
- •Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Kuban State Medical University" of
- •Conductive system of the heart:
- •Sinus tachycardia:
- •Sinus tachycardia:
- •Sinus bradycardia:
- •Sinus bradycardia:
- •Sinus arrhythmia:
- •Sinus arrhythmia:
- •Extrasystole:
- •Supraventricular extrasystole:
- •Supraventricular extrasystole:
- •Ventricular extrasystole:
- •Ventricular extrasystole:
- •Ventricular extrasystole:
- •Paroxysmal tachycardia:
- •Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia:
- •Atrial fibrillation and flutter:
- •Atrial fibrillation:
- •Atrial flutter:
- •Ventricular fibrillation:
- •Atrioventricular block:
- •Atrioventricular block:
- •Atrioventricular block:
- •1st degree AV block:
- •Mobitz type I:
- •3rd degree AV block (complete AV- block):
- •Right bundle branch block:
- •Right bundle branch block:
- •Left bundle branch block :
- •Main ECG signs of incomplete blockade of the anterior branch of the left
- •The main ECG signs of incomplete blockade of the posterior branch of the
- •Premature arousal syndromes ventricles:
- •Shortened P-Q (R) interval syndrome:
- •The main ECG signs of WPW syndrome:
- •Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW):
- •Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW):
- •Thank you for Attention!
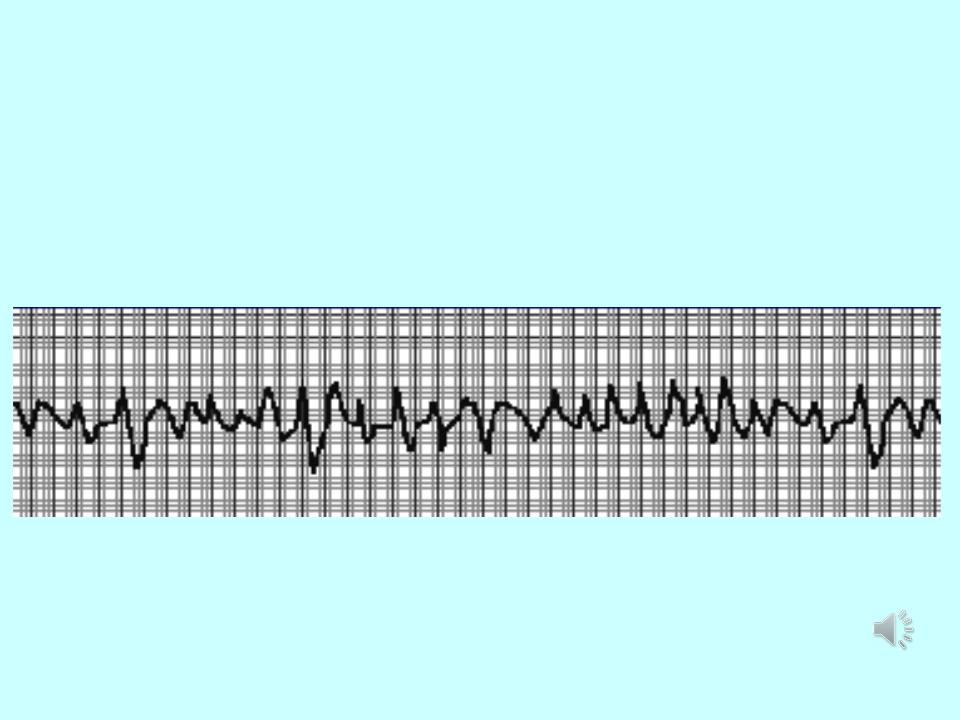
Ventricular fibrillation:
1.Ventricular fibrillation irregular ventricular rate is 200-600 twitches/min.
2.The heart does not pump blood.
3.It leads to unconsciousness within 5 seconds.
4.The trigger is anoxia.
