
- •Fundamental Economic Principles and Economic Models. Фундаментальные принципы экономики и экономические модели.
- •Supply and Demand. Спрос и предложение.
- •Consumer and Producer Surplus. Market Reaction to Government Intervention. Излишек потребителя и производителя. Реакция рынка на вмешательство правительства.
- •Elasticity. Эластичность.
- •Theory of Consumer Behavior and Rational Choice. Теория потребительского поведения и рационального выбора.
- •Basic Economic Theory of Risk. Expected Utility Function, Risk Premium and Risk Aversion Measures. Основы экономической теории риска. Функция ожидаемой полезности. Премия риска и избегание риска.
- •Profit Maximization and Theory of Firm and Industry Supply. Максимизация прибыли и теория предложения фирмы и отрасли.
- •Production Costs in Short Run vs. Long Run. Производственные затраты в краткосрочном и долгосрочном периоде.
- •The Model of Perfect Competition. Модель совершенной конкуренции.
- •The Theory of Monopoly. Теория монополии.
- •Oligopoly and Game Theory. Олигополия и теория игр.
- •Monopolistic Competition. Монополистическая конкуренция.
- •The Economic Theory of Taxation. Экономическая теория налогообложения.
- •The Economics of Welfare State. Экономика государства всеобщего благоденствия.
- •Externalities and Transaction Costs. Экстерналии и транзакционные затраты.
- •Public Goods, Common Resources, and Artificially Scarce Goods. Общественные товары, общие ресурсы и искусственно редкие товары.
- •Information Asymmetry. Adverse Selection and Moral Hazard. Информационная асимметрия. Враждебный выбор и моральный ущерб.
- •Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply. Model ad-as. Совокупный спрос и совокупное предложение.
- •Consumption, Savings, and Investments. Income and Expenditure. "Keynesian Cross". Потребление, сбережение. Инвестирование. Доход-затраты. Кейнсианский крест.
- •Long Run Economic Growth. Долгосрочный экономический рост.
- •The Theories of Business Cycles. Теории экономических циклов.
- •Inflation, Disinflation, and Deflation. Инфляция, Дизинфляция и Дефляция.
- •Unemployment and Inflation. Безработица и инфляция.
- •Fiscal Policy. Фискальная политика.
- •Monetary Policy. Монетарная политика.
- •28. The Theories of International Trade. Теории международной торговли.
- •29. Open Economy Macroeconomics. (Balance of Payments, Exchange Rates, ppp). Открытая экономика (платежный баланс, обменные курсы валют, ппс)
- •30. The composition of the global financial market: instruments, participants, sources of information. Состав глобального финансового рынка: инструменты, участники, источники информации.
- •32. Types of banks and their role in the international financial market. Типы банков и их роль на международном финансовом рынке.
- •33. The global equities market: size, indicators, principles of organization. Глобальный рынок капитала: размер, индикаторы, принципы организации.
- •34. The global debt securities market: types, composition, principles of organization. Глобальный долговой рынок ценных бумаг: типы ценных бумаг, состав, принципы организации.
- •36. The government bond markets: size, composition, significance. Рынки правительственных облигаций: размер, состав, значение.
- •37. Rating agencies and their role in the global financial market. Рейтинговые агентства и их роль и значение на глобальном финансовом рынке.
- •38. Types of institutional investors and their role in the global financial markets. Типы институциональных инвесторов и их роль на мировых финансовых рынках.
- •39. The functions of the international financial organizations (imf, World Bank, bis). Функции международных финансовых организаций (мвф, Всемирный банк, Банк международных расчетов.)
- •International trade financing: International banks are the leading source of credit for multinational corporations and many governmental units. They provide both st & lt financing.
- •41. Fighting International Money Laundering and Offshore Banking Markets. Борьба с международным отмыванием денег и оффшорные банковские рынки.
- •42. Mergers and Acquisitions in Financial Services Markets. Слияния поглощения на рынках финансовых услуг.
- •43. International Financial Centers. Международные финансовые центры.
- •46. European Stability Mechanism and Fiscal Compact. Европейский стабилизационный механизм и пакт о финансовой стабильности и росте.
- •47. European Debt Crisis, us Fiscal Cliff, and Federal Budget Sequester. Европейский долговой кризис. Фискальный обрыв и секвестр федерального бюджета сша.
- •48. Wto and the problems of the Russian Federation participation in it. Вто и проблемы участия в ней рф.
- •50. Stabilization Funds. Стабилизационные фонды.
- •51. Necessity and preconditions of Appearance and Applications of Moneys. Evolution of Forms and Types of Moneys.Необходимость и предпосылки появления и применения денег. Эволюция форм и видов денег.
