
Cardiology / ЭКГ 2 инглиш
.pdf
Main ECG signs of incomplete blockade of the anterior branch of the left leg bundle of His:
1.Pronounced deviation of EOS to the left (angle alpha exceeds -30 °). B I and aVL leads the QRS complex of the qR type, and in II III and aVF leads of the rS type.
2.An increase in the amplitude of the S wave in the V5, V6 leads.
3.Normal or somewhat broadened (up to o, 1o-o, 11 s) QRS complex.

The main ECG signs of incomplete blockade of the posterior branch of the left bundle branch of Gis:
1.Expressed deviation of EOS to the right (angle alpha exceeds + 120 °). In I and aVL leads a QRS complex of the rs type, and in III, aVF, sometimes II leads - of the qR type.
2.Normal or somewhat broadened (up to o, 10-o, 11 c) QRS complex.

Premature arousal syndromes ventricles:
Arise as a result of the simultaneous carrying out of excitatory pulse along the main conductive system and additional conductive paths bypassing the AV node. With Wolff- Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) the impulse is conducted to the ventricles by additional abnormal beams Kent, with shortened P-Q (R) interval syndrome atypical WPW syndrome, Clerk-Levi-Cristesco syndrome, or Launa- Ganong-Levin). - on a beam of James
Main ECG signs of shortened P-Q (R) interval syndrome:
1.Shortening (less than about 12 s) of the P-Q (R) interval.
2.Normal (no delta waves and undeformed) QRS complexes.

Shortened P-Q (R) interval syndrome:

The main ECG signs of WPW syndrome:
1.Shortening (less than about 12 s) of the P-Q (R) interval.
2.The presence of a delta wave on the ascending or descending knee of the complex
3.Widening (more about, 11 s) and slight deformation of the QRS complex.
4.Discordant displacement of the R (S) -T segment and the T wave (asymmetric biphasic or negative) in relation to the main tooth complex QRS (intermittent signs).
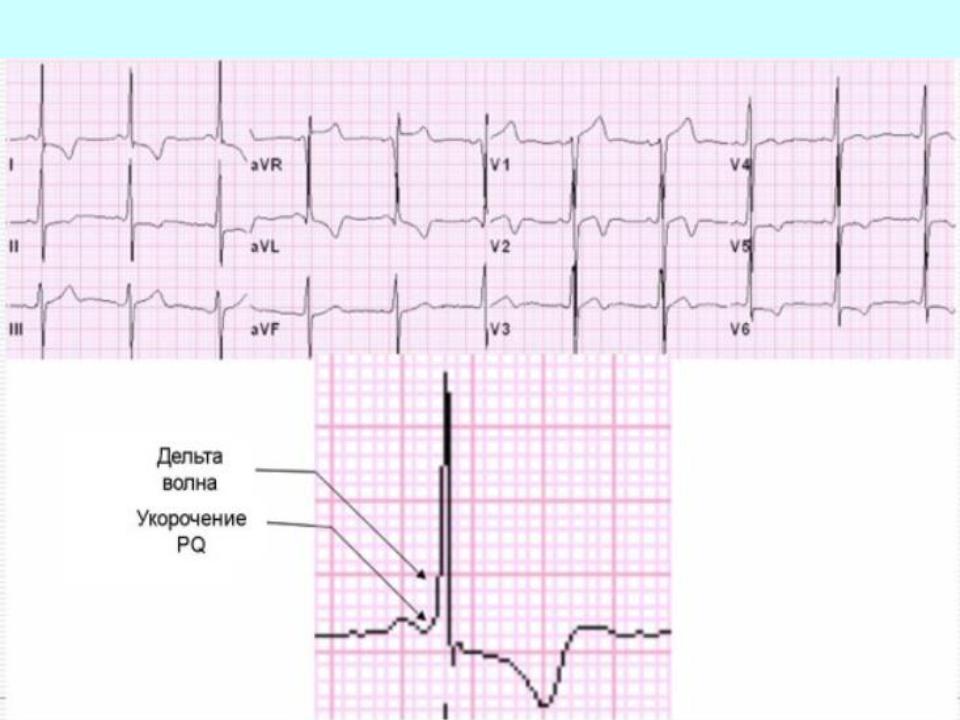
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW):

Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW):

Thank you for Attention!
