
- •Английский язык
- •655017, Абакан, ул. Щетинкина, 27 оглавление
- •Введение
- •Unit I. Electrical Engineering
- •I. Before reading the text try to predict what information you will find in it, choosing the statements from the list below.
- •II. Read the text to find out if you are right.
- •Vocabulary
- •Electric Motor
- •VII. Explain each of the methods of connection.
- •I. Read the statements given below and if you think the statement is true agree to it saying “That’s right”. If you think it is not true, disagree “That’s wrong” and make the necessary corrections.
- •II. Read the text and say if you are right or wrong.
- •Vocabulary
- •Operating Principles of an Electric Motor
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •V. Find in the Text 2 and put down key words that can be used to speak about operating principles of an electric motor.
- •VI. Match each of these components to its function, and then describe its function in a sentence.
- •VII. Match the given words to sentences 1–7.
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Alternator
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Find in the text and put down key words to speak about an alternator.
- •IV. Find words with similar meanings.
- •V. Use the verbs given below to complete the text about a versatile device (Fig. 3).
- •VI. Match each of these terms with the correct description.
- •I. Read the text and write an outline for it.
- •Vocabulary
- •The First Maglev Train
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Write the summary of the Text 4.
- •IV. Scan the table and find a material which is:
- •V. Scan the table to find:
- •VI. Make definitions of each of the materials in column a, choosing the correct information in columns b and c.
- •I. Read the statements given below and if you think the statement is true agree to it saying “That’s right”. If you think it is not true, disagree “That’s wrong” and make the necessary corrections.
- •II. Read the text and say if you are right or wrong.
- •Vocabulary
- •Electrodynamic Suspension System
- •VII. Complete the safety report with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •VIII. Ask the questions for these answers about the near miss incident in the task VII.
- •IX. Write a set of safety rules based on the report in the task VII.
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Strain Gauge
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Find in the text and put down key words to speak about a strain gauge.
- •IV. Find words with similar meanings.
- •VI. Read the three texts. Match the titles with the texts.
- •VII. Decide whether the sentences are “true” or “false”. Correct the false parts of the sentences.
- •Unit II. Traditional sources of energy
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Wood Fuel
- •II. Match the English and Russian equivalents:
- •III. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •IV. Put the following sentences in the correct order according to the text.
- •V. Answer the following questions:
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •II. Finish the following sentences according to the text.
- •III. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.
- •IV. Combine the words:
- •V. Answer the questions:
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •II. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •III. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Natural Gas
- •II. Finish the following sentences according to the text.
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Find in the text and put down key words to speak about natural gas.
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Electric power plants
- •II. Translate the following word combinations:
- •III. Fill in the blanks with the prepositions.
- •IV. Test. Choose the correct variant:
- •V. Answer the questions:
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Thermal Electrical Plants
- •II. Translate the following word combinations:
- •III. Fill in the blanks with the verbs.
- •IV. Test. Choose the correct variant:
- •V. Answer the questions:
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •The Atomic Power Plant (1)
- •II. Translate the following expressions:
- •III. Test. Choose the correct variant:
- •IV. Answer the following questions:
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •The Atomic Power Plant (2)
- •II. Translate the following word combinations:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Find in the text and put down key words to speak about nuclear power plants.
- •I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
- •Vocabulary
- •Pros and Cons of Nuclear Power Plants
- •II. Decide whether the following statements are true or false according to the text.
- •III. Match the synonyms:
- •IV. Combine the words. Translate them into Russian.
- •V. Read the following sentences and fill in the words listed below.
- •VI. Answer the following questions and give examples:
- •Unit III. Alternative sources of energy
- •I. Choose the right option. Renewable Energy Sources
- •II. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it. The Pros and Cons of Alternative Energy
- •III. Match the English and Russian equivalents:
- •IV. Answer the following questions:
- •V. Agree or disagree with the following statements:
- •Comfortable ['kʌmfətəbl]
- •Vocabulary
- •How Solar Energy Works
- •III. Give the English equivalents about the text:
- •IV. Agree or disagree with the following statements:
- •V. Answer the following questions and give examples:
- •Vocabulary
- •Wind Energy
- •II. Fill in the correct prepositions, translate the phrases, then choose any five items and make up sentences of your own:
- •III. Put the following sentences in the correct order according to the text:
- •IV. Make the following statements true according to the text:
- •V. Answer the following questions and give examples:
- •VI. Fill in the gaps with the words from the text.
- •VII. Write a summary of the Text 3.
- •VIII. Discuss with your groupmates or in pairs:
- •IX. Fill in the words listed below.
- •X. Translate the following text into Russian in written form paying attention to –ing forms.
- •XI. Read the following text and make an abstract of the text in some sentences.
- •XII. Fill in the gaps with the omitted words.
- •I. Answer the following question and read the text below to check your answer.
- •Vocabulary
- •Hydroelectric Power: How it Works
- •II. Answer the following questions:
- •III. Complete the following sentences according to the text.
- •IV. Combine the words and translate them:
- •V. Fill in the correct prepositions, translate the phrases, then choose any five items and make up sentences of your own.
- •Wave Energy Converter
- •Библиографический список
II. Finish the following sentences according to the text.
Coal is composed of …
The energy in coal comes from the energy …
A layer of dead plants was covered by …
The rank of a deposit of coal depends on …
Bituminous coal contains …
…is the lowest rank of coal with the lowest energy content.
