
- •Electronically Controlled On-Demand 4wd System
- •Contents
- •1. Introduction
- •1.1 Application
- •1.2 Advantages
- •Variable Torque Control
- •2. T/m & transfer case
- •3. Coupling & rear axle assembly
- •3.2 Location
- •3.3 Structure
- •3.4 Components
- •3.5 Operation of coupling
- •1) Modulating primary clutch
- •2) Apply force amplifier
- •3) Secondary wet friction clutch
- •4. Inputs and outputs
- •5. Diagnosis
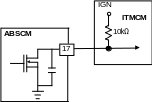
- •6 . Wiring diagram (for cbs)
- •7. 4Wd coupling assembly
- •7.1 Specal tools
- •7.2 Torque
- •7.3 Removal and installation
- •7.4 Disassembly
- •7.5 Reassembly
3) Secondary wet friction clutch
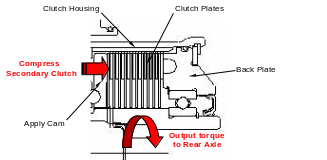
The apply force from the Apply Cam compresses the Secondary Clutch and it increases the frictional force between inner plates which is splined with a Input Shaft and outer plates which is splined to a Clutch Housing. The more frictional force generates the higher output torque.
4. Inputs and outputs
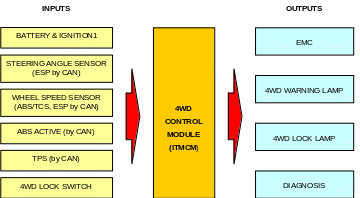
* CAN (Controller Area Network)
S
 TEERING
ANGLE SENSOR (Refer
to ESP
section
for detailed information)
TEERING
ANGLE SENSOR (Refer
to ESP
section
for detailed information)
Steering angle signals of the vehicle with ESP (Electronic Stability Program) come to the ITMCM through the CAN BUS line. However without ESP, steering angle signals directly come to the ITMCM from the sensor side. With the steering angle information, the ITMCM detects the amount of steering and it controls the EMC coil current to prevent torque conflict between the front wheels and the rear wheels.
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Refer to ESP section for detailed information)
W heel
speed sensor signals of the vehicle with ABS/TCS, ESP come to the
ITMCM through the CAN BUS line. However vehicle with a conventional
brake system, wheel speed signals directly come to the ITMCM from the
sensor side. 4WD system always comes with ABS/TCS, ESP or
conventional brake system not with ABS only.
heel
speed sensor signals of the vehicle with ABS/TCS, ESP come to the
ITMCM through the CAN BUS line. However vehicle with a conventional
brake system, wheel speed signals directly come to the ITMCM from the
sensor side. 4WD system always comes with ABS/TCS, ESP or
conventional brake system not with ABS only.
ITMCM varies the EMC current by the Information of the speed difference between the front wheels and the rear wheels.
For example, if the speed difference is high, more EMC current is applied by the ITMCM to reduce the speed gap.
Front wheel speed = (FL Wheel Speed + FR Wheel Speed) / 2
Rear wheel speed = (RL Wheel Speed + RR Wheel Speed) / 2
ABS ACTIVE SIGNAL
Vehicle is in ABS control, ITMCM does not control the EMC current. Vehicle condition is in 2WD state.

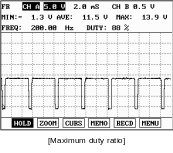
TPS
TPS information comes from the ECM through the CAN BUS line. TPS is an input torque data. TPS angle suddenly increases, then the applied current to an EMC goes up. Therefore the torque distribution to rear wheels goes up.
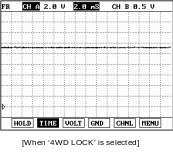
4WD LOCK SWITCH
T his
switch is selected 4WD LOCK lamp comes on. The ITMCM applies maximum
current to the
EMC resulting
in 50 to 50 torque distribution.
his
switch is selected 4WD LOCK lamp comes on. The ITMCM applies maximum
current to the
EMC resulting
in 50 to 50 torque distribution.

EMC (Electro Magnetic Clutch)
The ITMCM varies the applied current to the EMC to make a torque distribution to the rear wheels. The EMC current increases then the magnetic force increases. Stronger magnetic force results in higher pressing force to secondary clutch.


4WD WARNING LAMP
4WD warning lamp blinks (2Hz) when a system failure is detected.
