
- •Swot analysis
- •Marketing Environment
- •Analyzing the environment - Five Forces Analysis
- •Arthur d Little (adl) Стратегическое Условие Матрицы
- •Ansoff's Matrix - Planning for Growth
- •Balanced Scorecard
- •Benchmarking
- •The Boston Consulting Group's Product Portfolio Matrix
- •Bowman's Strategy Clock
- •Marketing and Core Competences (Маркетинг и ключевых Компетенций)
- •Gap Analysis
- •The General Electric Business Screen (Бизнес-Экран)
- •The Pareto Principle
- •Shell Directional Policy Matrix
TOPIC (THEME) OF THE LECTURE
MATRIX ANALYSIS IN MARKETING
Lecturar: Dr. Mahbubur Rahman, Ph.D. in economics
Department of Marketing and Management of Foreign Economic Activity
Data 11.10.13 auditorium 4/14, time 15 - 15
2- nd course groups: Marketing and Management of Foreign Economic Activity
«Marketing is the management process for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably».
The Chartered Institute of Marketing (CIM). Accessed 2012
Swot analysis
SWOT analysis is a tool for auditing an organization and its environment. SWOT analysis is the first stage of planning and helps marketers to focus on key issues. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal SWOT factors. Opportunities and threats are external SWOT factors. A strength is a positive internal factor. A weakness is a negative internal factor. An opportunity is a positive external factor. A threat is a negative external factor.
The main purpose of SWOT analysis has to be to add value to our products and services so that we can recruit new customers, retain loyal customers, and extend products and services to customer segments over the long-term. If undertaken successfully, we can then increase our Return On Investment (ROI).
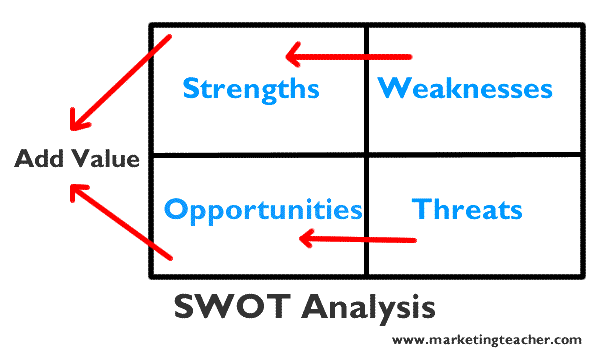
A SWOT strength could be:
Your specialist marketing expertise.
A new, innovative product or service.
Location of your business.
Quality processes and procedures.
Any other aspect of your business that adds value to your product or service.
A SWOT weakness could be:
Lack of marketing expertise.
Undifferentiated products or services (i.e. in relation to your competitors).
Location of your business.
Poor quality goods or services.
Damaged reputation.
A SWOT opportunity could be:
A developing market such as the Internet.
Mergers, joint ventures or strategic alliances.
Moving into new market segments that offer improved profits.
A new international market.
A market vacated by an ineffective competitor.
A SWOT threat could be:
A new competitor in your home market.
Price wars with competitors.
A competitor has a new, innovative product or service.
Competitors have superior access to channels of distribution.
Taxation is introduced on your product or service.
Simple rules for successful SWOT analysis.
Be realistic about the strengths and weaknesses of your organization when conducting SWOTanalysis.
SWOT analysis should distinguish between where your organization is today, and where it could be in the future.
SWOT should always be specific. Avoid grey areas.
Always apply SWOT in relation to your competition i.e. better than or worse than your competition.
Keep your SWOT short and simple. Avoid complexity and over analysis
SWOT analysis is subjective.
A word of caution - SWOT analysis can be very subjective. Do not rely on SWOT too much. Two people rarely come-up with the same final version of SWOT. TOWS analysis is extremely similar. It simply looks at the negative factors first in order to turn them into positive factors. So use SWOT as guide and not a prescription
Marketing Environment
The marketing environment surrounds and impacts upon the organization. There are three key elements to the marketing environment which are the internal environment, the microenvironment and the macroenvironment. Why are they important? Well marketers build both internal and external relationships. Marketers aim to deliver value to satisfied customers, so we need to assess and evaluate our internal business/corporate environment and our external environment which is subdivided into micro and macro.


The organization's marketing environment is made up of:
1. The internal environment e.g. staff (or internal customers), office technology, wages and finance, etc.
2. The micro-environment e.g. our external customers, agents and distributors, suppliers, our competitors, etc.
3. The macro-environment e.g. Political (and legal) forces, Economic forces, Sociocultural forces, and Technological forces. These are known as PEST factors.
