
- •Содержание
- •Предисловие
- •Составление реферата-резюме
- •Причастие (Participle)
- •Формы Participle I и Participle II
- •Функции Participle I
- •Функции инфинитива в предложении
- •Условные предложения (Conditional Sentences) Типы условных предложений
- •Вопросы для повторения изученного материала
- •Вопросы к экзамену
- •Библиографический список
- •Приложение а (рекомендуемое) словарь
- •Приложение б
- •Краткий грамматический справочник Модальные глаголы (Model Verbs)
- •Страдательный залог (Passive Voice)
- •Значение и употребление времен глагола в страдательном залоге
- •Особенности употребления страдательного залога в английском языке по сравнению с русским языком
- •Причастие (The Participle)
- •Функции причастия в предложении и основные способы перевода причастий на русский язык
- •Употребление форм причастий Употребление форм причастия для выражения соотнесенности во времени
- •Употребление причастий для образования сложных глагольных форм
- •«Объектный предикативный причастный оборот»1
- •«Субъектный предикативный причастный оборот»1
- •Независимый причастный оборот
- •Инфинитив (The Infinitive)
- •Функции инфинитива в предложении
- •Употребление инфинитива с частицей to
- •Употребление инфинитива без частицы to
- •Употребление форм инфинитива
- •«Объектный предикативный инфинитивный оборот»1
- •«Субъектный предикативный инфинитивный оборот»1
- •Инфинитивные обороты с предлогом for
- •Согласование времен
- •Косвенные вопросы
- •Проверочный тест
- •Наклонение (The Mood)
- •Придаточные условные предложения Придаточные условные предложения I типа Реальные условия (Probable Condition)
- •Придаточные условные предложения II типа Нереальное условие в настоящем или будущем времени
- •Придаточные условные предложения III типа Нереальное условие в прошедшем времени (Impossible Condition)
- •Реферирование Развернутый план реферирования
- •Учебное издание английский язык Практикум
- •3 46500, Г. Шахты, Ростовская обл., ул. Шевченко, 147
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНТСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ
Государственное образовательное учреждение
высшего профессионального образования
«Южно-Российский государственный университет экономики и сервиса»
(ГОУ ВПО «ЮРГУЭС»)
АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ЯЗЫК
Практикум
для студентов 2 курса ОФО и ЗФ
(с использованием дистанционных технологий)
специальности 200503 «Стандартизация и сертификация»

ШАХТЫ
ГОУ ВПО «ЮРГУЭС»
2009
УДК 811.111(076)
ББК 81.2Англ-923
А647
Составитель:
преподаватель кафедры «Иностранные языки»
Т.Ю. Иванченко
Рецензенты:
доцент кафедры «Иностранные языки»
В.И. Белай
доцент кафедры «Иностранные языки»
Т.В. Трусова
Рекомендован к внутривузовскому изданию
редакционно-издательским советом ЮРГУЭС
А647 Английский язык : практикум для студентов 2 курса ОФО и ЗФ (с использованием дистанционных технологий) специальности 200503 «Стандартизация и сертификация» / [составитель Т.Ю. Иванченко]. – Шахты : ГОУ ВПО «ЮРГУЭС», 2009. – 118 с.
Практикум включает в себя 10 уроков, аутентичные тексты для аудиторной и самостоятельной работы и приложения, в которых содержится словарь, краткий грамматический справочник и клише для аннотирования и реферирования.
Основная цель практикума – совершенствование навыков просмотрового, ознакомительного и поискового чтения аутентичных текстов по специальности с опорой на лексико-грамматический материал, а также совершенствование техники перевода и реферирования.
Может оказать помощь студентам, специализирующимся в области стандартизации и сертификации, при овладении навыками устной речи в пределах изучаемого материала по дисциплине, расширении словарного запаса и активизации грамматического материала.
