
new_insights_into_business_studen
.pdf
unit nine |
|
Reading |
The bill of lading |
|
The bill of lading is a transfer document. The exporter writes the importer's |
|
name on the bill of lading, and in this way the importer becomes the legal |
|
owner of the goods. |
CODE NAME: 'CONGENBILL', EDITION 1994
- • Shipper
TRANSEA & Co .
-# Consignee
ASIAN GOODS IMPORTING EMPORIUM
Notify Address
Unit 18, Walterstown
Industrial Estate, Dover
Vessel |
r |
Port of loading |
Star of the East |
|
Bangkok |
-# Port of discherge |
|
|
BILL OF LADING
TO BE USED WITH CHARTER PARTIES
B/L.No. 689381
|
|
^r* Telefax |
• - * |
+1302 |
487862 |
1*. |
+2644 |
8483 |
|
|
Dover
e |
Shipper's description of goods |
|
|
Gross weight |
|||
|
-• 100 cardboard cartons of porcelain items |
1000 |
kg |
||||
|
150 |
cardboard |
cartons |
of |
Christmas decorations |
150 |
kg |
|
200 |
cardboard |
cartons |
of |
rice cookers |
700 |
kg |
Freight payable as per |
. . . |
CHARTER-PARTY dated |
i.V/.ii/.?..? |
FREIGHT ADVANCE
Received on account of freight:
Paid
Time used for loading |
I./.?. |
days |
Hours |
Freight payable at
O [I |
1 D D C r^ at tne Port of Loading in apparent |
O II |
I r r C L/ good order and condition on board |
the Vessel for carriage to the Port of Discharge or so near thereto as she may safely get the goods specified above. Weight, measure, quality, quantity, condition, contents and value unknown.
IN WITNESS whereof the Master or Agant of the said Vessel has signed the number of Bills of Lading indicated below all of this tenor and date, any one of which being accomplished the others shall be void.
FOR CONDITIONS OF CARRIAGE SEE OVERLEAF
Place and date of issue
Bangkok |
Bangkok |
Number of original Bs/L |
Signature |
|
TParfc |
90

The future
Practice
Import Export
Match the parts of the bill of lading opposite with the descriptions below.
1 The date of the contract between the exporter and the shipping company, a
2The name of the importer.
3Details of the goods.
4The name of the ship.
5Money paid to the shipping company before the journey.
6The place where the goods are unloaded.
7The name of the shipping company.
8The place where the goods are loaded.
LanguageFocus
Which sentence below refers to
1a future fact?
2a prediction not based on present evidence?
3a degree of probability or certainty?
4a decision made now?
5something decided before, an intention?
6a prediction based on present evidence?
aIs it urgent? OK, I'll do it right now.
bNext year, we're going to start exporting to Japan.
cHis overseas trip will be a success.
dExports are slowing down; there's going to be a recession.
eThe market will definitely be there in a few years.
fThis company will be 100 years old next year.
••For more information on will and going to, turn to page 167.
Complete this dialogue between Steve, an export manager, and Bob, his agent in Australia, using will or going to and the verbs in brackets.
Steve: Hello Bob, I'm phoning to check a few things with you about my trip next
week. |
|
Bob: Hold on Steve, I 1 |
(get) the file out. Right, how can I help you? |
Steve: Well, we've had a few problems here in the European office so I've decided to
|
stay and book a later flight. |
Now 12 |
|
(leave) on the 5th, not the |
||||||
|
3rd. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bob: |
Actually that suits me better, that way 13 |
|
|
(have) time to finish the |
||||||
|
monthly sales figures before you come. |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Steve: Good, I think we 4 |
|
(need) to have a look at those together. |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Bob: |
Don't forget, we 5 |
|
|
(visit) the Melbourne office when you're here. |
||||||
Steve: I haven't forgotten, I'm sure it 6 |
|
(be) interesting to see how they |
||||||||
|
run their operation. OK, see you next month. |
|||||||||
Bob: Looking forward to it. Bye. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Steve: Bye. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
91
unit nine
Describing
trends
Practice
Unit 1 looked at some of the nouns and verbs used to describe changes in price, quantity and amount, for example:
Noun |
Verb |
an increase |
to increase |
a rise |
to rise |
a decrease |
to decrease |
a drop |
to drop |
a fall |
to fall |
These can be qualified with an adjective or adverb to describe a change more precisely. Complete the table.