- •52. The Problem of Money Supply Measurements in Modern Economy. The Specifics of Russia.Проблемы измерения денежной массы в современной экономике. Особенности России.
- •53. Monetary Emission and Printing Money.Выпуск денег в хозяйственный оборот и денежная эмиссия.
- •54. Modern Basics of Cash at Bank monetary Circulation: Russian Specifics. Современные основы организации безналичного денежного оборота: особенности России.
- •55. The Development of Forms of Credit and their Role in Modern Economy. Развитие форм кредита и их роль в современной экономике России.
- •56. Economic Foundations of Forming the Level of Loan Interest and its Role in the Market Economy.Экономические основы формирования уровня ссудного процента и его роль в рыночной экономике.
- •57. The Conditions and Specifics of Modern Banking System in Russia. Состояние и особенности развитие современной банковской системы России.
- •58. The Role of Banks and Non-Banking Credit Organization in Modern Market Economy in Russia.Роль банков и небанковских кредитных организаций в современной рыночной экономике России.
- •61. Classified Financial Statements and Ratios. Corporate Financial Statements. Классифицированные финансовые отчеты и показатели. Корпоративная финансовая отчетность.
- •62. Merchandising Operations. Merchandising Income Statement. Inventories. Торговые операции. Отчет о прибыли торговой организации. Товарные запасы.
- •63. Internal Control. Внутренний контроль.
- •64. Cash and Receivables. Денежные средства и дебиторская задолженность.
- •65. Short-Term Investments, Long-Term Investments (Debt, Equity). Краткосрочные инвестиции. Долгосрочные инвестиции (долг, капитал).
- •66. Current Liabilities. Текущие обязательства.
- •67. Long Term Liabilities. Долгосрочные обязательства.
- •68. Long Term Assets. Долгосрочные активы.
- •69. Contributed Capital. Акционерный капитал.
- •Cash Flow Statement. Отчет о движении денежных средств.
- •71. Consolidated Financial Statements. Консолидированная финансовая отчетность.
- •74. Capital Structure Concept. Dividend Policy. Концепция структуры капитала. Дивидендная политика.
- •75. Arbitrage Pricing Theory (apt). Capital Asset Pricing Model (capm). Теория арбитражного ценообразования. Модель оценки капитальных активов.
- •77. Asset Based Valuation Model, Residual Income Valuation Model. Модель оценки на основе активов. Модель оценки на основе остаточного дохода.
- •78. Dividend Discount Model. Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Model. Модель дисконтированных денежных потоков.
- •Risky assets and portfolio optimization problem. Рисковые активы и проблема оптимизации портфеля.
- •Credit Risk Models. Модели кредитного риска.
- •Translation Exposure. Трансляционная экспозиция.
- •Transaction Exposure. Транзакционная экспозиция.
- •Operating Exposure. Операционная экспозиция.
- •Classification and comparative characteristics of derivatives: options, swaps, futures, forwards. Классификация и сравнительные характеристики деривативов: опционы, свопы, фьючерсы, форварды
- •Interest Rate Derivatives: Interest Rate Agreements, Interest Rate Swaps, etc. Деривативы процентных ставок: соглашения по процентным ставкам, свопы процентных ставок, и т.П.
- •Exotic Derivatives.Экзотические деривативы.
- •Advanced Structured Financial Products.Продвинутые структурные финансовые продукты.
- •Financial Risk Forecasting Techniques. Методы прогнозирования финансовых рисков.
Theory of Consumer Behavior and Rational Choice. Теория потребительского поведения и рационального выбора.
T
 he
utility
of a consumer is a measure of the satisfaction the consumer derives
from consumption of goods and services. An individual’s consumption
bundle
is the collection of all the goods and services consumed by that
individual. An individual’s
utility function
gives the total utility generated by his or her consumption bundle.
The unit of utility is a util.
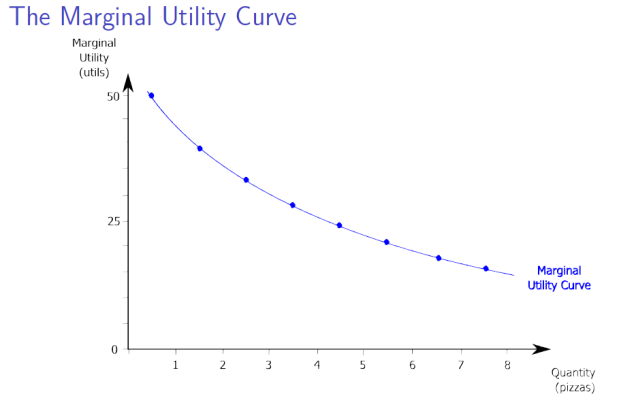
The marginal
utility of
a good or service is the change in total utility generated by
consuming one additional unit of that good or service. The marginal
utility curve shows
how marginal utility depends on the quantity of a good or service
consumed.