УДК 811.111(076)
ББК 81.2Англ-923
© ГОУ ВПО «Южно-Российский государственный
у ниверситет
экономики и сервиса», 2009
ниверситет
экономики и сервиса», 2009
Содержание
Предисловие 4
Lessоn 1 5
Lesson 2 13
Lesson 3 18
Lesson 4 28
Lesson 5 34
Lesson 6 40
Lesson 7 46
Lesson 8 52
Lesson 9 58
Lesson 10 64
Вопросы для повторения изученного материала 70
Вопросы к экзамену 71
Supplementary Reading 72
Библиографический список 82
Приложение А. Словарь 83
Приложение Б. Краткий грамматический справочник 91
Приложение В. Клише для аннотирования и реферирования 115

Предисловие
Данный практикум разработан согласно требованиям примерной Программы для неязыковых вузов и предназначен для студентов 2 курса очной формы обучения и ЗФ (с использованием технологий дистанционного обучения) специальности 200503 «Стандартизация и сертификация».
Цель практикума – развитие и совершенствование компетенций в различных видах чтения текстов по специальности с опорой на лексико-грамматический материал, а также совершенствование техники перевода.
Практикум состоит из 10 уроков, Supplementary Reading (аутентичные тексты для домашнего чтения) и приложений A, Б и В, которые содержат словарь, краткий грамматический справочник и пояснения и клише для аннотирования и реферирования. Каждый урок включает 2 текста (основной и дополнительный) с глоссарием и упражнениями, направленными на проверку понимания содержания прочитанного, закрепление и повторение специальной лексики, упражнения на закрепление грамматического материала и развитие навыков устной речи.
Учебные тексты дают возможность преподавателю организовать свою работу так, чтобы она была нацелена на развитие всех видов чтения.
Грамматический материал охватывает систему времен в активном и пассивном залоге, модальные глаголы, инфинитивные и причастные обороты, косвенную речь и условные предложения.
Дополнительные тексты предназначены для самостоятельного внеаудиторного чтения.
Успешное выполнение лексико-грамматических заданий существенно повысит профессиональный и общеобразовательный уровень студентов.
Целесообразность написания и публикации данного практикума вызвана отсутствием аутентичного учебного материала по специальности «Стандартизация и сертификация», что негативно сказывается на качестве подготовки будущих специалистов в области стандартизации и сертификации.
LESSON 1
Прочитайте текст и выполните упражнения к нему.
ISO (INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDISATION)
(Part 1)
What are standards ?
Standards are documented agreements containing technical specifications or other precise criteria to be used as rules, guidelines, or definitions of characteristics, to ensure that materials, products, processes and services are fit for their purpose.
For example, the format of the credit cards, phone cards, and "smart" cards that have become commonplace is derived from an ISO International Standard. Adhering to the standard, which defines such features as an optimal thickness (0,76 mm), means that the cards can be used worldwide.
International Standards thus contribute to making life simpler, and to increasing the reliability and effectiveness of the goods and services we use.
What is ISO ?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is a worldwide federation of national standards body, one from each country. It is located in Switzerland and was established in 1947 to develop common international standards in many areas. Its members come from over 120 national standards bodies. ISO now is the world's largest developer of standards. Although ISO's principal activity is the development of technical standards, ISO standards also have important economic and social repercussions. ISO standards make a positive difference, not just to engineers and manufacturers for whom they solve basic problems in production and distribution, but to society as a whole.
The International Standards which ISO develops are very useful. They are useful to industrial and business organizations of all types, to governments and other regulatory bodies, to trade officials, to conformity assessment professionals, to suppliers and customers of products and services in both public and private sectors, and, ultimately, to people in general in their roles as consumers and end users. ISO standards contribute to making the development, manufacturing and supply of products and services more efficient, safer and cleaner. They make trade between countries easier and fairer. They provide governments with a technical base for health, safety and environmental legislation. They aid in transferring technology to developing countries. ISO standards also serve to safeguard consumers, and users in general, of products and services – as well as to make their lives simpler. When things go well – for example, when systems, machinery and devices work well and safely – then it is because they conform to standards.
And the organization responsible for many thousands of the standards which benefit society worldwide is ISO. ISO's work results in international agreements which are published as International Standards.