Used to show a small change:
Used to show a regular movement:
Used to show considerable, striking or unexpected change:
Adjective Adverb
aslight
bgradual
csteady
dsharp
edramatic
fsudden
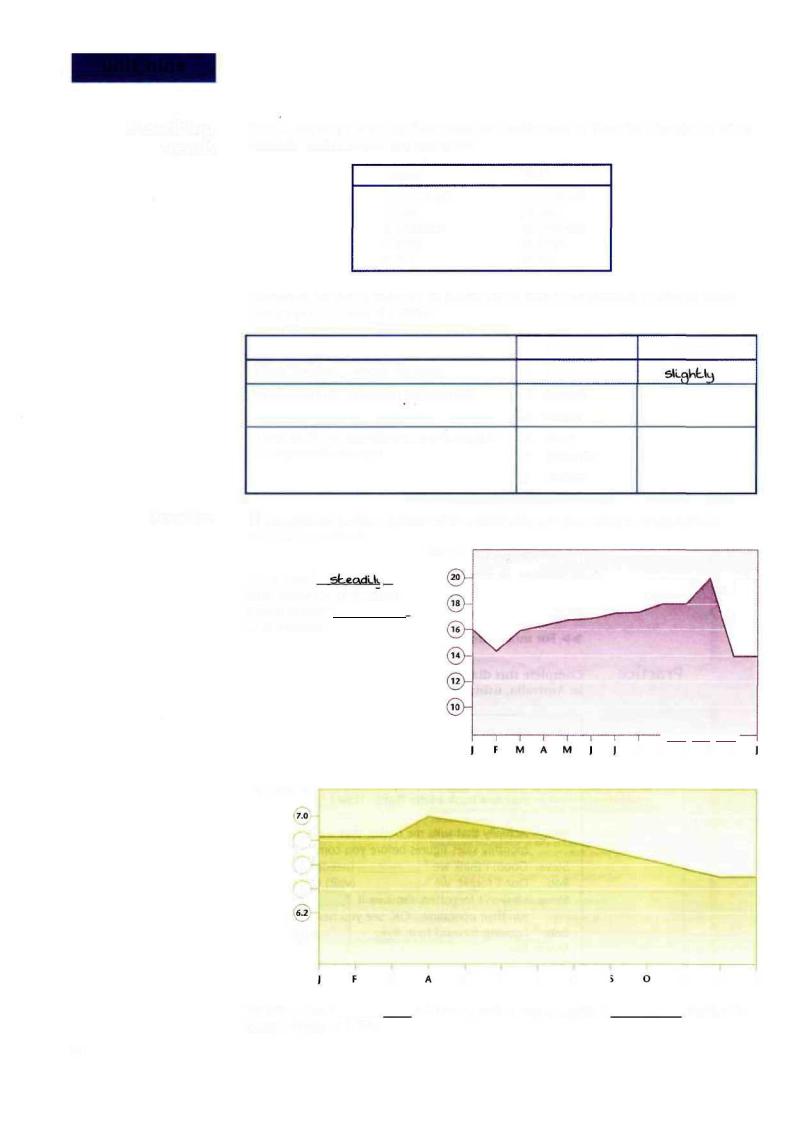
1 Complete the descriptions of the following graphs using an appropriate adjective or adverb.
Prices £
Prices rose 1 ) from February to October, before falling 2
in November.
