
III(2)_Unit_4_Communication_ST
.pdf
Unit 4
Lesson 1 |
Lead-in |
Let’s Talk |
p.1 |
Lesson 2 |
Body Never ‘Sleeps’ |
||
Lesson 3 |
Theme One |
Whose Language? |
p.8 |
Lesson 4 |
Theme Two |
Across Cultures |
p.14 |
|
Theme Three |
|
p.21 |
Lesson 5 |
Talking Points |
Manny? |
p.28 |
|
Vocabulary |
|
p.30 |
|
Vocabulary Practice |
|
p.35 |

Lead-In: Let’s Talk
 Here some English sayings and proverbs about communication. What do the sayings imply?
Here some English sayings and proverbs about communication. What do the sayings imply?
1.The more elaborate our means of communication, the less we communicate.
JosephPristley
2.Good communication is as stimulating as black coffee and just as hard to sleep after.
AnnMorrow Lindberg
3. I have often regretted my speech, never my silence.
Anonymous
4. First learn the meaning of what you say, then speak.
Epictetus
5.All noise is waste. So cultivate quietness in your speech, in your thoughts, in your emotions. Speak habitually slow. Wait for attention and then your slow words will be charged with dynamite.
E.Hubbard
6.A good conversationalist is not one who remembers what was said, but one whosays what someone wantsto remember.
J.M.Brown
7. Men andwomen belong to different species and communication between them is still in itsinfancy.
1 |
• Dis/agree withthe quote |
B.Cosby |
8. Honestdisagreement is often a good sign of |
||
|
• Interpret the quote |
|
progress. Ghandi
• Support your opinion with arguments
2
• Make a conclusion
3
 Answer the following questions.
Answer the following questions.
1.Who do you communicate with every day? Do you communicatewell with them? Why/Why not?
2.What forms of spoken and written communication do you likeusing? Why?
3.What problems can people have with the different forms of communication?
4.How do you think those problems can be solved?
5.When did you last have acommunication problem? Who was it with? What happened?
6.Who is the best communicator you know? Why?
To begin with …
To my way of thinking, … From my experience, …
In conclusion …
Unit 4: Student’s Book
 Complete the sentences on the right with the words in the box.
Complete the sentences on the right with the words in the box.
|
|
What makes a good communicator? |
|
A good communicator is someone who: |
|
appearance |
1. |
is a good …………………… and shows interest in other people; |
charisma |
||
cultures |
2. |
has an awareness of body ……………………; |
digressions |
3. |
is not a …………………… and doesn't get easily sidetracked; |
eye |
||
humor |
4. |
doesn't suffer from …………………… and is relaxed when meeting new |
language |
5. |
people; |
listener |
is sensitive to people from other ……………………; |
|
nerves |
6. |
has an extensive ……………………; |
pace |
7. |
has a good sense of ……………………; |
rambler |
8. |
has an attractive …………………… and is well dressed; |
vocabulary |
9. |
maintains …………………… contact with the listener(s); |
10.speaks at a reasonable …………………… - not too fast and not too slow; 11.has …………………… and can hold the attentionofthe listener(s);
12.keeps to the point and doesn't have a lot of long ……………………;
 Which of the points in ex.3 do you agree/disagree with? Is there anything elseyou
Which of the points in ex.3 do you agree/disagree with? Is there anything elseyou
would add?

 Which of these words apply to good communicators and which apply to bad communicators? Add 2 adjectives of your own to the list.
Which of these words apply to good communicators and which apply to bad communicators? Add 2 adjectives of your own to the list.
articulate |
responsive |
rambling |
focused |
eloquent |
vague |
reserved |
inhibited |
succinct |
coherent |
sensitive |
fluent |
hesitant |
extrovert |
persuasive |

 Listen to seven people talking aboutwhat makes a good communicator. Match the
Listen to seven people talking aboutwhat makes a good communicator. Match the
person with the main point they make.
They ...
a)listen carefully.
b)don't ramble.
c)clarify difficult expressions
d)don'tdigress too often.
e)don't confuse listeners.
f)explain clearly.
g)don't interrupt.
2
Unit 4: Student’s Book


 Ask and answer the following questions.
Ask and answer the following questions.
1.How do you feel when someone interrupts you?
2.What do you do when someone isn't paying attention to you?
3.How do you deal with someone who is rambling?
4.What techniques do you use to explain complicated things?
5.Is it always bad to digress when talking?