Vocabulary:
repercussions – отражение, влияние
distribution – распределение
regulatory bodies – регулирующие органы
conformity – соответствие
assessment – оценка
contribute – делать вклад
fairer – более честной
provide – обеспечивать
legislation – законодательство
aid – помогать
to benefit – помогать, содействовать
to safeguard – охранять, гарантировать
Exercise 1. Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
1) What is ISO?
2) What is ISO’s principal activity?
3) To whom do ISO standards make positive difference?
4) Are the International Standards which ISO develops very useful?
5) What do ISO standards contribute to?
6) ISO standards make trade between countries easier and fairer, don’t they?
7) Why do things, systems, machinery and devices work well?
Exercise 2. Определите, какие предложения соответствуют тексту.
1) ISO's principal activity is the development of technical standards.
2) ISO standards make a positive difference to society as a whole.
3) ISO standards make a positive difference only to engineers and manufacturers.
4) The International Standards are useful to tourism.
5) Many interdependent standards and specifications affect the development and administration of web sites.
6) ISO standards also serve to safeguard consumers, and users in general, of products and services.
Exercise 3. Найдите в тексте русские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
National standards bodies, development of technical standards, conformity assessment professionals, suppliers and customers of products and services; base for health, safety and environmental legislation.
Exercise 4. Сделайте аннотацию текста. Клише для аннотации вы можете найти в Приложении В.
Грамматика: Страдательный залог.
Если подлежащее обозначает лицо или предмет, подвергающийся действию со стороны другого лица или предмета, то глагол-сказуемое употребляется в форме страдательного залога (Passive Voice).
Если указано, кем производится действие, то употребляется предлог bу, а если указано чем (с помощью чего произведено действие) – предлог with.
Изучите таблицу форм пассивного залога.
|
Simple |
Progressive |
Perfect |
Общая фор-мула |
A
I are |
A m
I are |
Have/has + been + V3 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Present |
I am asked He is asked She is asked We are asked You are asked They are asked |
I am being asked He is being asked She is being asked We are being asked You are being asked They are being asked |
I have been asked He has been asked She has been asked We have been asked You have been asked They have been asked |
|
Am I asked? Is he/she asked? Are you/we/they asked? |
Am I being asked? Is he/she being asked? Are we/you /they being asked? |
Have I/we/you/they been asked? Has he/she been asked? |
|
I am not asked He/she is not asked We/you/they are not asked |
I am not being asked He is not being asked They are not being asked |
I have not been asked He has not been asked
|
Past |
I was asked He was asked She was asked You were asked We were asked They were asked |
I was being asked He was being asked She was being asked We were being asked You were being asked They were being asked |
I had been asked He had been asked She had been asked We had been asked You had been asked They had been asked |
|
Was I/he/she asked? Were you/we/they asked? |
Was I being asked? Were you being asked? |
Had I been asked? |
Окончание табл.