T |
1 |
1 |
r |
A S |
O |
N |
D |
Inflation %
"/o
6.8
6.6
6.4
©-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
|
|
M |
M |
j |
j |
A |
: |
N |
D |
j |
Inflation rose 3 |
|
|
in March, before beginning its 4_ |
descent to |
|
|||||
today's figure of 6.5%. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
92
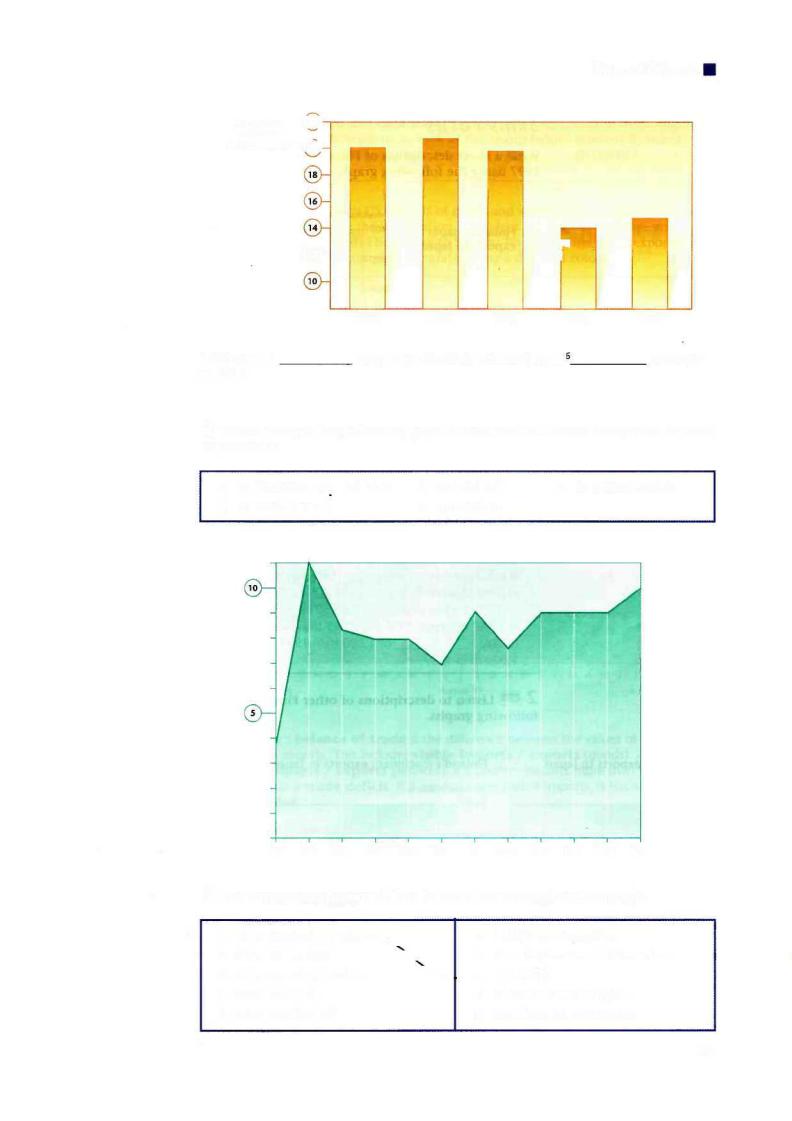
Import Export
No of units |
(22) |
produced |
|
(in thousands) |
^ g ) |
®- |
|
|
|
r |
|
|
1995 |
1996 |
1997 |
1998 |
1999 |
1998 saw a 5_ |
drop in production, followed by a ' |
. recovery |
|||
in 1999. |
|
|
|
|
|
2 Which parts of the following graph would you talk about using each of these expressions?
a |
to fluctuate MOWJ to Sep |
b |
to level off |
c to remain stable |
d |
to reach a peak |
e |
to stand at |
|
Jan |
Feb Mar Apr May Jun |
Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec |
3 Join expressions from each box to make sentences about the graph.
1 |
Sales reached a peak —^ |
|
a |
10,000 in December. |
2 |
Sales fluctuated |
>v |
b |
from September to November. |
3 |
Sales remained stable |
^— - |
c |
of 11,000. |
4 |
Sales stood at |
|
d |
at about 8,000 in April. |
5 |
Sales levelled off |
|
e |
from May to September. |
93
unit nine
Skills Focus
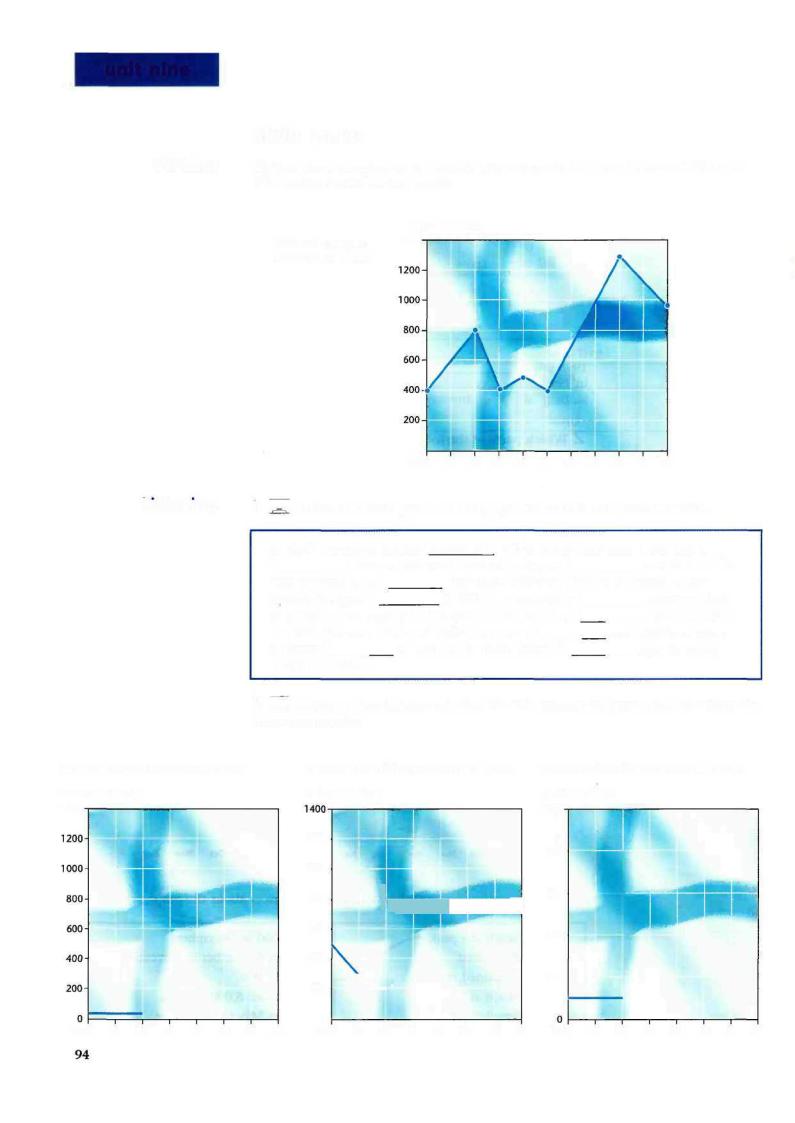
Writing Write a short description of Finnish paper exports to Japan between 1987 and 1997 using the following graph.
Finland's paper exports to Japan
markkaa (millions)
1400
0
1987 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97
Listening |
1 |E=a| Listen to a description of the graph above and complete the text. |
|||||||||||||
|
In 1987 the export figures 1sbood ah 400 m Finnish markkaa. There was a |
|||||||||||||
|
2 |
|
|
between 1987 and 1989 when figures 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