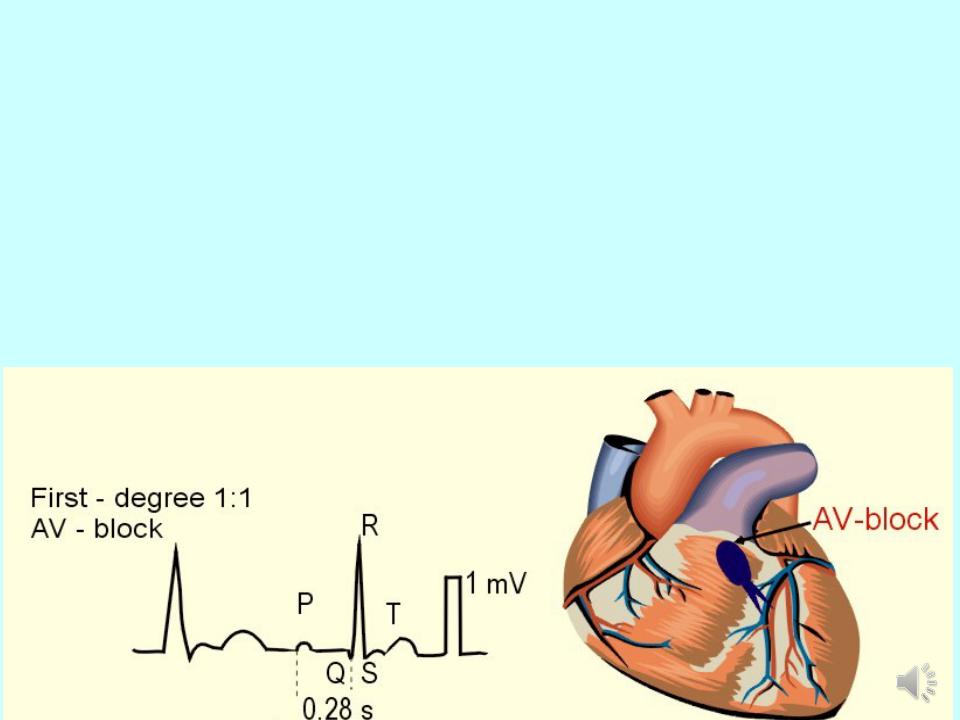
Atrioventricular block:
1.Atrioventricular block is the blockage of the conduction from the atria to the AV- node. Three degrees of AV block are known.
2.1st degree AV block: PQ - above 0.2 s
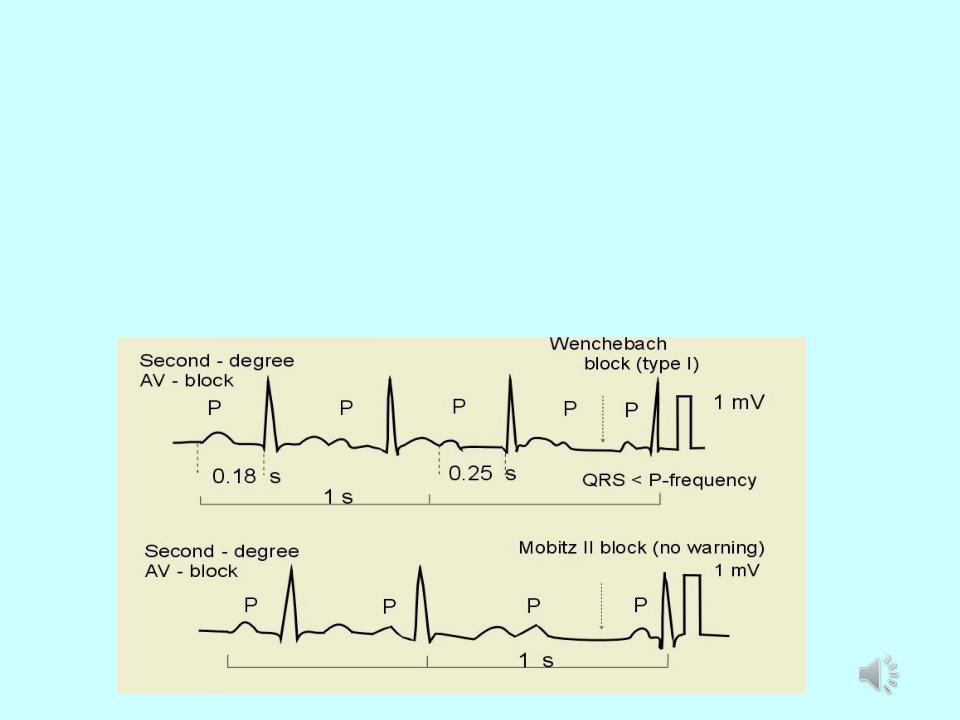
Atrioventricular block:
1.2nd degree AV block- some of the P-waves are not followed by QRS-complexes
2.Mobitz type I - PQ-interval is increased progressively until a P-wave is not followed by a QRS-complex. (Wenchebach block).