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
I was not asked You were not asked |
I was not being asked You were not being asked |
I had not been asked
|
Future |
I shall be asked He will be asked She will be asked We shall be asked You will be asked They will be asked |
---------------------------- |
I shall have been asked He will have been asked She will have been asked We shall have been asked You will have been asked They will have been asked |
|
Shall I be asked? Will you be asked? |
---------------------------- |
Shall I have been asked? Will you have been asked? |
|
I shall not be asked I will not be asked |
---------------------------- |
I shall not have been asked You will not have been asked |
Future-in-the-Past |
I should be asked He would be asked She would be asked We should be asked You would be asked They would be asked |
---------------------------- |
I should have been asked He would have been asked She would have been asked We should have been asked You would have been asked They would have been asked |
|
I should not be asked |
---------------------------- |
I should not have been asked |
Пассивные конструкции с разными типами дополнений
|
Прямое дополнение (o. l) |
Косвенное дополнение (o. 2) |
Предложное дополнение |
Active |
They visited the British Standards Institute. (what?) |
She gave а magazine to me. |
We were speaking about certification. |
|
The Queen awarded them. (whom?) |
(to /for whom?) |
I’ll send for help. |
Passive |
The British Standards Institute was visited by them. |
I was given a magazine. |
Certification was being spoken about. |
|
They were awarded by the Queen. |
A magazine was given to me. |
Help will be sent for. |
1. Страдательный залог используется как в разговорной, так и в письменной речи; наиболее характерен в описаниях, в безличных предложениях, в случаях, когда надо подчеркнуть агента действия (a “by” phrase) или же, напротив, избежать ссылки на него (когда упоминание агента не важно/не информативно (e.g.: the umbrella was lost) или же он не известен (e.g.: a TV set was made in Japan). У ряда глаголов с двойным управлением: buy, get, sell, offer, give, send, hand, promise, ask, pay, show, tell, teach etc возможны следующие пассивные конструкции:
Глаголы с двумя дополнениями
v.+ o.l+(to/for) + o.2 |
v.+ o.2 + o.l |
||
Active |
Passive |
Active |
Passive |
I told the news to him. I teach English to her. |
The news was told to him. English is taught to her. |
I told him the news. I teach her English. |
He was told the news. She is taught English. |
Выбор конструкции в таких случаях обусловливается отношением говорящего: самая важная информация должна быть в конце предложения.
Способы перевода пассивных конструкций на русский язык
1) пассивной конструкцией |
---------- |
Книга опубликована |
2) возвратным глаголом |
Ей говорилось |
Книга публиковалась |
3) неопределенно-личной конструкцией |
Ей говорили |
Книгу публикуют |
4) безличной конструкцией |
Ей было сказано |
--------- |
2. Трудности могут возникать и при переводе предложных конструкций (начинающихся с предлога, типа: за ним следили; о нем говорили) и глаголов have, get в конструкциях, характерных для страдательного залога: to have /get something done. Сравните: A church was built /They had a church built; My hair was cut /I got my hair cut.
Exercise 5. Переведите предложения. Обратите внимание на пассивные конструкции.
1) The process is guided by the principles of consensus.
2) Many organizations are involved in certification.
3) Certifier’s report is being accompanied by tables and diagrams.
4) Our laboratory has been equipped with new testing facilities.
5) New tests will be carried out soon.
6) The tests had been done before the conference.
7) The advantages of this technique over others was recognized by many scientists.
8) Nature is often hidden, sometimes overcome, seldom extinguished. (F. Bacon).
Exercise 6. Перепишите предложения, раскрывая скобки и употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени в Passive Voice.
1) The British Institute of Standards (to create) under the initiative of certain societies.
2) The sanction (to sign) last week.
3) When signed by the representative of the council the standard (to accept).
4) An International Conference on Certification (to expect) in May.
5) The capital of the USA (to name) after the first president George Washington.
6) Many famous people (to be born) and (to live) in London.
7) These data (to present) in Figure 2.
8) The information (to use) in preparing the program.
9) Genius must (to bear), and never can (to teach).
Exercise 7. Переведите предложения, назовите глагол-сказуемое и укажите его время. Обратите внимание на особенности перевода пассивных конструкций.
1) A certification of conformity is granted in one participated country and recognized in other participating countries.
2) The sanction was signed by the representative of supervising branch council.
3) The British Institute of Standards has been created under the initiative of certain societies.
4) The process is guided by the principles of consensus.
5) The Institute was based on the National Center of Standardization, Metrology and Certification as a state enterprise.
6) Certifier’s report is being accompanied by tables and diagrams.
7) An International Exhibition «CERTIFICATION AND REGULATION 2009» is expected in May.
8) Our laboratory has been equipped with new testing facilities.
Прочитайте текст.
Пояснения к тексту:
ISO – International Organization for Standardization (ИСО)
BS – British Standard
PDCA – Do / Plan / Check / Act
WHAT IS ISO 9000?
ISO 9000 applies to all types of organizations. It doesn't matter what size they are or what they do. It can help both product and service oriented organizations to achieve standards of quality that are recognized and respected throughout the world.
