
English-Повн термін-біохімія-03-Р-ни---2013
.pdf
Solutions are homogenous thermodynamically stable systems of variable composition which are contained of two or more components and
products of their interaction.
Components of solutions are the chemical substances which form solution during their mixing and these components could be isolated with high purity degree.
Solvent is a substance which does not change its aggregate state during its dissolving or it is component of larger amount in composition of solution
Solute (one or more) is the second component of solution. Its particles are separate molecules or ions (which have size smaller than 1 nm) and are uniformly distributed between molecules of solvent.
!!! During formation of solution, its components lose partially their physical properties.
11

Solution has place between mechanical mixtures and chemical substances.
What its difference from the mixture is?
Some microscopic volume of solution is in the state of thermodynamic equilibrium and has the same chemical composition and physical properties as a whole solution.
Formation of solution is accompanied by heat effect and volume change.
What its difference from chemical substances is?
Composition of solution can be changeable depends on amount of the components.
Solutions are not under law of constant composition and aliquot ratios that’s why they are called combinations of changeable composition.
Solutions have weak van-der-vaalse forces and even
hydrogen-bonds.
12
Classification of solutions (according different characteristics)
1.According aggregate state, solution are divided into gaseous, liquids and solids
What do you know example of gas solutions? (Air) How could be liquid solutions formed ?
-by gases dissolving in liquid ? Example.
-by solid substances dissolving in liquid ? Seawater, the salted water.
-by liquid dissolving іn liquid ? Example.
What do you know example of solid solutions? Example.
13

2.According to content of the dissolved substance (solute), solutions are divided into diluted and concentrated.
What is the diluted solution? (The diluted solution is the solution with the dissolved
content less than 30% of substance)
How is content of solute in the diluted
solution? (less than 30% solutions)
What is the concentrated solution? (the
concentrated solution is the solution with the dissolved content more than 30% of substance)
How is content of solute in the concentrated solution? (more than 30%
solutions)
more or less than 30% solutions
14
3. According to solubility under the certain conditions in the certain mass of solvent, solutions are unsaturated, saturated, supersaturated.
The unsaturated solution
АВ (solid phase) → АВ (solution)
The saturated solution
АВ (solid phase) АВ (solution)
The supersaturated solution
АВ (solid phase) АВ (solution)
Homework: Electrolytic and not electrolytic solutions
15
Theories of solutions
Historically, how many theories of solutions are:
Physical theory of solution
С. Arrhenius, J. van't Hoff, V. Osvald considered dissolving substances as a process of uniform distribution particles of solute between particles of solvent. Solution is a mechanical mixture.
Chemical (or solvate, or hydrate) theory, (D. Mendeleyev, І. Kablukov, М. Kurnakov) is based on what?
Formation of unstable complexes (solvate) between particles of solute and solvent.
Which complexes are called hydrate? (Hydrate is unstable complexes between particles of solute and solvent (water).)
Is CuSO4 5H2O stable? (Yes, it is.)
16
Modern theory of solutions joins physical and chemical points of view. Could you formulate definition of modern
theory of solutions ? (Try, to joins physical and chemical points of view)
What do you think about the sole theory of solutions? ()
According the sole theory of solutions, it would be possible to determine characteristics of solutions depending on the known characteristics of components in their pure state. Did this theory form? (Not, yet !!!)
Main physical and chemical index, for solvent nature and polarity of its molecules is dipole moment μ.
What polar solvents do you know?
The highest dipole moment is the dipole moment of water (μ=6,1 10-30 Кл м). Does dipole moment of water play role in dissolving substances with ionic and covalent bonds? (Yes, it does)
Are substances with non-polar covalent bond dissolved easy in non-polar solvent or not? (Yes)
17
Formation of ideal solutions is accompanied change of volume and heat effect or not ?
??? Which model of ideal solution could be a very diluted solution,
high concentrated solution or solution of 50% of the substance?
18
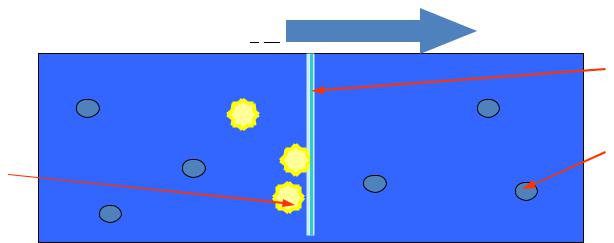
Diffusion
Diffusion - is arbitrarily process of equalization of concentration of substances in the whole volume of the solution caused by the thermal motion of particles of solute and solvent
Diffusion occurs from solution of greater concentration of solute in a solution with a lower concentration of this substance.
Direction of diffusion 


1
2
3
1 – a permeable membrane; 2 – molecules of solvent; 3
– particles of solute
19
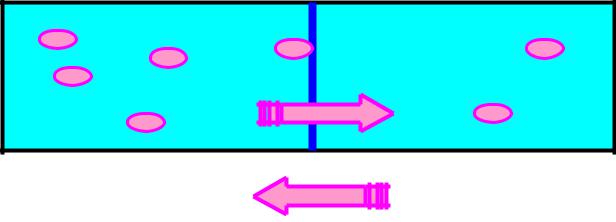
Penetration of charged particles (ions) through membranes depends on
concentration and electrochemical gradient.
In biological systems:
Diffusion of neutral (molecules, atoms) and charged particles (ions, electrons).
Does diffusion of ions, electrons depend only on difference of their concentrations?
Diffusion is a cause of biological potentials.
20
