
Полезные материалы за все 6 курсов / Ответы к занятиям, экзаменам / 4. Пищеварительная
.pdf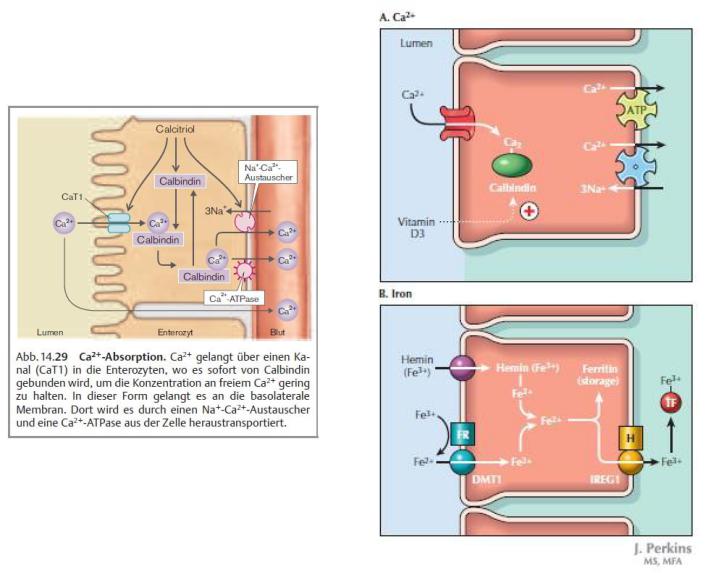
Important action of vitamin D is to promote Ca2+ absorption from the small intestine by inducing the synthesis of vitamin D– dependent Ca2+-binding protein (calbindin D-28K) in intestinal epithelial cells

M cells are epithelial cells that overlie Peyer’s patches and other large lymphatic nodules; they differ significantly from the surrounding intestinal epithelial cells
M cells have microfolds rather than microvilli on their apical surface, and they take up microorganisms and macromolecules from the lumen in endocytotic vesicles. The M cell is an antigen-transporting cell. The vesicles are transported to the basolateral membrane where they discharge their contents into the epithelial intercellular space in the vicinity of CD4 T lymphocytes. Thus, substances that gain access to the body from the intestinal lumen via M cells come into contact with cells of the immune system as they reach the basolateral surface. Antigens that reach lymphocytes in this manner stimulate a response in the GALT that is described
below.
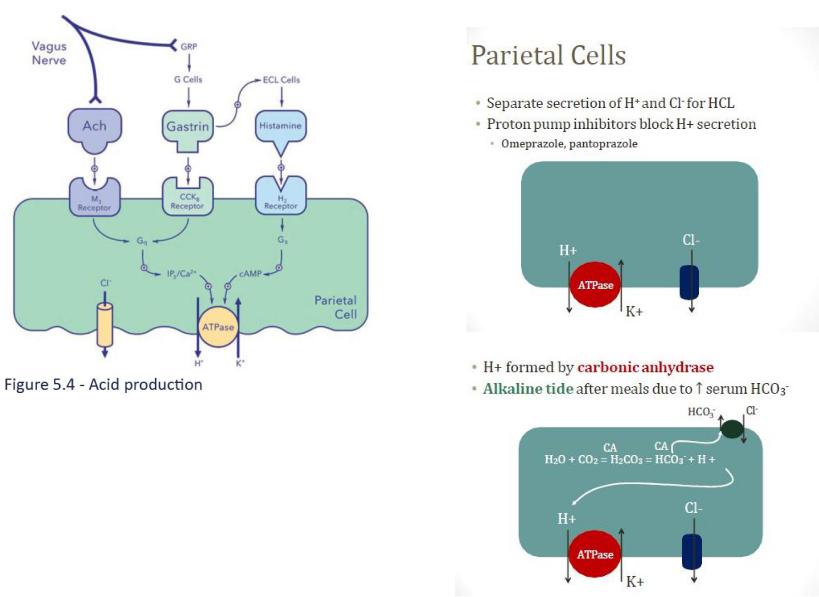
in persons whose gastric antrum is resected (which removes the source of gastrin, the G cells), H+ secretion is decreased and the gastric mucosa atrophies.
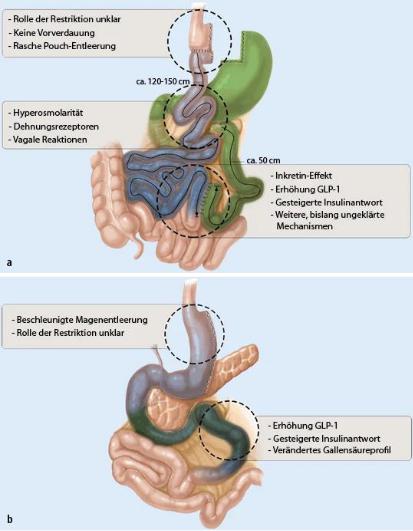
Nach einer Magenresektionsoperation (Billroth II) kann es im blind endenden duodenalen Abschnitt zu einer bakteriellen
Überwachsung kommen (Blindsacksyndrom, blind loop syndrome). Es kommt dabei zum bakteriellen Abbau der
Gallensäuren mit Gallensäureverlustsyndrom, schmerzhaften Blähungen, Durchfall und Erbrechen. Dieses muss je nach
Ursache behandelt werden. Eine weitere Komplikation nach Magenresektion ist das Dumping-Syndrom, bei dem es nach
Speiseaufnahme zum beschleunigten Übertritt der Speise in den Dünndarm kommt. Beim Frühdumping (ca. 30 min nach Speiseaufnahme) führt der osmotisch wirksame Speisebrei zu einer raschen Flüssigkeitsumverteilung in das Dünndarmlumen. Die Folge ist ein Blutdruckabfall bis hin zum
Volumenmangelschock, oft verbunden mit Bauchkrämpfen und Übelkeit. Beim Spätdumping (ca. 2 h nach Speiseaufnahme) bewirkt die aufgrund der fehlenden Pylorusfunktion vergleichsweise rasche Glukoseresorption eine überschießende Insulinsekretion. Die daraus resultierende Hypoglykämie hat Herzrasen, Schwindel und Schweißausbrüche zur Folge.