3.Mobitz type II block - the ventricles drop some beats
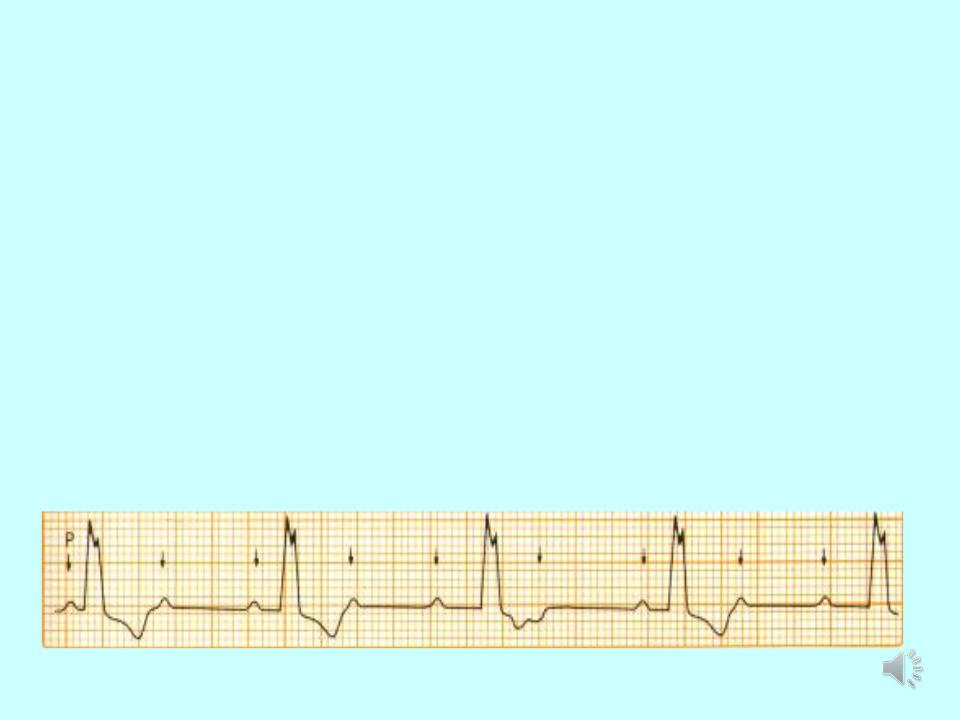
Atrioventricular block:
1.3rd degree AV block (complete AV-block) is a total block of the conduction between the SN and the ventricles.
