
Хорошев / ИЛП_материал_маг_02.15 / Спецификация AECMA Specification 2000M / MIL-STD-1388-2B
.pdfMIL-STD-1388-2B
1.SCOPE.
1.1 Purpose. This standard prescribes the data element definitions (DED), data field lengths, and formats for Logistic Support Analysis (LSA) Record (LSAR) data. It identifies the LSAR reports that are generated from the LSAR data and identifies the LSAR relational tables and automated data processing (ADP) specifications for transmittal and delivery of automated LSAR data.
1.2 Application of standard. This standard applies to all system/equipment acquisition programs, major modification programs, and applicable research and development projects through all phases of the system/equipment life cycle. This standard is for use by both contractor and government activities. As used in this standard, the requiring authority is generally a government activity but may be a contractor when LSA documentation requirements are levied on subcontractors. The performing activity may be either a contractor or government activity. The use of the term, contract, in this standard includes any document of agreement between organizations to include between a government activity and another government activity, between a government activity and a contractor, or between a contractor and another contractor.
1.2.1 Content of appendices. There are six appendices in the standard. Appendix A contains the LSAR relational tables necessary for the development of a relational LSAR database. A description and the required format for each LSAR report is contained in appendix B. All reports contained in appendix B may be generated either manually or via automated techniques by using the LSAR data defined in this military standard. Appendices C, D, and F are guidance appendices covering assignment of the key data elements LSA Control Number (LCN), Alternate LCN Code (ALC), Usable On Codes (UOC); tailoring of the LSAR data; and, LSAR acronyms. Appendix E contains an LSAR Data Element Dictionary providing definitions for all data specified by appendix A. All appendices, except for C, D, and F, establish requirements and can be included/referenced in contractual documents.
