- •1 Cut from Solid
- •2 Sheet
- •3 Continuous
- •4 Thin & Hollow
- •5 Into Solid
- •6 Complex
- •7 Advanced
- •8 Finishing Techniques
- •Introduction
- •Volumes of production
- •1: Cut from Solid
- •1 A very simple setup for milling a chunk of metal. The cutting tool, which resembles a flat drill bit, can be seen fitted above the clamped work piece.
- •2 A straightforward setup for a lathe operation in which the tube of metal to be cut is clamped into a chuck. The cutter is poised ready to make a cut.
- •Volumes of production
- •1 The individual sheets of cut plywood are clamped together before being machined.
- •2 View showing the machined internal structure before the external surface is cut.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •1 The mortar bowl is being turned by hand, using a profiled metal tool to achieve a precise profile.
- •2 A ceramic pestle being finished using a flat smoothing tool.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •2: Sheet
- •Industrial Origami®
- •Inflating Metal
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •1 Preparation of the wooden mandrel.
- •2 The metal is pushed against the mandrel as both metal and mandrel are spinning.
- •3 The metal component taking shape over the mandrel.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Industrial Origami®
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Inflating Metal
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •3: Continuous
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •1 Individual strands of fiber are fed into a die where they will be soaked in resin and formed into their final profile.
- •2 A finished tube emerges through the cutter, ready to be cut to length.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Veneer Cutting
- •Volumes of production
- •4: Thin & Hollow
- •1 A mass of molten glass is gathered onto the end of a steel tube, ready to be blown.
- •2 Various hand tools are used to shape the hot glass, in this case a stack of wet fabric.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Injection Blow Molding
- •Injection stretch molding is a method used for high-end products (such as bottles) made from polyethylene terephthalate (pet) which uses a rod to stretch a pre-form into the mold before blowing.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •1 Empty plaster molds.
- •2 Molds filled with slip.
- •Volumes of production
- •1 An example of the tooling and the die cavity into which the metal is placed.
- •2 Semifinished hydroformed components.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Vacuum Infusion Process (vip)
- •Volumes of production
- •Imagine impregnating the thread on a cotton reel with resin and then being able to pull the wound thread off its reel to form a rigid plastic cylindrical part: this is the essence of filament winding.
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •5: Into Solid
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Inflating Wood
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •6: Complex
- •Injection Molding
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Insert Molding
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Investment Casting
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Viscous Plastic Processing (vpp)
- •Volumes of production
- •7: Advanced
- •Inkjet Printing
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •Volumes of production
- •1 Winding onto the purple Smart Mandrel begins.
- •2 The Smart MandrelTm is heated and softened for easy removal from the completed winding.
- •Volumes of production
- •Incremental Sheet-Metal Forming
- •Volumes of production
- •8: Finishing Techniques
- •In his visionary book The Materials of Invention, Ezio Manzini defines the surface of objects as “the location of the points where an object’s material ends and the surrounding ambient begins.”
- •Vacuum Metalizing
- •Vapor Metalizing
- •Vitreous Enameling
- •Inflating metal 10-11, 76-7
Volumes of production
Suited to batch production.
Unit price vs. capital investment
Low capital investment as there is no tooling because the cuts are determined by a CAD file.
Speed
As with all methods of cutting, the speed of this process is dependent on the type of material used and its thickness. As a rough estimate, titanium alloys between 1/50 and 3/8 inch thick can be cut at a rate of 8 to 40 feet per minute.
Surface
The process will leave burn marks on wood, but on metal can give a clean edge with no need for post finishing. However, metal surfaces should be left unpolished before cutting, as highly polished surfaces act as reflectors and decrease the effectiveness of the process.
Types/complexity of shape
Depending on the machinery, the laser can be mounted horizontally or on a multi-axis head, allowing for highly complex shapes to be cut in three dimensions, a method that is sometimes called laser-beam machining.
Scale
Limited to standard sheet sizes.
Tolerances
Tolerances are extremely high, with holes of as little as 1/1000 inch in diameter being possible.
Relevant materials
Often used on hard steels such as stainless and carbon steel. Copper, aluminum, gold, and silver are more difficult due to their ability to conduct the heat. Nonmetallics can also be laser cut, including woods, paper, plastics, and ceramics. Materials such as glass and ceramics are especially suited to laser cutting, since it would be difficult to cut the materials in intricate patterns using any other techniques.
Typical products
Model components, surgical instruments, wooden toys, metal meshes and filters. Laser-cut ceramics can be used as industrial insulators and furniture can be produced using laser-cut glass or metal.
Similar methods
Water-jet cutting (p.42), die cutting (p.40), electron-beam machining (EBM) (p.24), and plasma-arc cutting (p.33).
Sustainability issues
Laser cutting is very energy intensive in order to sustain the beam intensity, and the speed is considerably slower when working with thick or large pieces. However, as no contact is made between the tool and the substrate, maintenance is low and this reduces material consumption through replacement parts. As with all sheet cutting techniques, material wastage is often high. The nature of the material determines whether waste can be reheated and recycled.
Further information
www.miwl.org.uk
www.ailu.org.uk
www.precisionmicro.com
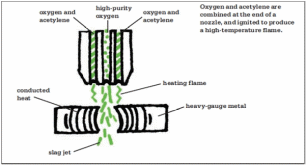
Oxyacetylene Cutting
AKA Oxygen Cutting, Gas Welding, or Gas Cutting
This is a process for cutting metal plate in which oxygen and acetylene are combined at the end of a nozzle and ignited, producing a high-temperature flame. The metal is preheated with this mixture of gases, and then a stream of high-purity oxygen is injected into the center of the flame, which rapidly oxidizes the work piece. Because thermal cutting methods are based on a chemical reaction between the oxygen and iron (or titanium), thin or narrow materials are not suited to the process because the heat can cause them to distort.
This sort of cutting can be undertaken either manually or as an automated process. In the manual operation, the familiar worker in coveralls, with full-face protection, provides the traditional image that sums up this process. In this scenario, the worker may often be welding, rather than cutting, materials.
– Suited to thick metal plate.
– Adaptable to hand or automated use.
– Restricted to a narrow range of materials.