 Match the idioms with theirdefinitions, find Russian equivalents andmake your
Match the idioms with theirdefinitions, find Russian equivalents andmake your
own questions using these idioms and to askyour partner.
1. |
be driving at sth |
a) |
talk about the most important thing immediately |
2. |
(can't) get a word in edgeways |
b) |
share similar ideas |
3. |
be on the same wavelength |
c) |
hear about a rumor passed from one person to |
4. |
have a quick word with |
d) |
another |
5. |
someone |
(not) get a chance to say something |
|
get straight to the point |
e) |
communicate what you want to say |
|
6. |
think before you speak |
f) |
talk briefly to someone |
7. |
get one’s message across |
g) |
to misunderstand someone |
8. |
drop/ give/ throw the hint |
h) |
say sth without getting straight to the point |
9. |
get someone wrong |
i) |
don't start talking until you have thought aboutwhat |
10.actions speak louder than |
j) |
you want to say |
|
|
words |
what you do is more important than what you say |
|
11.hear it on the grapevine |
k) |
to imply, to mean sth |
|


 In pairs, answer the following questions.
In pairs, answer the following questions.
1.Does it irritate you when people do not get straight to the point?
2.When was the last time you felt you were reallyon the samewavelength as someone else?
3.Who was the last person to ask to have a quick wordwith you?
4.What have you heard on the grapevine recently?

 In groups, talk about current trendsin communication. Think about:
In groups, talk about current trendsin communication. Think about:
reading |
writing letters |
texting |
writing emails |
the Internet |
using libraries for research |
audiobooks |
e-books |
telephoning |
social networks |
 Look at the front cover of a well-known academic book
Look at the front cover of a well-known academic book
on the right. What is it about?
Unit 4: Student’s Book
3