1.2.2Tailoring. This standard shall not be specified in a contract without also specifying MIL-STD-1388-1, LSA. The requiring authority will use MIL-STD-1388-1 in the selection of tasks for inclusion in the contract statement of work (SOW) and shall establish the LSA documentation requirements based upon the elements identified in those tasks. Further tailoring of LSA documentation requirements shall be based on MIL-STD-1388-1 tasks performed in previous program phases, other system engineering program requirements, and logistics related data item descriptions (DID) included in the solicitation document. Detailed guidance on tailoring the LSAR data requirements is included in appendix D.
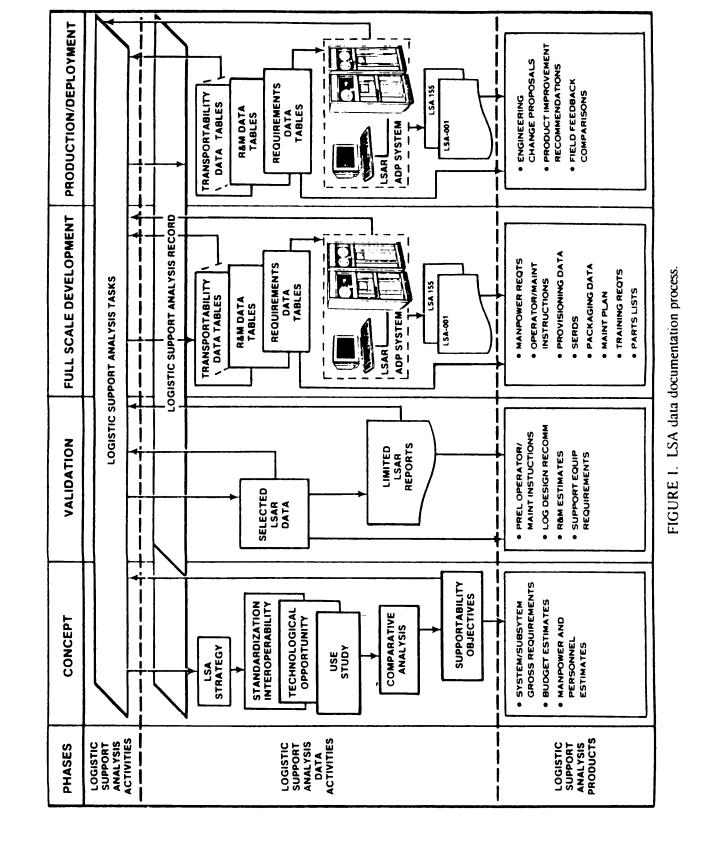
1.2.3LSA data documentation process. The LSA process is conducted on an iterative basis through all phases of the system/equipment life cycle to satisfy the support analysis objectives. Similarly, LSA data is generated in all phases of the system/equipment life cycle and is used as input to
follow-on analyses and as an aid in developing logistics products. Although automation of the LSAR data as depicted on figure 1 is not mandatory, it is strongly encouraged and should be a consideration in tailoring the LSA data effort. A more detailed display of the LSAR data flow and its interface, with the system engineering and the logistics functional organizations, is
- 1 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
- 2 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
- 3 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
- 4 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
:
- 5 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
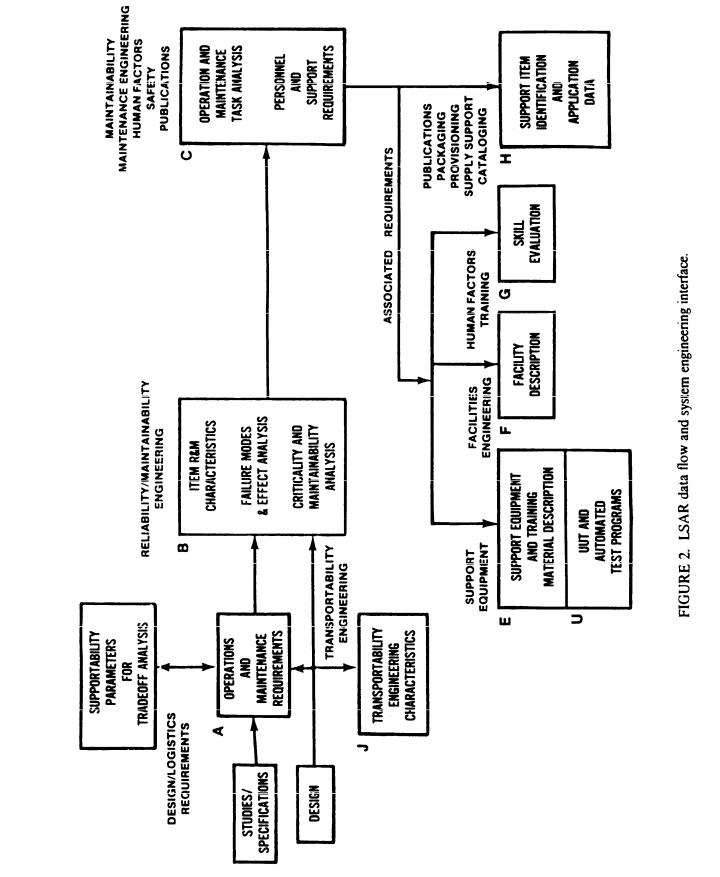
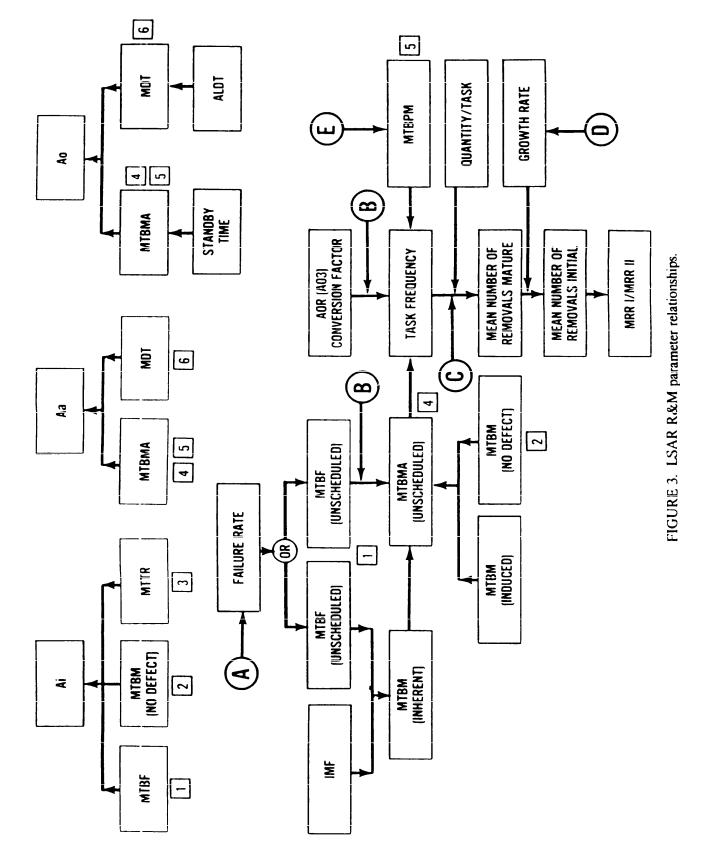
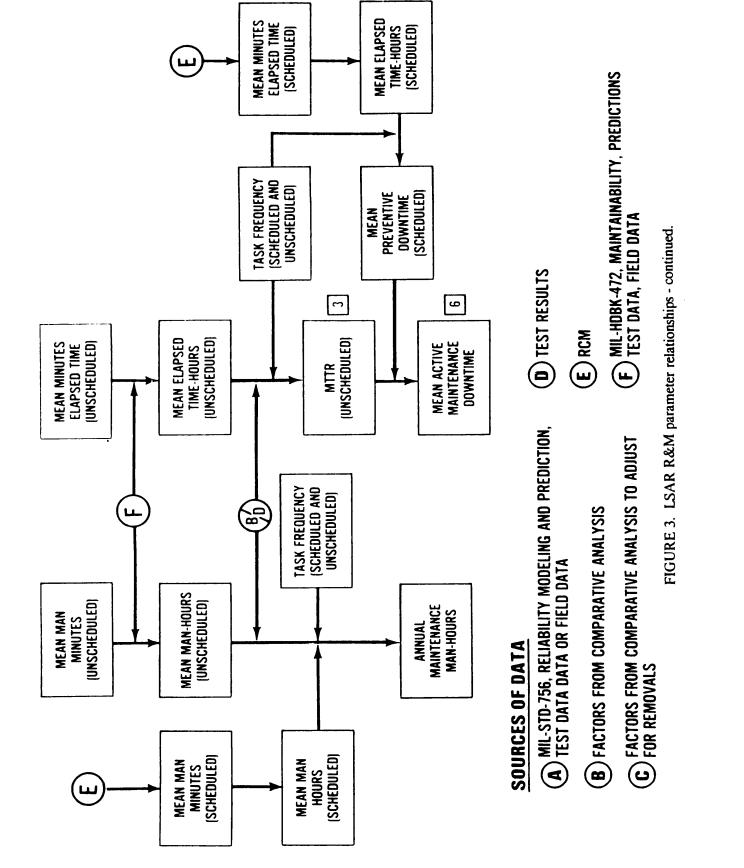
provided on figure 2. The figure represents general data table generation relationships and organizational elements normally responsible for generation of LSAR data. Figure 2 should not be misconstrued to mean that one type of data table must be completed in its entirety before the next data table can be completed. For example, certain reliability and maintainability (R&M) estimates included on the B tables must be completed prior to estimating logistics elements on other tables (R&M relationships are shown on figure 3). However, generation of LSAR data is also dependent on the design engineering process and release of drawings (preliminary, development, or final). Completion of B and C tables for a single assembly would provide the information necessary for initiation of data tables associated with support items (H tables), and also data related to support and test equipment (E & U tables), facilities (F tables), and skills evaluation and justification
(G tables) when peculiar requirements are identified. The LSAR data flow will be repeated for each repairable item comprising a system/end item until the total logistics data requirements are established.
2.REFERENCED DOCUMENTS.
2.1 General. Completion of the LSAR data requires use of many related documents from which the appropriate data/codes can be obtained. The specific use of each document is identified in the appropriate section or appendix of this standard. Unless otherwise specified, the following standards and handbooks of the issue listed in that issue of the Department of Defense Index
of |
Specifications and Standards |
(DODISS), specified in the solicitation form, |
a |
Part Of this standard to the |
extent specified, herein. |
Military Standards.