ISO 9000 is a family of ISO standards for Quality Management Systems. ISO 9000 was developed from the British Standards Institution's BS 5750. The ISO 9000 standards are maintained by ISO and administered by accreditation and certification bodies. Although the standards originated in manufacturing, they are now employed across a wide range of other types of organizations. In fact, according to ISO in 2004, "service sectors now account by far for the highest number of ISO 9001:2000 certificates – about 31 % of the total" – source: the ISO Survey 2004.
Some countries re-label ISO 9000 as a national standard. ISO 9000 does not guarantee the quality of end products and services; rather, it certifies that consistent business processes are being applied.
ISO 9001:2000 is based on:
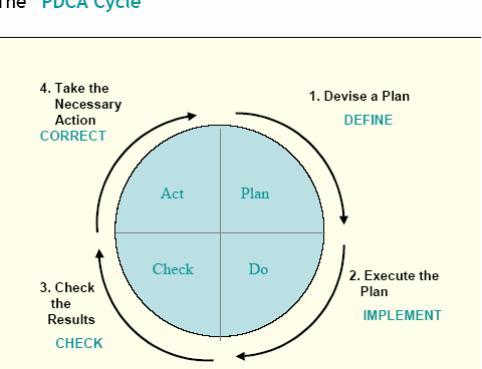
• The “PDCA Cycle”
• The “8 Quality Management Principles”
The “PDCA Cycle”
The “8 Quality Management Principles”:
* Organizations rely on customers. Therefore: organizations must understand customer’s needs, meet customer’s requirements. Organizations must exceed customer’s expectations.
* Organizations rely on leaders. Therefore: leaders must establish a unity of purpose and set the direction the organization should take. Leaders must create an environment that encourages people to achieve the organization's objectives.
* Organizations rely on people. Therefore: organizations must encourage the involvement of people at all levels. Organizations must help people to develop and use their abilities.
* Organizations are more efficient and effective when they use a process approach. Therefore: organizations must use a process approach to manage activities and related resources.
* Organizations are more efficient and effective when they use a systems approach. Therefore: organizations must identify interrelated processes and treat them as a system. Organizations must use a systems approach to manage their interrelated processes.
* Organizations are more efficient and effective when they continually try to improve. Therefore: organizations must make a permanent commitment to continually improve their overall performance.
* Organizations perform better when their decisions are based on facts. Therefore: organizations must base decisions on the analysis of factual information and data.
* Organizations must maintain a mutually beneficial relationship with their suppliers.
Vocabulary:
are recognized – признаны
are respected – уважают(ся)
oriented – ориентированные
a wide range – широкий перечень
originated – происходящий; берущий начало
consistent – последовательный
exceed – превышать, превосходить
rather – скорее; до некоторой степени
rely – полагаться
encourage – поощрять
involvement – вовлечение
interrelated – взаимный
Exercise 8. Найдите в тексте эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний, которые помогут вам лучше понять текст:
Достичь стандартов качества, стандарты защищены ИСО, органы по аккредитации и сертификации, качество конечных продуктов и услуг, принципы качества управления, соответствовать запросам покупателей, создать обстановку, развивать и использовать свои способности, управлять деятельностью, анализ информации и данных.
LESSON 2
Прочитайте текст и выполните упражнения к нему.
ISO (NTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDISATION)
(Part 2)
How it all started
International standardization began in the electrotechnical field: the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) was created in 1906. Pioneering work in other fields was carried out by the International Federation of the National Standardizing Associations (ISA), which was set up in 1926. The emphasis within ISA was laid heavily on mechanical engineering.
ISA's activities ceased in 1942, owing to the Second World War. Following a meeting in London in 1946, delegates from 25 countries decided to create a new international organization "the object of which would be to facilitate the international coordination and unification of industrial standards". The new organization, ISO, began to function officially on 23 February 1947.
The first ISO standard was published in 1951 with the title, " Standard reference temperature for industrial length measurement ".