over 800 m. This |
||||
|
was followed by a 4_ |
_ between 1989 and 1990 when Finnish paper |
||||||||||||
|
exports to Japan 5_ |
to 400 m. There was a 6 |
|
|
|
|
between 1990 |
|||||||
|
and 1991 when exports hit the 450 m mark but they 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
again to 400 m |
|||||||
|
in 1992. Between 1992 and 1995 there was a 8 |
|
|
|
and exports of paper |
|||||||||
|
to Japan 9 |
|
|
|
of 1,300 m in 1995, before10. |
|
|
|
again to under |
|||||
|
1,000 m in 1997. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2 [ml Listen to descriptions of other Finnish exports to Japan and complete the following graphs.
Finland's wood exports to Japan |
Finland's machinery exports to Japan |
Finland's chemical exports to Japan |
||||||
markkaa (millions] |
markkaa (millions) |
|
|
|
|
markkaa (millions) |
||
1400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1000 |
|
1200- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800- |
|
1000- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800- |
|
) |
• • • • • • 1 |
600- |
|||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
400- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
400- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
200- |
|
200- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
i |
i |
i |
i |
i |
i |
|
1990 |
91 |
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 |
96 |
97 |
1990 |
91 |
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 |
96 |
97 |
1990 |
91 |
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 |
96 |
97 |

Import Export
1 Work in pairs. You will each study a graph showing US trade from August 1996 to August 1998. Student A, look at the graph below. Student B, turn to page 160.