2.Atriums are regulated by SA node, ventricles by AV node
P P P P P P P P
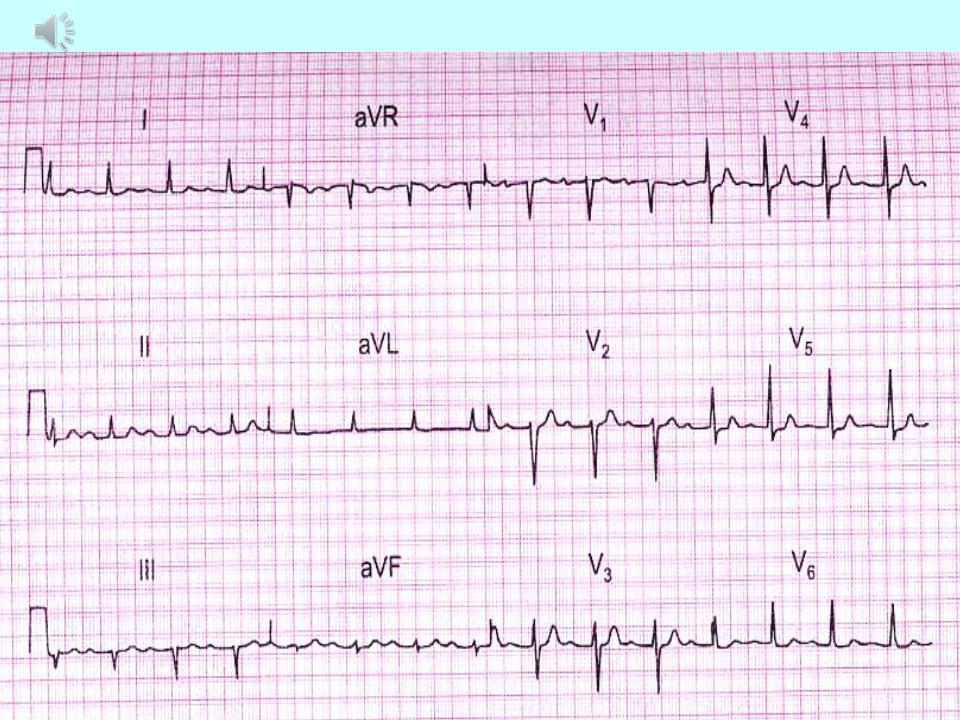
1st degree AV block:
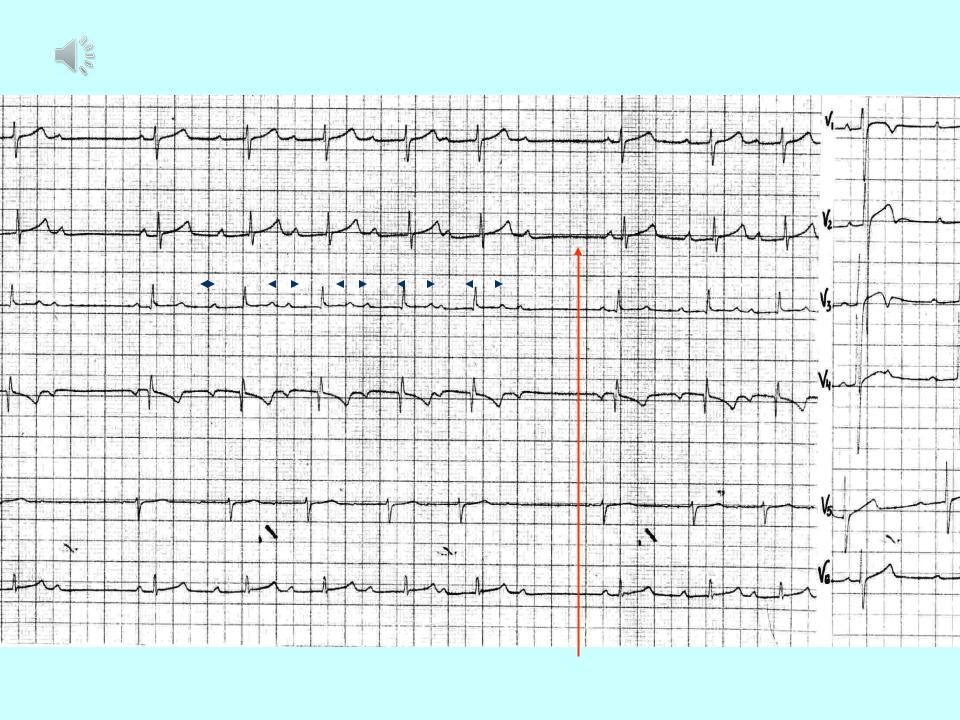
Mobitz type I:
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V1 |
II |
p |
p |
p |
|
p |
p |
p |
p |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V2 |
III |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AVR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AVL
V5
AVF
V6
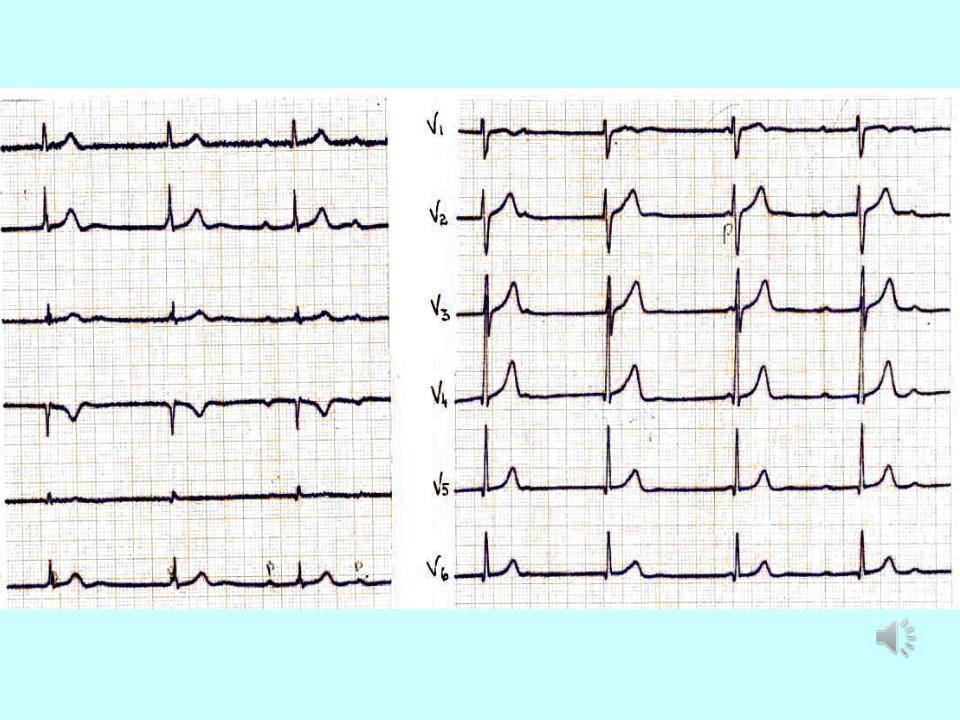
3rd degree AV block (complete AV- block):
I
II
III
AVR
AVL
AVF
V1
p |
p |
p |
p |
p |
V2
V3
V4
V5
V6
Независимое сокращение предсердий и желудочков

Right bundle branch block:
Main ECG signs of incomplete right bundle branch block:
1.Cleavage of the QRS complex in lead V1 like rSr or rSR '.
2.Broadened (up to o, 11-o, 12s) or normal duration of the QRS complex
3.Increase in the activation time of the right ventricle in lead V1 more than o, o3 from.
4.Absence of typical widening and deepening of the S wave in V6 and I standard leads.
Main ECG signs of complete right bundle branch block:
1.A split, M-shaped QRS complex of the rSR ', rsR', RSR 'or RsR '(and R'> R) in V1 V2 sometimes II and aVF leads.
2.Broadened (up to about, 12 s and more) QRS complex, as well as an increase in time internal deviation (activation of the right ventricle) in V1 V2 leads more about, about7 - 0.08 s.
3- Discordant downward displacement of the R (S) -T segment and the T wave (asymmetric biphasic or negative) in relation to the main tooth of the complex QRS in V1 sometimes V2 III and aVF leads.