ISO's name: a user's guide. In fact, "ISO" is a word, derived from the Greek isos, meaning "equal ", which is the root of the prefix " iso-" that occurs in a host of terms, such as " isometric " (of equal measure or dimensions - Shorter Oxford English Dictionary) and " isonomy " (equality of laws, or of people before the law - ibid.). From "equal" to "standard", the line of thinking that led to the choice of "ISO" as the name of the organization is easy to follow.
In addition, the name has the advantage of being valid in each of the organization's three official languages – English, French and Russian. The confusion that would arise through the use of an acronym is thus avoided, e.g. "IOS" would not correspond to the official title of the organization in French – Organisation Internationale de Normalisation.
International standardization: What does it achieve?
Industry-wide standardization is a condition existing within a particular industrial sector when the large majority of products or services conform to the same standards. It results from consensus agreements reached between all economic players in that industrial sector – suppliers, users, and often governments. They agree on specifications and criteria to be applied in the choice and classification of materials, the manufacture of products, and the provision of services. The aim is to facilitate trade, exchange and technology transfer through: enhanced product quality and reliability at a reasonable price, improved health, safety and environmental protection, and reduction of waste, greater compatibility and interoperability of goods and services, simplification for improved usability, reduction in the number of models, and thus reduction in costs, increased distribution efficiency, and ease of maintenance.
Users have more confidence in products and services that conform to International Standards. Assurance of conformity can be provided by manufacturers' declarations, or by audits carried out by independent bodies.
Why is international standardization needed?
The existence of non-harmonized standards for similar technologies in different countries or regions can contribute to so-called "technical barriers to trade". Export-minded industries have long sensed the need to agree on world standards to help rationalize the international trading process. This was the origin of the establishment of ISO.
Vocabulary:
Cease – прекращать(ся)
derive – происходить (от)
dimensions – размеры, объем
valid – действительный, имеющий силу
provision – снабжение, обеспечение
Exercise 1. Сделайте аннотацию текста.
Exercise 2. Завершите предложения согласно содержанию текста.
The Capability Maturity Model is intended to help software organizations improve the maturity of their software processes in terms ………….
The focus is on identifying key process areas and ……………… .
Practices are defined sufficiently to allow for …………….. .
An organization develops the ability to assess the impact of ……………… .
The purpose of the CMMI is to: support process and product improvement to reduce …………….. .
Выполните упражнения по грамматике.
Exercise 3. Повторите модальные глаголы (используйте грамматический материал Приложения Б). Выполните упражнениe письменно. Подчеркните в каждом предложении модальные глаголы или их эквиваленты. Переведите предложения на русский язык.
1) Тhe sponsor of the third- party program (the certifier) may be responsible for collecting the required data.
2) The manufacturer’s design specifications can produce the product that conforms to a particular standard.
3) The student must know and be able to use basic concepts in the field of standardization and certification.
4) States may regulate products under their own authority for health and safety reasons.
5) A product can meet one or more standards.
6) The student should know aims, tasks, and types of certification tests.
7) They are able to develop procedure of carrying out certification of forest management.
8) Students should know schemes of products certification used in Russia.
9) A mechanism must exist for the development and coordination of positions.
10) The student should be able to use standards of Pan-European system of forest certification.
11) Just over 50 years ago US drug manufacturers could produce and sell drugs without testing them on animals or humans.
12) The International Conference on Metrology is to start very soon.
Exercise 4. Вместо пропуска употребите нужную форму модального глагола (can, may, should).
1) Some problems … be solved more easily within smaller groups of states.
2) Certifiers … wish to provide information on the quality or safety of one certified product.
3) The student … know ecological certification.
4) The lesson is over, you … go now.
5) Their children … read English books quite easily.
6) “Whoever knocks at the door, you (must/may) not open it,” mother told her children before going out.
Exercise 5. Выберите правильный модальный глагол в соответствии со значением и временем.