MIL-STD-12
DOD-STD-100
MIL-STD-155
MIL-STD-196
MIL-M-49502
MIL-STD-470
MIL-STD-482
MIL-STD-785
MIL-STD-815
MIL-STD-875
Abbreviations for Use on Drawings, Specifications, Standards, and in Technical Type Publications
Engineering Drawings Practices
Joint Photographic Type Designation System
Joint Electronics Type Designation System
Manuals, Technical: Repair Parts and Special Tools List
Maintainability Program for Systems and Equipment
Configuration Status Accounting Data Elements and
Related Features
Reliability Program for Systems and Equipment Development and Production
Designation System for Liquid, Solid and LiquidSolid (Hybrid) Propellant Rocket Engines and Motors
Type Designation System for Aeronautical and Support Equipment
- 6 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
MIL-STD-879 MIL-STD-882 MIL-STD-965 MIL-STD-1388-1 MIL-STD-1390 MIL-STD-1478 MIL-STD-1519 MIL-STD-1561 MIL-STD-1629
MIL-STD-1839
MIL-STD-1843
MIL-STD-2073-1
MIL-STD-2073-2 MIL-STD-2097
MIL-STD-2173
DOD-STD-2121(Navy)
Designation of Aircraft Propulsion Gas Turbine Engines System Safety Program Requirements
Parts Control Program
Logistic Support Analysis
Level of Repair
Human Performance Analysis
Test Requirements Documents, Preparation of Provisioning Procedures, Uniform Department of Defense
Procedures for Performing a Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis
Calibration and Measurement Requirements
Reliability Centered Maintenance for Aircraft Engines and Equipment
DOD Materiel, Procedures for Development and Application of Packaging Requirements
Packaging Requirement Codes
Requirements for Acquisition of End Items of Support Equipment, Associated Integrated Logistics Support, and Related Technical Data for Air Systems
Reliability Centered Maintenance for Naval Aircraft Weapon Systems and Support Equipment
Determination of Electronic Test Equipment Parameters
Military |
Handbooks. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIL-HDBK-59 |
Computer-Aided Acquisition and Logistic Support (CALS) |
||||||
|
|
Program |
Implementation Guide |
|
|
||
MIL-HDBK-217 |
Reliability Prediction of Electronic Equipment |
|
|||||
Military |
Specifications. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIL-T-31OOO |
Technical Data Packages, |
General |
Specifications |
for |
|||
MIL-F-7024 |
|
Fluids, |
Calibrating, |
for |
Aircraft |
Fuel System Components |
|
MIL-M-63036A |
Manuals, |
Technical: |
Operator’s, |
Preparation of |
(Army) |
||
- 7 -
MIL-M-63038B
MIL-M-83495
MIL-STD-1388-2B
Manuals, Technical: Organizational or Aviation Unit Direct Support, or Aviation Intermediate, and General Support Maintenance (Army)
Manuals, Organizational Maintenance Manual Set, General
Requirements for Preparation of(for Aircraft Missles and
Space Vehicles)
Federal Manuals and Catalogs. |
|
H4/H8 |
Commercial and Government Entity Code |
H6-1 |
Federal Item Name Directory for Supply Cataloging |
(Unless otherwise indicated, copies of federal and military specifications,
standards, |
and handbooks are available from the Standardization Documents |
|||||
Order Desk, |
Building |
4D, 700 |
Robbins Avenue, Philadelphia, PA, 19111-5094.) |
|||
Bulletins. |
|
|
|
|
||
ANA |
Bulletin |
306 |
Engines, |
Aircraft Turbine and Jet, Designation of |
||
ANA |
Bulletin |
395 |
Engines, Aircraft Reciprocating, Designation of |
|||
Other Documents. |
|
|
||||
DOD 41OO.38-M |
DOD Provisioning and Other Preprocurement Screening |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Manual |
|
DOD 5000.12-M |
DOD Manual for Standard Data Elements |
|||||
DODD 5000.39 |
|
Acquisition and Management of Integrated Logistic |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Support for Systems and Equipment |
|
AR |
70-50 |
|
|
Designating and Naming Defense Equipment |
||
NAVMATINST |
8800.4 |
Rockets and Guided Missiles |
||||
AFR |
82-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
AR |
700-26 |
|
|
|
|
|
NAVAIRINST 131OO.3 Designating and Naming Military Aircraft |
||||||
AFR |
66-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
AR |
700-82 |
|
|
Joint Regulation Governing the Use and Application |
||
OPNAVINST |
4410.2 |
|||||
AFR |
66-45 |
|
|
of Uniform Source Maintenance and Recoverability Codes |
||
MCO |
4400.120 |
|
|
|||
DSAR 4100.6 |
|
|
|
|||
NAVFAC |
P-72 |
|
Category Codes for Real Property, Navy |
|||
NAVPERS |
15839 |
Manual of Navy Officer Classifications |
||||
NAVPERS |
18068 |
Manual of Navy Enlisted Manpower and Personnel |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Classifications and Occupational Standards |
