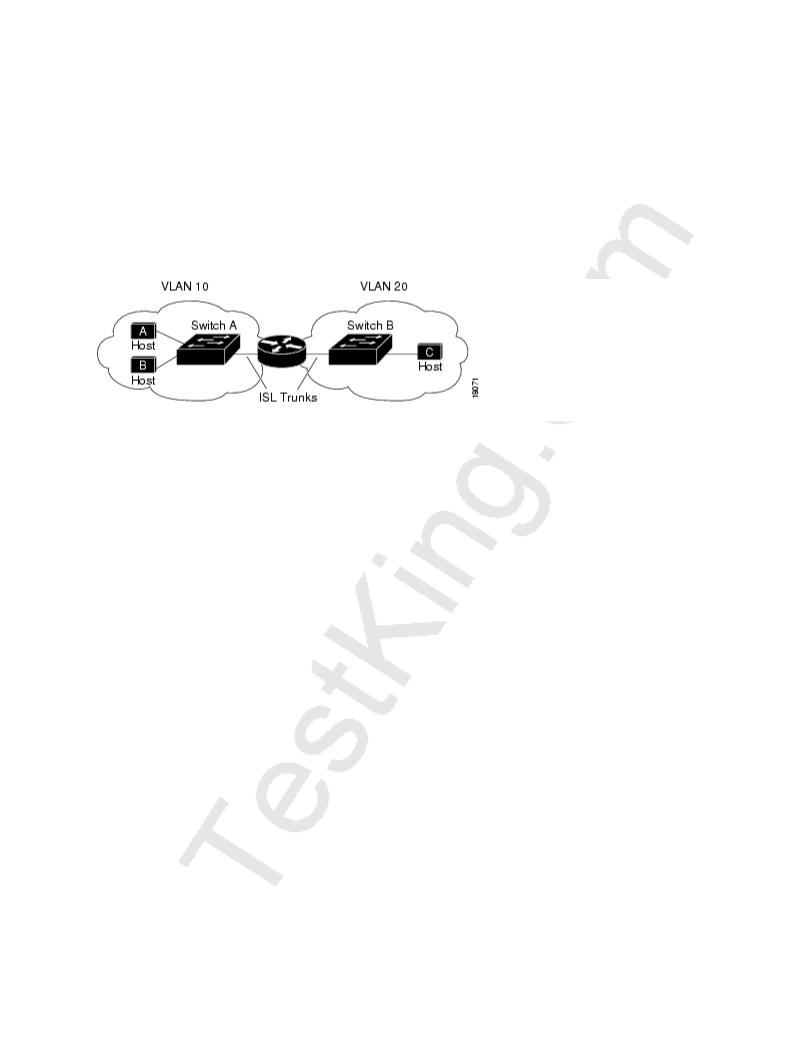
Configuring VLANs helps control the size of the broadcast domain and keeps local traffic local. However, when an end station in one VLAN needs to communicate with an end station in another VLAN, interVLAN communication is required. This communication is supported by interVLAN routing. You configure one or more routers to route traffic to the appropriate destination VLAN.
The diagram below shows a basic interVLAN routing topology. SwitchA is in VLAN 10 and SwitchB is in VLAN20. The router has an interface in each VLAN.
Basic InterVLAN Routing Topology:
When HostA in VLAN10 needs to communicate with HostB in VLAN10, it sends a packet addressed to that host. SwitchA forwards the packet directly to HostB, without sending it to the router.
When HostA sends a packet to HostC in VLAN20, SwitchA forwards the packet to the router, which receives the traffic on the VLAN10 interface. The router checks the routing table, determines the correct outgoing interface, and forwards the packet out the VLAN20 interface to SwitchB. SwitchB receives the packet and forwards it to HostC.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/lan/cat5000/rel_5_2/layer3/routing.htm#wp13354
QUESTION NO: 9
The TestKing network is displayed below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 194 -

Study the exhibit: the topology and the partial switch command output.
The internetwork shown in the exhibit is experiencing connectivity problems. Host TestKing1 is unable to ping Host TestKing2.
What needs to be done to enable these hosts to ping each other?
A.The gateway on Host TestKing1 needs to be changed.
B.The IP address on Host TestKing2 needs to be reconfigured.
C.VLAN2 must be named.
D.The Fa0/1 interface on the TestKingA switch must be configured as a trunk port.
E.Switch port Fa0/1 must be moved to a different VLAN.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 195 -

Answer: D Explanation:
Interface FA0/1 should be in any case configured as a trunk port so that a router could switch packets between the VLANs. The IP addresses are acceptable, so no issues should be caused due this.
QUESTION NO: 10
A TestKing network is displayed below:
Host TestKingB in the diagram is experiencing connectivity problems. Further Testing reveals that it cannot ping the default gateway. Based on the information shown in the exhibit, what is the problem?
A.The IP address of TestKingB is on a different subnet than the default gateway.
B.The Fa0/1 interface on the switch is administratively shutdown.
C.The switch is connected to the wrong interface on the TestKing1 router.
D.The FastEthernet interface on the TestKing router is not configured for trunking.
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 196 -