1. She doesn’t look too well today, she (should/ought to) see a doctor.
2. Jane is seriously ill, you (should/be to) visit her in the hospital.
3. I (am/have) to meet the tourists in the airport.
4. He (was/had) to get up at 5 o’clock every morning, although he hated it.
5. The manager came here in person, it must (be/have been) something important.
6. You don’t know any foreign language, you (mightn’t/couldn’t) apply for this job.
7. I cannot find my book. I (could/should) have lost it.
Прочитайте и переведите текст.
SIX SIGMA
What is Six Sigma?

Six Sigma is a highly disciplined process that helps to develop and deliver near perfect products and services. The central idea behind Six Sigma is that if you measure how many defects we have in a process, we can systematically figure out how to eliminate them and get close to ZERO Defects.
The key features of Six Sigma are:
• A statistical measure of variation. Full Six Sigma equals 99,9997 % accuracy.
• Methodology for improving key processes.
• A “tool box” of quality and management tools for problem resolution.
• A business philosophy focusing on continuous improvement.
• An organized process for structured analysis of data.
History of Six Sigma
Motorola developed the Six Sigma methodology in the mid 1980’s as a result of recognizing that products with high pass yield rarely failed in use. Statistical term dates back to the 1800’s (Carl Frederick Gauss).
Six Sigma Methodology
• D.M.A.I.C (Define. Measure. Analyze. Improve. Control).
• Provides a logical sequence for applying existing problem solving tools and concepts. Repacks existing tools and concepts.
• Various quality/ management tools applied at each step.
• Project sponsor review recommended at conclusion of each step before moving to next step.
When to use Six Sigma?
• Unknown causes / situations.
• Problems are common place and not well defined.
• When “broad spectrum” approach is inappropriate.
• When other problem solving methods fail.
• In a complex situation with many problems.
Vocabulary:
figure out – вычислять
eliminate – устранять; исключать
accuracy – точность
yield – количество добываемого или производимого продукта; выход
Exercise 6. Ответьте на вопросы к тексту.
1) What is the central idea behind Six Sigma?
2) When did Motorola develop the Six Sigma methodology?
3) What does Six Sigma provide?
4) When is Six Sigma used?
Exercise 7. Вставьте вместо пропуска необходимое по смыслу слово.
1) Six Sigma is a highly … process that helps to develop and deliver near perfect products and services.
a) organized b) developed c) disciplined
2) If you measure how many … we have in a process, we can systematically figure out how to eliminate them.
a) problems b) defects c) mistakes
3) Motorola … the Six Sigma methodology in the mid 1980’s.
a) designed b) developed c) fulfilled
It’s interesting to know:
Пояснения к тексту:
IT – internal translator (внутренний транслятор)
CRM – управление по работе с клиентами
IL – Infrastructure Library
BS – British Standard.
ITIL
The IT Infrastructure Library is the most accepted approach to IT Service Management in the world. ITIL is based around five overlapping principle elements, namely the business perspective, application management, IT service delivery, service support, and ICT infrastructure management. It supports the BS 15000 and underpins ISO 9000.
CRM
CRM is a set of methodologies, software, and usually Internet capabilities that help an enterprise manage customer relationships in an organized way. It includes all business processes in sales, marketing, and service that touch the customer. For example, an enterprise might build a database about its customers that describes relationships in sufficient detail so that management, salespeople, people providing service, and even the customer can access information, match customer needs with product plans and offerings, remind customers of service requirements, and know what other products a customer has purchased, and so on.
Vocabulary:
underpin – подводить фундамент
(in)consistency – (не)последовательность
endeavor – пытаться, стараться; попытка
overlapping – частично совпадающий
sufficient – достаточный
match – подходить
LESSON 3
Прочитайте и переведите текст.
Пояснения к тексту:
The CMM – the Capability Maturity Model
The CRM – the Customer Relationship Management
The BS – the British Standard
THE CAPABILITY MATURITY MODEL
The CMM Integration Project was formed in 1997 to build an initial set of integrated models and establish a framework to enable integration of future models create an associated set of appraisal and training products.