 Listen to an introduction to a radio programme about Deborah Tannen and check
Listen to an introduction to a radio programme about Deborah Tannen and check
your answer to ex. 11. Say what she is famous for.
 Do you agree with the followingstatements?
Do you agree with the followingstatements?
1.Women talk far more thanmen.
2.Men talk about sport. Women talk about their feelings.
3.Women and men communicate differently.
 Completeeach sentence with one of the words or phrases given.
Completeeach sentence with one of the words or phrases given.
1. |
politically correct |
|
|
|
|
6. |
|
impact |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. superior |
|
|
|
||||||
2. |
nationalstereotype |
|
|
|
|
7. |
|
social |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12. body language |
|
||||||||
3. |
trait |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
|
breeds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. communicate |
|
||||||
4. |
reserved |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
|
commitments |
|
|
|
|
14. arrogance |
|
|
|||||||
5. |
image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10. credibility |
|
|
|
|
15. assertiveness training |
|
||||||||||
1. |
Whenever foreign visitors come into Mrs. Jones’s shop she can’t help judging then according to |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
2. |
…………………………………..… . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
…………………………………..… |
. |
|
|
||||||||
A successful businessman has learnt how to project a positive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
3. |
…………………………………..… |
can be a useful asset to people whose self-esteem is low or who are reluctant |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
to speak up for themselves. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
4. |
Maxim is very quiet, very |
…………………………………..… |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
. You never know what's going on in his mind. |
|
||||||||||||||
5. |
|
|
…………………………………..… |
in his personality that encouraged people to trust him. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
There was a…………………………………..… |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
6. |
Some very |
|
|
|
|
|
|
parents won't let their children play with toy guns. |
|
|
||||||||||||||
7. |
…………………………………..… |
exclusion" seems to be the latest euphemism for poverty. |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
8. |
He could |
…………………………………..… |
a feeling of intense excitement to his audience. |
|
|
|
Book |
|||||||||||||||||
9. |
One of the most powerful forms of nonverbal communication is |
…………………………………..… |
. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
10. |
Ignorance only |
…………………………………..… |
fear and contempt of the unknown. |
|
|
|
4:Student’s |
|||||||||||||||||
11. |
I can't get engagedwith this job right now as I have other |
…………………………………..… |
. |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
effective member of the team. |
|
|
|
|
|
…………………………………..… |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
12. |
The new authority is losing |
…………………………………..… |
by its failure to act quickly. |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
13. |
His |
…………………………………..… |
and unwillingness to learn from others prevent him from being an |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
14. |
Internetshopping has begun to have a serious |
|
|
|
|
|
|
onthe traditional bookshops. |
|
|||||||||||||||
15. |
He loves making fun of women. It makes himfeel |
…………………………………..… |
. |
|
|
|
Unit |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
 Complete the text using the wordsand phrases given.
Complete the text using the wordsand phrases given.
1. |
stereotype |
6. |
silence |
10. talkative |
|
2. |
rapport |
7. |
contradictory |
11. gestured |
|
3. |
verbal |
8. |
negotiating |
12. independence |
|
4. |
status |
9. |
the life ofthe |
13. |
observation |
5. |
approached |
party |
|
||
Iwas sitting in a suburban living room, speaking to a women's group that had invited men to join them for the occasion of my talk about communication between women and men. During the discussion, one man was particularly  , full of lengthy comments and explanations. When I made the
, full of lengthy comments and explanations. When I made the  that women often complain that their husbands don't talk to them enough, this
that women often complain that their husbands don't talk to them enough, this
man volunteered that he heartily agreed.
He  toward his wife, who had sat silently beside him on the couch throughout the evening, and said,"She's the talker in our family."
toward his wife, who had sat silently beside him on the couch throughout the evening, and said,"She's the talker in our family."
Everyone in the room burst into laughter. The man looked puzzled and hurt. "It's true," he explained. "When I come home from work, I usually have nothing to say, but she never runs out. If it weren't for her, we'd spend the whole evening in  " Another woman expressed a similar paradox about her husband: "When we go out, he's
" Another woman expressed a similar paradox about her husband: "When we go out, he's . If I happen to be in another room, I can always hear his voice above the others. But when we're home, he doesn't have that much to say. I do most of the talking."
. If I happen to be in another room, I can always hear his voice above the others. But when we're home, he doesn't have that much to say. I do most of the talking."
Who talks more, women or men? According to the  women talk too much.
women talk too much.
… Yet study after study finds that it is men who talk more - at meetings, in mixed-group discussions, and in classrooms where girls or young women sit next to boys or young men. For example, communications researchers Barbara and Gene Eakins tape-recorded and studied seven university faculty meetings. They found that, with one exception, men spoke more often and, without exception, spoke for a longer time. …
Who talks more, then, women or men? The seemingly evidenceis reconciled by the difference between what I call public and private speaking. More men feel comfortable doing "public speaking," while more women feel comfortable doing "private" speaking. Another way of capturing these differences is by using the terms report-talk and rapport-talk. For most women, the language of conversation is primarily a language of rapport: a way of establishing connections and
evidenceis reconciled by the difference between what I call public and private speaking. More men feel comfortable doing "public speaking," while more women feel comfortable doing "private" speaking. Another way of capturing these differences is by using the terms report-talk and rapport-talk. For most women, the language of conversation is primarily a language of rapport: a way of establishing connections and  relationships. Emphasis is placed on displaying similarities and matching experiences. From childhood, girls criticize peers who try to stand out or appear better than others. People feel their closest connections at home, or in settings where they feel at home--with one or a few people they feel close to and comfortable with--in other words, during private speaking.
relationships. Emphasis is placed on displaying similarities and matching experiences. From childhood, girls criticize peers who try to stand out or appear better than others. People feel their closest connections at home, or in settings where they feel at home--with one or a few people they feel close to and comfortable with--in other words, during private speaking.
But even the most public situations can be approached like private speaking. For most men, talk is primarily a means to preserve  and
and
negotiate and maintain |
in a |
hierarchical social order. This is done by exhibiting knowledge and skill, and by holding center stage through 
 performance such as storytelling, joking, or imparting information. From childhood, men learn to use talking as a way to get and keep attention. So they are more comfortable speaking in larger groups made up of people they know less well--in the broadest sense, "public speaking." But even the most private situations can be
performance such as storytelling, joking, or imparting information. From childhood, men learn to use talking as a way to get and keep attention. So they are more comfortable speaking in larger groups made up of people they know less well--in the broadest sense, "public speaking." But even the most private situations can be

 like public speaking, more like giving a
like public speaking, more like giving a
report |
than |
establishing |
. |
 Decide whether the information inthe statements is true √, false or not given−.
Decide whether the information inthe statements is true √, false or not given−.
1. Women feel happy that their husbands don’ttalk much.
2. After work men are too tired to talk.
3. It is commonly believed than women talk too much.
4. Research proves that men talk for a longer time.
5. Accordingto the author men and women pursue different goals while talking.
6. For most men talking is more of a competition.
7. Men prefer to talk in small audiences.
8. Women are less efficient at public speaking.
5
Unit 4: Student’s Book