E.The Fastethernet 0/0.2 interface on the TestKing1 router is configured for the wrong VLAN.
F.The FastEthernet interface of the TestKing1 router is configured with the wrong Ethernet encapsulation.
Answer: E Explanation:
Based on the output shown above, the Fa 0/0.2 interface should be in VLAN 32, which is the same VLAN that other devices in the 192.168.2.X/24 subnet belong to. Interface FA0/0.1 should be configured for VLAN 22, while FA0/0/2 should be configured for VLAN 32.
Section 10: Configure, verify, and troubleshoot VLANs (11 questions)
QUESTION NO: 1
A TestKing switch is connected as shown below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 197 -
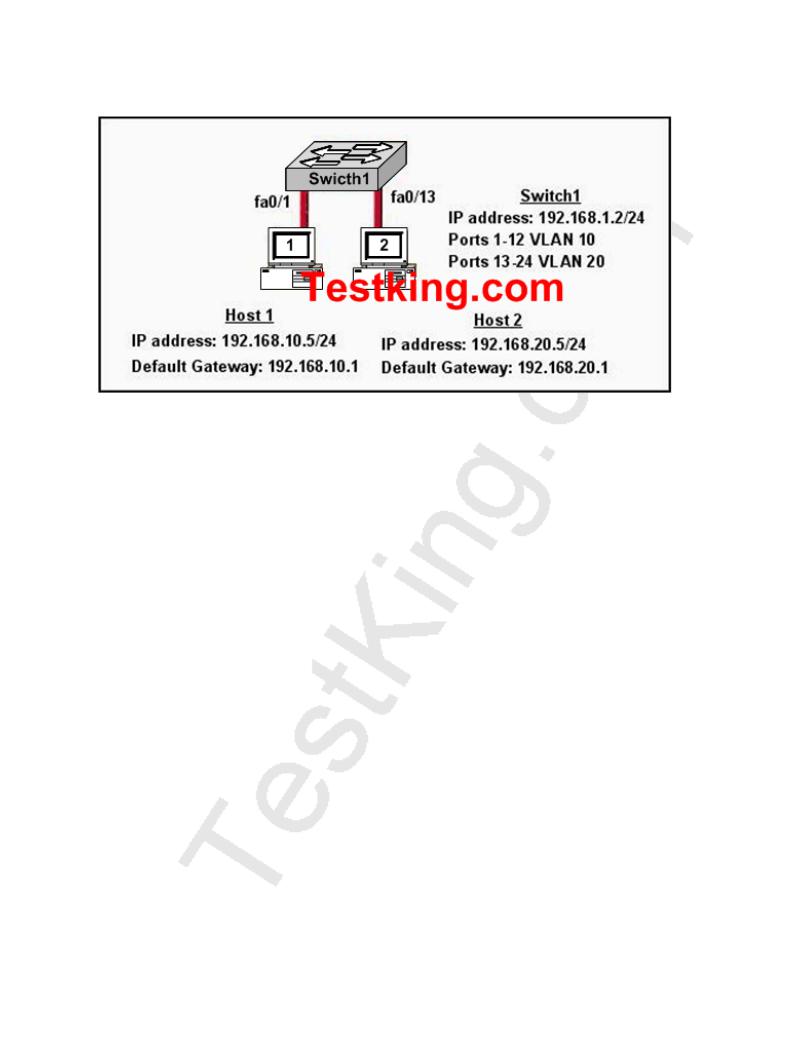
In the network above Host 1 cannot ping Host 2. What needs to be configured to allow host 1 and host 2 to communicate?
A.The switch needs to be configured with an IP address on the correct subnet.
B.The default gateway of the hosts should be configured to 192.168.1.2.
C.Spanning Tree Protocol needs to be configured on the switch.
D.A router needs to be configured to route between the VLANs.
E.VTP needs to be configured on the switch to create a trunk between the VLANs.
Answer: D Explanation:
By default only members of the same VLAN can communicate with each other. For inter-VLAN communication we require a router to route between the different VLANs. Alternatively, if Host1 and Host2 were in the same subnet and the same VLAN, then they would also be able to communicate.
QUESTION NO: 2
The TestKing network is shown below:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 198 -

The network administrator normally establishes a Telnet session with the switch from host A. However, host A is unavailable. The administrator's attempt to telnet to the switch from host B fails, but pings to the other two hosts are successful. What is most likely the issue?
A.Host B and the switch need to be in the same subnet.
B.The switch interface connected to the router is down.
C.Host B needs to be assigned an IP address in VLAN 1.
D.The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.
E.The switch interfaces need the appropriate IP addresses assigned.
Answer: D Explanation:
This scenario requires inter-VLAN routing, which requires a layer three device. Based on the information above, a trunk has indeed been set up to route traffic between VLAN's so the only logical explanation why a host in VLAN 32 can not reach a host in VLAN1 (which is where the IP address of the switch is) would be because no default gateway has been specified in the switch.
Incorrect Answers:
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 199 -

A, C: This is not a requirement, as a number of VLAN's can be configured within a switch, while the management IP address can reside in a different VLAN on a different subnet.
B: Based on the output above, the trunk link (fa 0/3) is indeed up and active.
E: Since switches operate at layer 2, each individual VLAN does not need its own IP address.
QUESTION NO: 3
A portion of the TestKing network is shown in the following exhibit:
Based on this diagram, which of the following is true?
A.Switch TK2 is the root bridge.
B.Spanning Tree is not running.
C.Host D and Server 1 are in the same network.
D.No collisions can occur in traffic between Host B and Host C.
E.If Fa0/0 is down on Router 1, Host A cannot access Server 1.
F.If Fa0/1 is down on Switch 3, Host C cannot access Server 2.
G.None of the above
Answer: E
Leading the way in IT testing and certification tools, www.testking.com
- 200 -