The CMM describes the principles and practices underlying software process maturity. It is intended to help software organizations improve the maturity of their software processes in terms of an evolutionary path from chaotic processes to mature, disciplined software processes. The focus is on identifying key process areas and the exemplary practices that may comprise a disciplined software process. The maturity framework provided by CMM establishes a context in which:
• Practices can be repeated. If you don't repeat an activity there is no reason to improve it. The focus is on identifying key process areas and commits the organization to implementing and performing consistently.
• Best practices can be rapidly transferred across groups. Practices are defined sufficiently to allow for transfer across project boundaries, thus providing some standardization for the organization.
• Variations in performing best practices are reduced. Quantitative objectives are established for tasks; and measures are established, taken, and maintained to form a base-line from which an assessment is possible.
• Practices are continuously improved to enhance capability (optimizing) structure of CMM Maturity Levels. A layered framework providing a progression to the discipline needed to engage in continuous improvement. An organization develops the ability to assess the impact of a new practice, technology, or tool on their activity. Hence it is not a matter of adopting these, rather it is a matter of determining how innovative efforts influence existing practices. This really empowers projects, teams, and organizations by giving them the foundation to support reasoned choice.
PURPOSE OF CMM INTEGRATION PROJECT
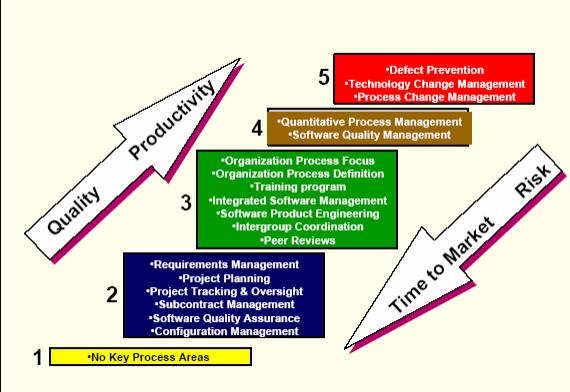
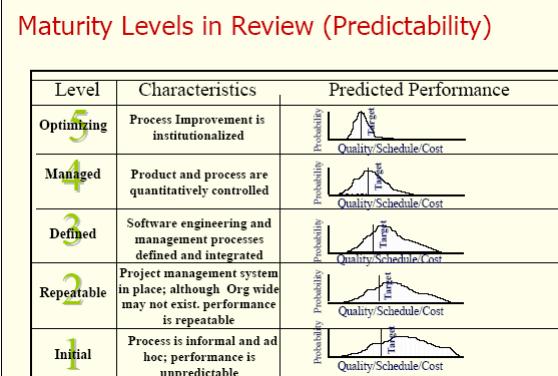
The purpose of the CMMI is to support process and product improvement, to reduce redundancy and eliminate inconsistency experienced by those using multiple standalone models. Integrate disciplines such as systems engineering and software engineering, which are inseparable in a product development endeavor.
Vocabulary:
аppraisal – оценка
mature processes – готовые процессы
maturity – готовность
comprise – включать
commit – поручать, передавать
boundaries – границы
reduce – сокращать
quantitative – количественный
enhance – повышать; увеличивать
capability – способность
engage – вовлекать
assess – оценивать
hence – отсюда; следовательно
adopt – принимать; заимствовать
empower – уполномочивать; давать возможность
associated set – объединенная серия
endeavor – усилие
Exercise 1. Завершите предложения согласно содержанию текста.
1) The Capability Maturity Model is intended to help software organizations improve the maturity of their software processes in terms …………. .
2) The focus is on identifying key process areas and ……………… .
3) Practices are defined sufficiently to allow for …………….. .
4) An organization develops the ability to assess the impact of ……………… .
5) The purpose of the CMMI is to: support process and product improvement to reduce …………….. .
Exercise 2. Внимательно прочитайте текст еще раз и письменно изложите его содержание, используя схему написания реферата-резюме и клише. Объем – 10 предложений.

 m
m
 s
V3
s
V3
 s
being --V3
s
being --V3