
- •Unit 3. Metallic structures
- •Text I. Metallic structures
- •1. Give the English equivalents for the following words and word combinations.
- •2. Match the words to make word combinations.
- •3. Make sentences using the parts from columns a and b.
- •4. Are the statements true or false?
- •4. Insert the scheme of different types of metallic constructions. Then use it as a plan to retell the text.
- •5 . The role game. Imagine that you are an architect; you have won the tender for the school construction design. Discuss with your colleagues the types of metallic constructions to be used for:
- •6. Match the words with their translations.
- •Installation
- •7. Match the words to make word combinations.
- •Which statements are true?
- •Put the questions using the answers. Present them in the form of a dialogue with your partner.
- •10. Match the photos and the key words describing the objects presented in them. Use them to make short monologues about these objects.
- •11. Watch the video about Eiffel Tower and fill in the gaps in the statements.
- •Discussion
- •12. Discuss the pros and cons of metallic structures in construction.
- •Project work
- •Make reports on the topics.
- •Unit 4. Frameworks
- •Match the terms and their Russian equivalents.
- •W hat types of frameworks do you know? What types of frameworks (by number of spans) are given in the pictures?
- •4.Name the advantages of frameworks.
- •Text 1. Frameworks
- •1.Find in the text English equivalents for the following words and word combinations.
- •2. Choose the word to finish each row.
- •3. Arrange the words and word combinations from the box and write them down into four groups.
- •4. Give all the types of frameworks by different criterion in the chart.
- •Frameworks
- •5. Сan you translate the sentences without a dictionary?
- •6. Discuss in pairs what kind of a framework (by the structure, material, by the kind of production and so on) possible to apply for:
- •1.A multi-storeyed dwelling 2. A country house
- •3. A sport stadium 4. A vegetable pavilion
- •5. A bakery text 2 unusual frameworks and architecture
- •Match the word combinations describing impressions with their translations.
- •Find the opposites.
- •Are the sentences true or false?
- •10. Arrange the words and word combinations from the box describing the Pompidou Centre into three groups.
- •11. Arrange the words and word combinations from the box describing the Dynamic Tower into three groups.
- •12. Retell text 2 using the following plan and the words from tasks 10, 11.
- •13.Watch an episode of “bbc World News Today”. What are the three questions Tony Bakers answers about the Dynamic Tower during the interview?
Unit 3. Metallic structures
LEAD-IN
What types of metallic structures do you know? Look at the picture and name the metallic structures used in it.
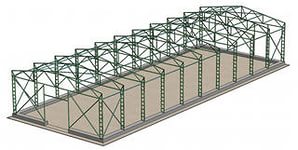
2. What constructive elements of the building can have metallic structures?
3. What are the advantages of such structures?
4. What famous world buildings do you know where metallic constructions were used?



Text I. Metallic structures
M etallic
structures are in great demand in industrial and civil construction.
Carbon and low-alloying steels, sometimes titanium and aluminum
alloys serve the material for metallic structures.
etallic
structures are in great demand in industrial and civil construction.
Carbon and low-alloying steels, sometimes titanium and aluminum
alloys serve the material for metallic structures.
The usage of a certain type of steel depends on the purpose of construction. The most spread steel in metallic structures is ST-3. The furnace steel type A is used for load-bearing elements of metallic structures.
The great variety of metallic structures exists nowadays: steel trusses, steel columns, beam structures, frame and arch structures, metallic membranes and others. Steel trusses are widely spread in many fields of construction: in floors and coverings of industrial and civil buildings, in bridges, in posts of power transmission, trestles, hydrotechnical locks, towers and others. A truss is a bar system linked in units and forming geometrically fix structure under hinge units. Trusses are more economical than beams but more laborious in installing. The efficiency of trusses grows with the span increasing and load decreasing compared to continuous beams. Trusses can be flat (all the bars lie in one flat) and spatial. The former can take the load only applied in their flat. The latter form a rigid spatial bar able to take the load acting in any direction.
Chords forming the outline of a truss and the framework with braces and struts are the main truss elements. The elements connection in units takes place by means of their siding. Depending on the load and functional purpose all trusses can be triangle, brace-shaped, cross-shaped, diamond-shaped and others. Depending on the shape of chords there are trusses with parallel chords, trapezoidal, triangle, polygonal and segmental trusses.
The chord outline of a truss determines its economy that is steel spending. For example, a segmental truss with a parabolic chord will be the most economical for a one-span beam system. The trusses with parallel chords are basically used for industrial buildings. The trusses with triangle outline are good for console systems. According to the type of elements connection in units welded, riveted and bolt trusses are applied.
In frameworks of one-storey industrial buildings steel columns of three types are used: columns with constant height of cross-section, columns with alternating height of cross-section and separate columns.
Beam load-bearing structures are used in long-span buildings of public and industrial purposes such as stadiums, concert halls, covered markets, railway stations, assembly shops, hangars, garages and transport parks. Beam systems are more suitable in those cases when the horizontal loads acting on a building (e.g. from wind) are transmitted on supporting structures. In the buildings of sport purpose stand structures are used for this aim.
In floors of buildings with long spans two-hinged or non-hinged frames are traditionally applied. Frame systems are cheaper and have more toughness compared to beam structures. In their turn non-hinged frames are more economical and harder than two-hinged ones, but the former require massive and expensive foundations. They are more sensitive to temperature changes and undergone to post shrinkage.
Arch coverings are often seen in civil buildings: pavilion, covered markets, gymnasiums and etc. They can be used for hangars and garages. Arch structure is a modification of frame one in which its longitudinal axis approaches to the pressure curve and the rate of curved momentum rapidly decreases.
(по материалам сайта www.en.metcon.ru)
TASKS