|
- 8 -
MCO P 1200.7
AR 415-28
AR 611-101
AR 611-112
AR 611-201
AFR 36-1
AFR 39-1
AFM 86-2
FPM Supplement
512-1
SB 700-20
JCS PUB 1
DA CPR 502
DA PAM 700-20
MIL-STD-1388-2B
Military Occupational Specialties
Department of the Army Facility Classes and Construction
Categories
Manual of Commissioned Officer Military Occupational
Specialties
Manual of Warrant Officer Military Occupational
Specialties
Enlisted Military Occupational Specialties
Officer Classification Manual
Airman Classification Manual
Standard Facility Requirements
Civil Service Commission, Job Grading Standard
Army Adopted/Other Items Selected for Authorization/ List of Reportable Items
Dictionary of United States Military Terms for Joint Usage
Department of Army - Civilian Personnel Regulations,
Standardized Job Descriptions
Department of Army - Test, Measurement, and Diagnostic
Equipment Register
Industry Documents.
ANSI Y32.16 Reference Designations for Electrical and Electronics Parts and Equipments
(Non-Government standards and other publications are normally available from the organizations that prepare or distribute the documents. These documents also may be available in or through libraries or other informational services.)
3. DEFINITIONS. The LSAR data elements are defined in the description of the LSAR reports contained in appendix B and in the LSAR data element dictionary comprising appendix E of this standard. In addition, for the purposes of this standard, the following definitions shall apply:
3.1 Assembly. A number of parts or subassemblies, or any combination thereof, joined together to perform a specific function and capable of disassembly (e.g., power shovel-front, fan assembly, audio frequency amplifier). NOTE: The distinction between an assembly and subassembly is
- 9 -
MIL-STD-1388-2B
determined by the individual application. |
An assembly, |
in |
one instance, may |
be a subassembly in another where it forms |
a portion of |
an |
assembly. |
3.2Attaching part. An item used to attach assemblies or parts to the equipment or to each other.
3.3Component. An assembly or any combination of parts, subassemblies, and assemblies mounted together normally capable of independent operation in a variety of situations.
3.4Design Change. An approved engineering change incorporated into the end item which modifies, adds to, deletes, or supersedes parts in the end item.
3.5 End Article/Product. A component, assembly or subassembly being procured as the top item on the contract.
3.6 End Item. A final combination of end products, component parts/materials which is ready for its intended use, e.g. , ship, tank, mobile machine shop, aircraft, receiver, rifle, or recorder.
3.7 LSA Candidate. A component, subassembly, assembly, software, or end item/article on which maintenance action is considered feasible as a result of a preliminary or detailed tradeoff analysis.
3.8 LSA Documentation. All data resulting from performance of LSA tasks, conducted under MIL-STD-1388-1, to include LSAR, pertaining to an acquisition program.
3,9 Manufacturers Part Number. See reference number.
3.10 Part. One, two or more pieces, joined together which are not normally subject to disassembly without destruction or impairment of designed use.
3.11Part Number. See reference number.
3.12Reference Number. Any number, other than a government activity stock number, used to identify an item of production, or used by itself or in conjunction with other reference numbers to identify an item of supply. Reference numbers include: manufacturer’s part, drawing, model, type, or source controlling numbers; manufacturer’s trade name; specification or standard numbers; and, specification or standard part, drawing, or type numbers. See appendix E, Data Element Definition 330.
3.13Subassembly. Two or more parts which form a portion of an assembly or a component replaceable as a whole, but having a part or parts which are individually replaceable (e.g., gun mount stand, window recoil mechanism, floating piston, telephone dial, mounting board with mounted parts, power shovel dipper stick).
3.14Topdown. A breakdown accomplished by sequencing all parts comprising
the end item in a lateral and descending “family tree/generation breakdown”. This breakdown shall consist of the end item, including all components, listing every assembly, subassembly, and parts which can be disassembled, reassembled/replaced. All parts are listed in their relation to the end item,