Student A
The graph below shows US imports of goods and services from August 1996 to August 1998. Describe the information to Student B using the language you have learnt in this unit. Then listen to Student B's description of US exports for the same period and complete the graph using a different colour.
US International Trade in Goods and Services
Billions $
95- |
95 |
- 90
75 |
|
|
70 |
|
70 |
65 |
|
- 6 5 |
|
S O N D J |
F M A M J |
August 96 |
August 97 |
August 98 |
2 A country's balance of trade is the difference between the values of its imports and exports. This includes visible imports / exports (goods) and invisible imports / exports (services). If a country imports more than it exports, it has a trade deficit. If it exports more than it imports, it has a trade surplus.
Look at the graph in Speaking 1.
1Did the US have a trade deficit or surplus?
2In pairs, calculate the balance of payments for the following periods.
a May 1997 deficit of |9 bo
bOctober 1997
cMarch 1998
3 a When did the US have the lowest deficit in the period from August 1996 to August 1997?
bWhen did the US import the most?
cWhen did the US export the most?
95

unit
CompanyPerformance
ry ^L Companies need to know how they are performing in order to analyse problems, find solutions and make plans for the future. Management accounts provide data about operational efficiency and financial accounts give information about financial performance. These tell the company not only how much it is selling, or how much revenue it is receiving, but also what its costs are - how much it has to pay for the different things that it needs in order to operate. With this information a company can then calculate how much money it has made (profits) or how much it has lost (losses) during a specific period. Listed companies, whose shares are sold on the stock exchange, have to present their accounts to the public in an annual report.
96

|
CompanyPerformance |
Lead-in |
1 With the increasing complexity of the modern business world, companies |
|
often need to seek the advice of specialist consultants, such as |
|
PricewaterhouseCoopers, who can help them improve their performance and |
|
prepare for the future. |
Match the departments of PricewaterhouseCoopers below with their functions.
1 |
FAS |
(Financial Advisory Services) |
a |
check company accounts |
2 |
MCS |
(Management Consulting Services) |
b |
provide advice on finance |
3 |
TLS |
(Tax and Legal Services) |
c |
advise on performance |
4 |
ABAS (Assurance Business Advisory Services) |
d |
provide taxation advice |
|
2 You will hear four managers from PricewaterhouseCoopers describing the services their departments provide. Before you listen, decide which department a client would contact to
1 arrange for an evaluation of its administration. |
MCS |
2obtain advice about new VAT laws.
3decide what to do about a subsidiaiy company that is losing money.
4look at ways of improving its computer network.
5decide which aspects of the business to concentrate on in the future.
6find out the value of a company.
7certify that the annual accounts are accurate.
[US Listen to the managers and check your answers.
3 Read the text below and answer the questions.
1 What is the purpose of an annual report?
2 What are stakeholders?
What's an
annual report?
An annual report is prepared by the management of a company whose stock is traded publicly. It discusses the company's financial affairs. An annual report performs a useful function in a free market system, transmitting information from the company to its shareholders and investing public. Although the report is addressed to shareholders, other people who have a stake in the business - stakeholders such as employees, suppliers, customers, and lenders - will find it informative.
MTS Employee Supplement to the 1994 Annual Report
97

unit ten
Reading
I Read the text and match the headings to the paragraphs.
Paragraphs 1-5 |
Paragraphs 6-10 |
Report of management |
Financial highlights |
Auditor's report |
Letter to stockholders |
Management discussion |
Corporate message |
Financial statements and notes |
Board of directors and management |
Selected financial data |
Stockholder information |
Anatomyofanannualreport
White most annual reports contain optional elements, all reports contain information required by the Securities Exchange Commission or SEC, the commission that controls and administers the activities of US stock exchanges.
SEC-required elements include:
reporfc. This summary by independent
public accountants shows whether the financial statements are complete, reliable, and prepared consistent with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
2 Reporfc. of manexae.rcAr\L This letter, usually from the
board chairperson and the chief financial officer, takes responsibility for the validity* of the financial information in the annual report, and states that the report complies with SEC and other legal requirements.