|
Vomiting |
|
• Loss of HCl • ↑ production HCl |
|
• HCO3generated during |
|
production |
|
• Metabolic alkalosis |
|
• Urinary chloride is low (<20) |
|
Urinary Chloride |
|
• Useful in metabolic alkalosis |
|
unknown cause |
|
• Low (<10-20) in vomiting • Loss |
|
of Cl in gastric secretions |
|
• High (>20) in diuretic use • |
|
Diuretics block NaCl resorption |
Effects - Gastrin |
|
• Stimulates H+ secretion by parietal cells |
• Classic scenario: • Young woman |
• Stimulates growth of gastric mucosa |
with unexplained metabolic |
• Important in gastrin tumors |
alkalosis |
• Hypertrophy and hyperplasia |
• Urinary Cl is low |
• Increases gastric motility |
• Diagnosis: surreptitious vomiting |
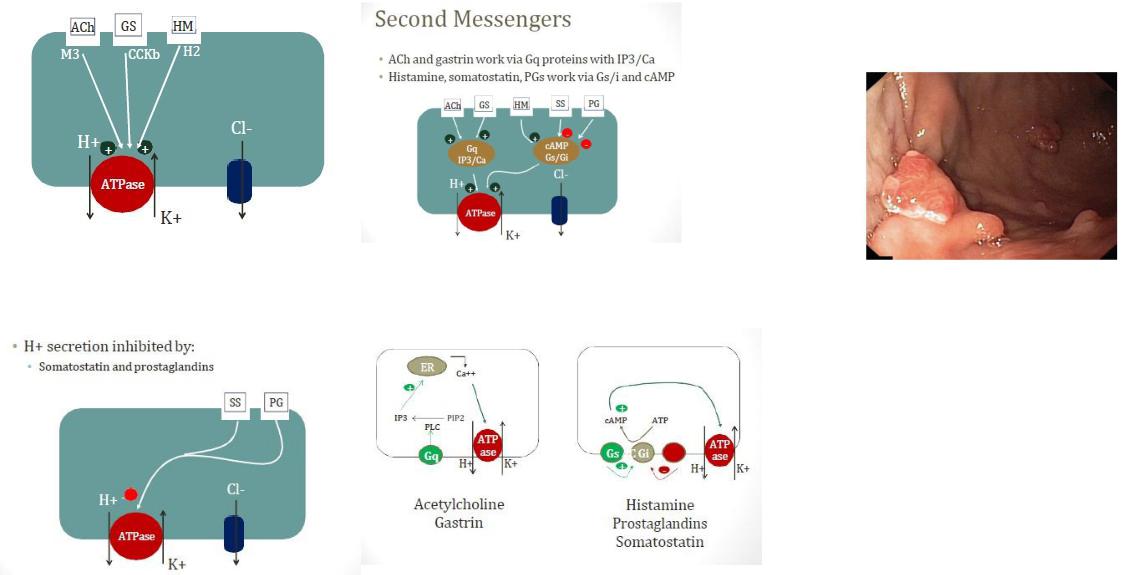
gastrin stimulates growth of the gastric mucosa, a trophic effect.
Wird die HCl-Sekretion durch H2-Blocker gehemmt, so sinkt auch die IF-Sekretion. Eine Hemmung der HClSekretion durch H+/K+- ATPase-Blocker (z. B. Omeprazol) beeinflusst die IF-Sekretion dagegen nicht

•Released in response to: • Stomach distention
•Alkalinization
•Amino acids (especially phenylalanine and tryptophan)
•Vagal stimulation (mediated by GRP – atropine does not block)
•Inhibited by low pH, somatostatin
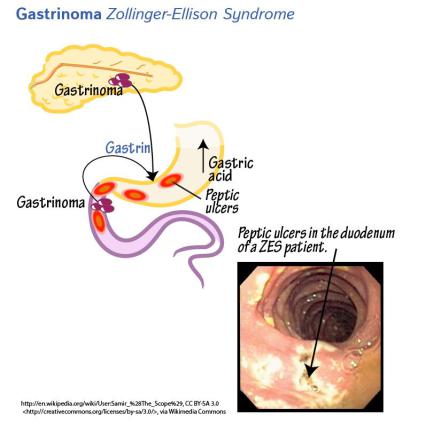
Gastrinoma
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
•Gastrin secreting tumors
•Occur in duodenum or pancreas •
G cells found in pancreas in fetus
•Excessive acid secretion
•Hypertrophy/hyperplasia of mucosa
•Abdominal pain
•Improves with food (raises pH)
•Chronic diarrhea
•Excessive gastric acid cannot be neutralized in intestines
•Low pH inactivates pancreatic enzymes
•Also inhibits sodium/water absorption in small intestines
•Result: Poor digestion, steatorrhea, secretory diarrhea
•Ulcers
•Most in distal duodenum (often past bulb) or jejunum
•Refractory to PPI therapy
•Heartburn
The increased H+ secretion also results in acidification of the intestinal lumen, which inactivates pancreatic lipase, an enzyme necessary for fat digestion.
As a result, dietary fats are not adequately digested or absorbed, and fat is excreted in the stool (steatorrhea).