6
Student’s Book: Notes

Hometask 1
 Get ready toretell the text from exercise 15.
Get ready toretell the text from exercise 15.
 Study the vocabulary from exercises 3,5, 8, 14, 15.
Study the vocabulary from exercises 3,5, 8, 14, 15.
 Which of the words in exercise 5have these meanings? Find Russian equivalents.
Which of the words in exercise 5have these meanings? Find Russian equivalents.
|
|
concise |
|
|
= |
|
clear andeasyto |
= |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
undrestand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
reluctant to speak |
|
= |
|
goodat influencing people |
= |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
talking in a confusedway |
= |
|
outgoing |
|
= |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ableto express ideas well |
= |
|
eager to react and |
= |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
communicate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Complete the extract below from a talk by a communication expert with the verbs |
||||||||
|
|
from |
the box. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
clarify |
|
confuse |
digress |
engage |
explain |
interrupt |
listen |
ramble |
|||
'Good communicators really l i s t e n 1 to people and take in what is said. They maintain eye
contact and have a relaxed body language, but they seldom  2 and stop people talking. If they don't understand and want to
2 and stop people talking. If they don't understand and want to 3 something, they wait for a suitable opportunity.
3 something, they wait for a suitable opportunity.
When speaking, effective communicators are good at giving information. They do not  4 their listener. They make their points clearly. They will avoid technical terms, abbreviations or jargon. If they do need to use unfamiliar terminology, they
4 their listener. They make their points clearly. They will avoid technical terms, abbreviations or jargon. If they do need to use unfamiliar terminology, they 5 by giving an easy-to-understand example. Furthermore, although they may
5 by giving an easy-to-understand example. Furthermore, although they may 6 in order to elaborate a point and give additional information and details where appropriate, they will not
6 in order to elaborate a point and give additional information and details where appropriate, they will not  7and lose sight of theirmain message. Really effective communicators who have the ability to
7and lose sight of theirmain message. Really effective communicators who have the ability to 
 8 with colleagues, employees, customers and suppliers are a valuable asset for any business.'
8 with colleagues, employees, customers and suppliers are a valuable asset for any business.'

 Now listen to the talk and check your answers.
Now listen to the talk and check your answers.