4. Wide (more about, 04 s), deep and often serrated S wave in V6, V5, I, aVL
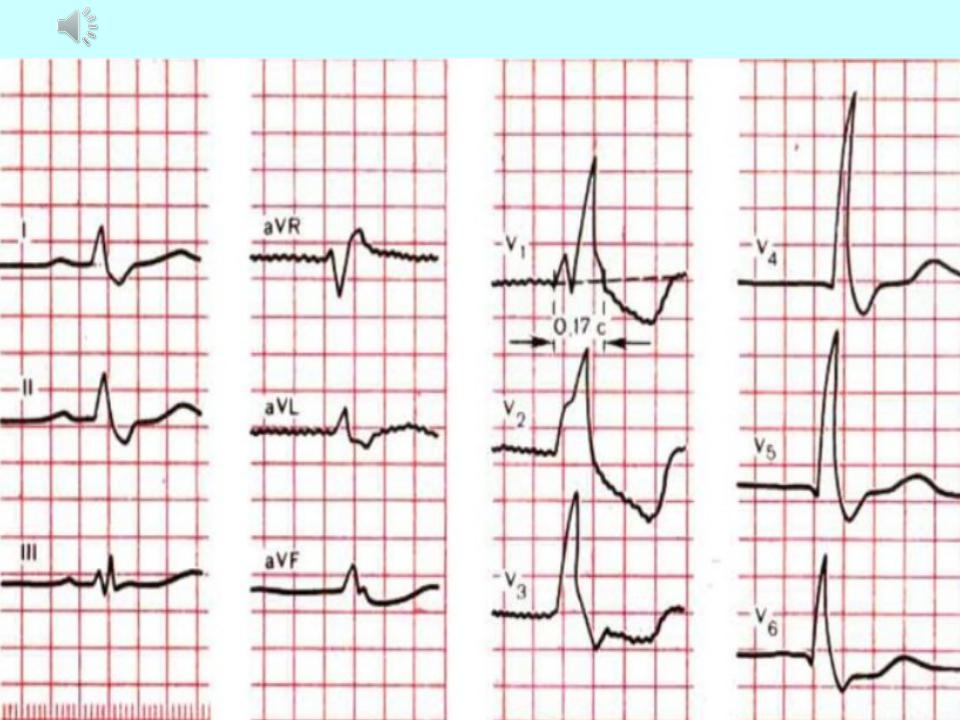
Right bundle branch block:
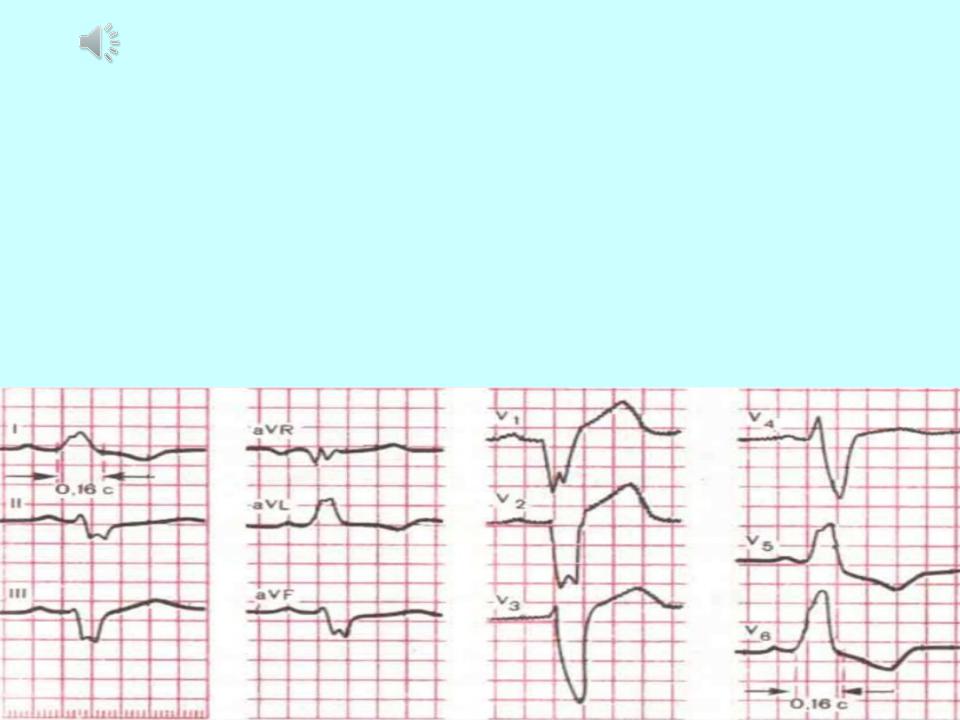
Left bundle branch block :
Main ECG signs of complete blockade of both branches of the left bundle branch
Gisa:
1.Wide (more than about 12 s), varied in shape, often split QRS complex, usually represented by one R wave in V, Vs, I, a VL leads.
2.Increasing the time of the internal deviation (activation of the left ventricle) more about, about8 s in V5, Vo leads.
3.Discordant downward displacement of the R (S) -T segment and the T wave (asymmetric biphasic or negative) in relation to the main tooth of the complex
QRS in V5, Vs, I and aVL leads.
4.Widened S wave (or QS) in V, 1 V2 leads.