3 These provide the complete numbers for the
company's financial performance and recent financial history. The SEC requires:
• Statement of earnings*
The statement of earnings shows how much revenue a company brings into the business, and the costs and expenses associated with earning that revenue during that time.
• Statement of cash flows*
The statement of cash flows reports the flow of cash into and out of a company in a given year. Cash is a company's lifeblood*. Cash includes currency and deposits in banks.
Cash equivalents are short-term, temporary investments that can be quickly and easily converted to cash.
• Statement of financial position*
The statement of financial position reports a company's financial status at a set date. The statement is like a snapshot* because it shows what the company is worth at that set date. The statement shows:
•what the company owns (assets)
•what the company owes (liabilities)
•what belongs to the owners (stockholders' equity)
4 This information summarizes a company's
financial condition and performance over five years or
longer, including gross profit and net earnings (net income).
5 This series of short, detailed reports
discusses and analyzes the company's performance. It covers results of operations, and the adequacy* of resources to fund operations.
Optional elements include:
6. This list gives the names and position titles of the company's board of directors and top management team. Sometimes companies include photographs.
7This information covers the basics - the
company's headquarters, the exchanges on which the company trades its stock, the next annual stockholders' meeting, and other general stockholder service information. It is usually in the back of the annual report.
8 This may be from the chairperson of the
board of directors, the chief executive officer, or both. It can provide an analysis and a review of the year's events, including any problems, issues, and successes the company had. It usually reflects the business philosophy and management style of the company's executives, and it often lays out* the company's direction for the next year.
9Some consider this an advertisement for the company. However, it almost always reflects how a company sees itself, or how it would like others to see it. Here, the company can explain itself to the stockholders, using photographs, illustrations, and text. It may cover the company's lines of business, markets, mission*, management philosophy, corporate culture, and strategic direction.
10Probably the most often-read section of any annual report, these give a quick summary of a company's performance. The figures appear in a short table, usually accompanied by supporting graphs.
International Business Machines
Guide to UnderstandingFinancials
Validity: correctness
'statement of earnings (US): profit and loss account (GB) 'statement of cash flows (US): cash flow statement (GB)
*lifeblood: the essential item
'statement of financial position (US): balance sheet (GB)
*a snapshot: information that quickly shows a situation at a point in time
'adequacy: sufficiency, whether there is enough
'to lay out: to present
*a mission: the aim of an organisation
98

Company Performance
2 Read the text again. Which section of a company's annual report would you read for information about these things?
1any difficulties the company has had to face during the last year
2how the company performed during previous years
3the company's results for the year
4whether the report satisfies government requirements
5the company's plans for the next year
Vocabulary 1 The article includes words for different people who are either directly or indirectly involved with a listed company. Match the words for people from the text with their corresponding definitions.
a director
a chief executive officer a stockholder
a chief financial officer
5a chairperson
6an auditor
ahas bought shares in the company
bis in charge of the board
cis a member of the board
dis an outside financial specialist
eis responsible for finance
fis responsible for all operations
2 Find words in the text which correspond to the following definitions.
Statement of earnings |
|
1 money received, generally |
|
from sales |
(_ |
2 money that is spent on such |
|
things as salaries, rent, |
|
office supplies, |
|
advertising and taxes |
(_ |
Statement of cash flows |
|
3 money in general use as cash, |
|
such as coins or bank notes |
(_ |
4 money or its equivalent paid |
|
into an organisation for safe keeping, |
|
or as security, or to bear interest |
(_ |
5 money that has been invested |
|
but that can be rapidly |
|
changed into cash |
(_ |
Statement of financial position
6anything with money value that a company owns
7 a company's debts
Selected Financial Data
8the difference between a company's total sales and costs of sales
9a company's total revenue minus total expenses, also known as 'the bottom line'
3 Complete the following extract from the financial highlights section of an annual report using words from Vocabulary 2.
a |
rcvcriue |
$1,145,773 |
b |
|
|
|
Materials and labor |
$794,780 |
c |
fa-W |
$350,993 |
d Selling and administration |
$230,153 |
|
|
Interest |
$14,435 |
e |
(c-d) |
$106,405 |
99
