
- •Английский язык
- •Предисловие
- •Part 1. Vocabulary practice
- •2. Read and translate the following text. Text 1 Electronics
- •3. Check your knowledge of the following terms.
- •4. Fill in the blanks with the words given below.
- •Part 2. Speaking practice
- •5. Answer the following questions to the text «Electronics».
- •6. Agree or disagree with the following statements. Use such word combinations as:
- •7. Make up a dialogue on the following situation:
- •Part 3. Translation practice
- •8. Выполните следующие предтекстовые задания:
- •Text 2 Fabrication Technology
- •Abstract
- •Unit 2. Vacuum Tubes part 1. Vocabulary practice
- •2. Read and translate the following text. Text 1
- •Vacuum Tubes
- •3. Give English equivalents to the following Russian terms.
- •4. Fill in the blanks with the words given in the text.
- •5. Translate into English.
- •Part 2. Speaking practice
- •6. Answer the following questions to the text “Vacuum Tubes”.
- •Part 3. Translation practice
- •Text 2 cmos Technology
- •Unit 3. Emission part 1. Vocabulary practice
- •1. Memorize the following words and word combinations.
- •2. Read and translate text 1. Text 1 Emission
- •3. Find English equivalents for the following terms.
- •4. Choose Russian equivalents for the following words from the list given below.
- •Part 2. Speaking practice
- •5. Name the main points of the text 1 basing on the following questions.
- •6. Suggest the answers to the following descriptions using the words given below.
- •7. Make up a dialogue on the following situation:
- •Part 3. Translation practice
- •8. Выполните следующие предтекстовые задания:
- •Text 2 cmos Technology
- •Unit 4. Tube Noise part 1. Vocabulary practice
- •2. Read and translate the text 1. Text 1 Tube Noise
- •3. Choose the proper word from the brackets.
- •4. Make up sentences out of the following words.
- •Part 2. Speaking practice
- •5. Point out which of these sentences does not contain the information from the text.
- •6. Give the main points of the text answering the following questions.
- •7. Write an annotation of the text. Use the following phrases.
- •8. Make up a dialogue on the following situation:
- •Part 3. Translation practice
- •9. Выполните следующие предтекстовые задания:
- •Text 2 Basic Microfabrication Steps
- •Unit 5. Compounds and Elements part 1. Vocabulary practice
- •2. Read and translate the text. Text 1 Compounds and Elements
- •3. Read the following international words and guess their meanings.
- •4. Give English equivalents for the following words and word combinations.
- •6. Translate into English.
- •Part 2. Speaking practice
- •7. Give definitions of the following words: “a compound”, “an element”, “a molecule”, “an atom”. Memorize them.
- •8. Answer the following questions to the text.
- •9. Read the following interesting facts about oxygen and discuss them in your group. Did You Know?
- •10. Reveal the structure of any element’s or compound’s molecule depicting it on the blackboard. Part 3. Translation practice
- •11. Выполните следующие предтекстовые задания:
- •Text 2 Thin-film Deposition
- •Научный редактор г.В. Царева Редактор издательства л.И. Афонина
Text 2 Basic Microfabrication Steps
The fabrication of integrated circuits (ICs) using CMOS or BiCMOS technology is based on four basic microfabrication techniques: deposition, patterning, doping and etching. Fig. 1.3 illustrates how these techniques are combined to build up an IC layer by layer: a thin film, such as an insulating silicon dioxide film, is deposited on the substrate, a silicon wafer. A light-sensitive photoresist layer is then deposited on top and patterned using photolithography. Finally, the pattern is transferred from the photoresist layer to the silicon dioxide layer by an etching process. After removing the remaining photoresist, the next layer is deposited and struc tured, and so on. Doping of a semiconductor material by ion implantation, the key step for the fabrication of diodes and transistors, can be performed directly after photolithography, i.e. using a photoresist layer as mask, or after patterning an implantation mask (e.g. a silicon dioxide layer).
Silicon is the standard substrate material for IC fabrication and, hence, the most common substrate material in microfabrication in general. It is supplied as single-crystal wafers with diameters between 100 and 300 mm. In addition to its favorable electrical properties, single-crystal silicon also has excellent mechanical properties [9], which enable the design of micromechanical structures. CMOS processes for digital electronics typically use low-doped (doping concentration in the 1016 cm–3 range) silicon wafers, whereas processes for mixed-signal or analog electronics are often based on high-doped (doping concentration in the 1019 cm–3 range) wafers with a low-doped epitaxial layer to minimize latch-up. The choice of the substrate material might already require a compromise between the requirements for the MEMS part and the on-chip electronics: the fabrication of membrane structures for, e.g., pressure sensors is typically based on anisotropic silicon etching in a potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution (see Section 1.2). High p-type doping (NA_1019 cm–3) substantially reduces the silicon etch rates in KOH solutions, thus preventing the use of highly p-doped CMOS substrates in combination with KOH etching.
In the following, a brief overview on the four basic microfabrication steps will be given. More details can be found in textbooks and reference books on semiconductor processing [6–8, 10, 11].


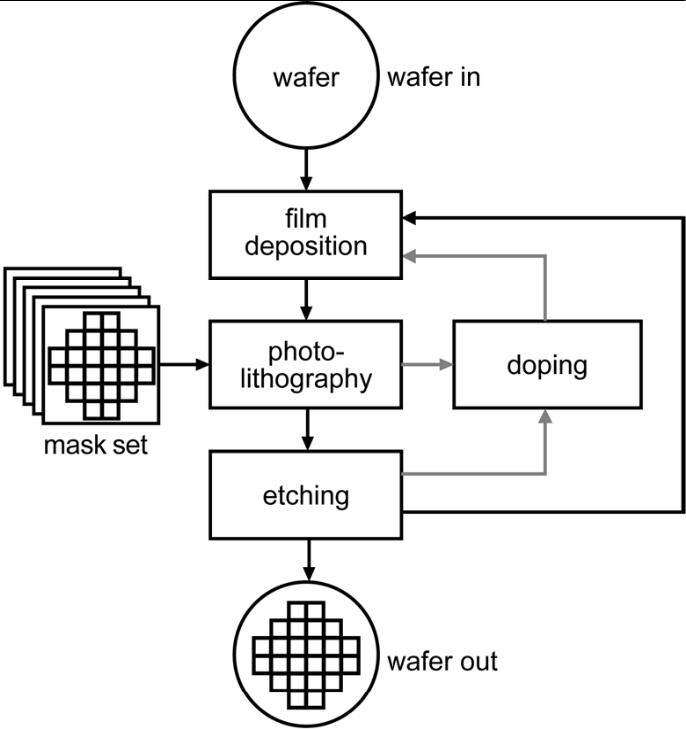

Fig. 1.3 Flow diagram of IC fabrication process using the four basic microfabrication techniques: deposition, photolithography, etching and doping.
Unit 5. Compounds and Elements part 1. Vocabulary practice
1. Memorize the following words and word combinations.
substance |
|
compound |
|
to decompose |
|
property |
|
oxygen |
|
hydrogen |
|
rare |
|
to contain |
|
to retain |
|
to constitute |
|
constituent |
|
particle |
|
charge |
|
to surround |
|
nucleus (мн. ч. nuclei) |
|
nuclear |
|
to remove |
|
removal |
|
shell |
|
outer shell |
|
valence shell |
|
valence electrons |
|
bond |
|
covalent bond |
|
parent atom |
|
neighbouring atom |
|
hole |
|
recombination |
|
constant |
|