 Listen to the interview with Alastair Dryburgh,an expert on communication.
Listen to the interview with Alastair Dryburgh,an expert on communication.
a.Does he think technology makes good communication easier?(the first listening)
b.What four key points does he make about communication?(the second listening)
Unit 4: Student’s Book
Theme One: Body Never “Sleeps”
 How do you understand the title Body Never‘Sleeps’ ?
How do you understand the title Body Never‘Sleeps’ ?
 Look at some facts given below. Did you know that?
Look at some facts given below. Did you know that?
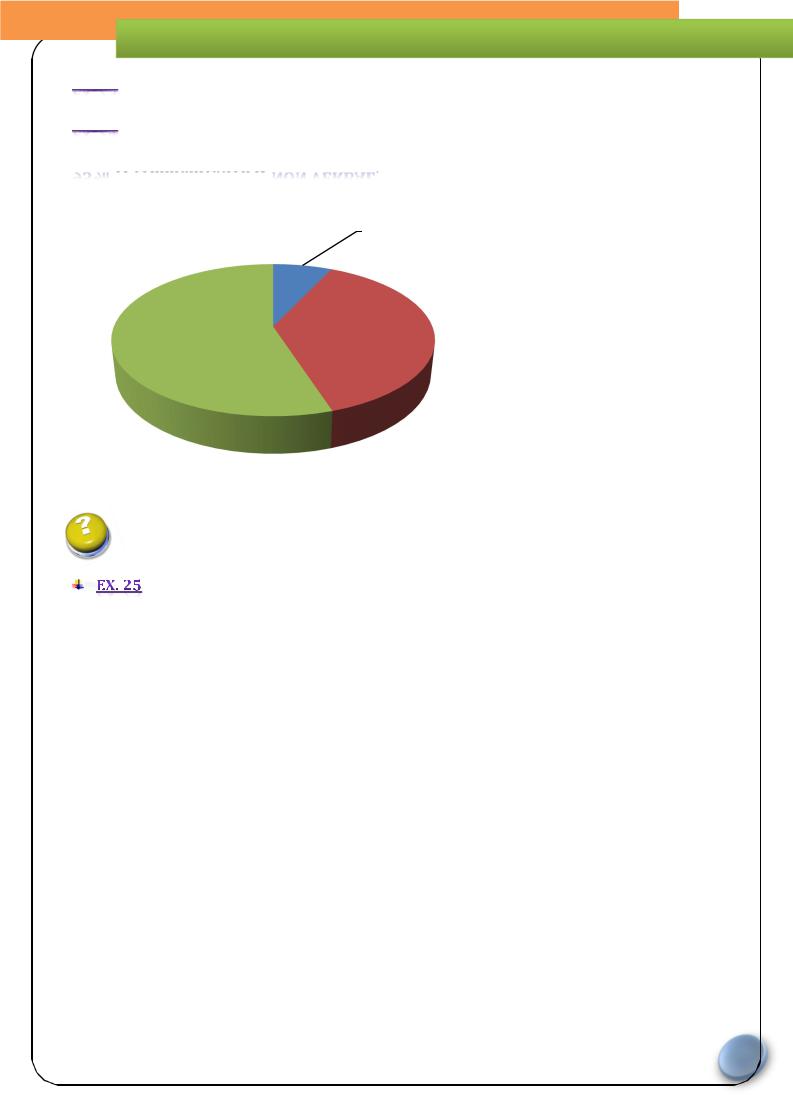
 of communication is
of communication is  :
:
Communication
verbal 7%
tone of voice body 38% language
55%
Body language: People use body language without thinking (unconsciously) to communicate or the message to another person. We are also constantly dropping clues about what is going on in our head, sometimes without even knowing.
Tone of voice: Emotions are often given away not so much by what people are saying but how they say it. For example speaking loudly in short sentences can show aggression, speaking gently and giving smiles and encouragement can show caring.
1.Do you find this information surprising? Why?
2.How do you think: what makes up human body language?
 Now read the text and check your assumptions.
Now read the text and check your assumptions.
When we communicate with other people it is not only our words that contain the meaning. An important part of that meaning comes from what is called 'non-verbal communication'. By this we mean facial expression; gestures with hands, arms, legs; the way we sit or stand; the way we touch other people; the distance we keep between ourselves and the people we are talking to; our dress and our appearance. All these say something to other people.
Facial expressions and gestures are used by everyone often spontaneously , even unconsciously. Smiling, for example, is found in most cultures as a sign of happiness or pleasure. Gestures such as pointing, waving, shaking or nodding the head are also widely used, although the gestures themselves do not always mean the same in every culture. I once asked a Portuguese student why bank officials in Lisbon seemed so dour – sorry Lisbon bank clerks, but it's true – and he told me that if they smiled too much they would not seem serious about theirwork.
Because many non-verbal messages are 'culture specific', they can cause a lot of misunderstanding between people from different backgrounds. Northern Europeans and Americans, for example, like to keep a certain 'personal space' between themselves and others and feel
uncomfortable if people come too close to them. In these samecultures it is considered impolite to stare , but Greeks, it is said, feel ignored if people do not stare at them in public. Europeans usually change their facial expression to show happiness, anger, boredom, sadness. For this reason they call oriental people 'inscrutable' because they change facialexpressionmuchless.
In styles of dress we also make important statements about ourselves. Dress codes vary greatly from one culture to another and it is easy to make mistakes about people's status if you don't know the cultural norm. In Mediterranean cultures bank officials and similar employees wear short-sleeved, open-neck shirts and no jackets. This casual dress would not be acceptable in northern Europe, where suits and ties are a sign of seriousness. Ambitious women in western cultures wear classic clothes in sober colours to indicate their dedication to career.
One of the main differences between verbal and nonverbal communication is that we are often not conscious of the expressions and gestures we use and so we are in danger of giving more information than we really want to, or even of giving a conflicting message with our body language to the one expressed in our words.
8
Unit 4: Student’s Book

 Complete theMindMap with the information from the text.
Complete theMindMap with the information from the text.
 Listen to a body language expert talking about first impressions and check the aspects of a person's appearance that the expert mentions.
Listen to a body language expert talking about first impressions and check the aspects of a person's appearance that the expert mentions.
|
build |
|
color |
|
face |
|
expression |
|
height |
|
clothes |
|
eyes |
|
gestures |
|
character |
|
posture |
|
hair |
|
voice |

 Complete these notes about first impressions.Listen again to check if
Complete these notes about first impressions.Listen again to check if
necessary.
1.We often make up our minds about people on the basis of ……………………..
2.There is a danger of …………………….. but first impressions are often ……………………..
3.People use clothes to ……………………..
4.The face is important but ……………………..
5.One of the most important things in forming opinions is ……………………..
Do you agree or disagree with the statements above? Why? / Why not?
Student’s