Lignite coal deposits were not subjected to …
Coal miners use giant machines …
Surface mining can be used when the coal is buried …
Underground mining is used when the coal is buried …
III. Decide whether the following statements are true or false.
Coal is inflammable black or brown sedimentary rock.
The pressure and heat from the top layers helped the plant remains turn into coal.
Bituminous coal formed about 100 to 300 million years ago is at the least widespread rank of coal in the US.
Bituminous coal has a higher heating value than subbituminous coal.
Lignite is a relatively young coal deposit.
Surface mining is cheaper than underground mining.
Rocks and dirt, sulfur and unwanted materials are removed from coal at a preparation plant.
Coal is burnt by power plants to make steam.
Coke is used for smelting iron ore into iron.
The strength and flexibility are given to steel by the use of coke.
IV. Combine the words:
1) sedimentary |
a) plants |
2) nonrenewable |
b) rock |
3) swampy |
c) value |
4) dead |
d) layer |
5) top |
e) forests |
6) plant |
f) energy |
7) heat |
g) energy source |
8) heating |
h) rank |
9) abundant |
i) remains |
10) raw |
j) materials |
11) moisture |
k) mining |
12) deep |
l) machines |
13) giant |
m) reserves |
14) coal |
n) content |
15) iron |
o) furnaces |
16) hot |
p) ore
|
V. Answer the questions:
1. Why is coal a nonrenewable energy source?
2. What does the classification of coal depend on?
3. How much carbon does anthracite contain?
4. Do the steel and iron industries use bituminous coal?
5. How much carbon does subbituminous contain?
6. What type of coal is crumbly and has a high moisture content?
7. What are the two methods of mining ?
8. What is done at the plant?
9. When is coal ready to be shipped to market?
10. How is coke made?
Text 3.
I. Read the text and be ready to do exercises that follow it.
Vocabulary
oil [ɔɪl] нефть
crudeoil [kru:d] сырой, неочищенный
plant [plænt] завод
environment [ɪn’vaɪrənmənt] окружающаясреда
smelly [’smelɪ] дурно пахнущий, зловонный
silt [sɪlt] ил, осадок
to explore [ɪk’splɔ:] исследовать
sample [’sæmpəl] образец
measurement [’me ʒərmənt] измерение
to promise [’prɔmɪs] обещать
derrick [’derɪk] деррик-кран, подъемная стрела
hole [həul] дыра
sour [sauə] скисать
remove [rɪ’mu:v] передвигать, перемещать
refinery [rɪ’faɪnərɪ] очистительный завод
employee [‚emplɔɪ’i:] работник, служащий
crayon [kreɪən] цветно́й каранда́ш,
tire [’taɪər] шина, покрышка
petroleum [pə’trəulɪəm] керосин, гудрон, нефть
Oil
Oil was formed from the remains of animals and plants (diatoms) that lived millions of years ago in a water environment before the dinosaurs. Over millions of years, the remains of these animals and plants were covered by layers of sand and silt. Heat and pressure from these layers helped the remains turn into what we today call crude oil (Fig. 1).
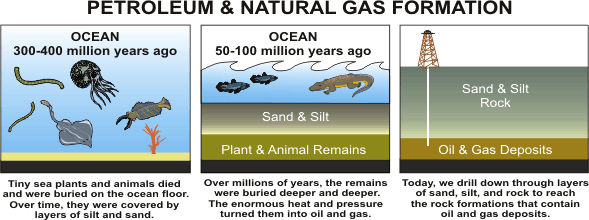
Fig. 1
Crude oil is a smelly, yellow-to-black liquid and is usually found in underground areas called reservoirs. Scientists and engineers explore a chosen area by studying rock samples from the earth. Measurements are taken, and, if the site seems promising, drilling begins. Above the hole a derrick is built to house the tools and pipes going into the well. When finished, the drilled well will bring a steady flow of oil to the surface.
Crude oil is called «sweet» when it contains only a small amount of sulfur and «sour» if it contains a lot of sulfur. Crude oil is also classified by the weight of its molecules. «Light» crude oil flows freely like water, while «heavy» crude oil is thick like tar. Crude oil is measured in barrels.
The world's top five crude oil-: producing countries are Russia Saudi Arabia, United States, Iran, China.
After crude oil is removed from the ground, it is sent to a re-finery by pipeline, ship, or barge. A typical refinery costs billions of dollars to build and millions more to maintain. A refinery runs 24 hours a day, 365 days a year and requires a large number of employees to| run it. A refinery can occupy as much land as several hundred football fields.
At a refinery, different parts of the crude oil are separated into useable petroleum products. Essentially, refining breaks crude oil, down into its various components, which then are selectively reconfigured into new products. All refineries perform three basic steps: separation, conversion and treatment.
One barrel of crude oil, when refined, produces about 19 gal-ions of finished motor gasoline, and 10 gallons of diesel, as well as other petroleum products. Most petroleum products are used to produce energy, to move merchandise and people, help make plastics, and do many other things. For instance, many people across the United States use propane to heat their homes.
Other products made from petroleum include ink, crayons, | bubble gum, dishwashing liquids, deodorant, eyeglasses, CDs and DVDs, tires, ammonia, heart valves.