The
principle
of diminishing marginal utility says
that each successive unit of a good or service consumed adds less to
total utility than the previous unit. The marginal
utility curve
slopes downward due to diminishing marginal utility.
he
utility
of a consumer is a measure of the satisfaction the consumer derives
from consumption of goods and services. An individual’s consumption
bundle
is the collection of all the goods and services consumed by that
individual. An individual’s
utility function
gives the total utility generated by his or her consumption bundle.
The unit of utility is a util.
The marginal
utility of
a good or service is the change in total utility generated by
consuming one additional unit of that good or service. The marginal
utility curve shows
how marginal utility depends on the quantity of a good or service
consumed.
The
principle
of diminishing marginal utility says
that each successive unit of a good or service consumed adds less to
total utility than the previous unit. The marginal
utility curve
slopes downward due to diminishing marginal utility.
A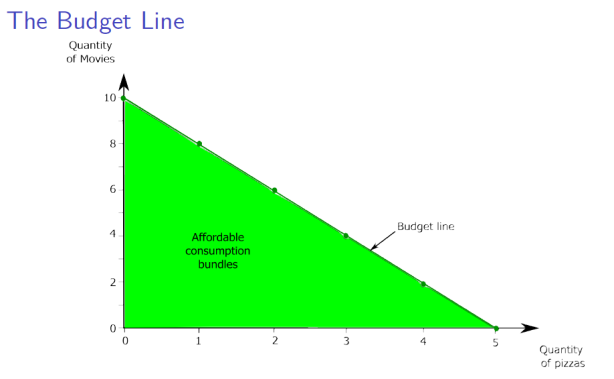 budget
constraint
limits a consumer’s spending to no more than his or her income. It
defines the consumer’s consumption
possibilities,
the set of all affordable consumption bundles. A consumer who spends
all of his or her income will choose a consumption bundle on the
budget
line.
An individual chooses the consumption bundle that maximizes total
utility, the optimal
consumption bundle.
budget
constraint
limits a consumer’s spending to no more than his or her income. It
defines the consumer’s consumption
possibilities,
the set of all affordable consumption bundles. A consumer who spends
all of his or her income will choose a consumption bundle on the
budget
line.
An individual chooses the consumption bundle that maximizes total
utility, the optimal
consumption bundle.
T he
marginal
utility per dollar spent
on a good or service is the additional utility from spending one more
dollar on that good or service. The optimal
consumption rule says
that when a consumer maximizes utility, the marginal utility per
dollar spent must be the same for all goods and services in the
consumption bundle (MU1/P1=MU2/P2).
he
marginal
utility per dollar spent
on a good or service is the additional utility from spending one more
dollar on that good or service. The optimal
consumption rule says
that when a consumer maximizes utility, the marginal utility per
dollar spent must be the same for all goods and services in the
consumption bundle (MU1/P1=MU2/P2).
Changes in the price of a good affect the quantity consumed in two possible ways: the substitution effect and the income effect. For normal goods, the substitution and income effects reinforce each other. For inferior goods, however, they work in opposite directions.
An indifference curve is a contour line that shows all the consumption bundles that yield the same amount of total utility for an individual. The entire utility function of an individual can be represented by an indifference curve map, a collection of indifference curves in which each curve corresponds to a different total utility level. General properties: 1) indifference curves never cross; 2) the farther out an indifference curve is from the origin, the higher the level of total utility it indicates; 3) they are downward sloping; 4) are convex as a result of diminishing marginal utility.
T he
marginal
rate of substitution,
or MRS,
of R in place of M—the rate at which a consumer is willing to
substitute more R for less M—is equal to MUR/MUM and is also equal
to minus the slope of the indifference curve when R is on the
horizontal axis and M is on the vertical axis. Convex indifference
curves get flatter as you move to the right along the horizontal axis
and steeper as you move upward along the vertical axis because of
diminishing
marginal utility:
a
consumer requires more and more units of R to substitute for a
forgone unit of M as the amount of R consumed rises relative to the
amount of M consumed.
he
marginal
rate of substitution,
or MRS,
of R in place of M—the rate at which a consumer is willing to
substitute more R for less M—is equal to MUR/MUM and is also equal
to minus the slope of the indifference curve when R is on the
horizontal axis and M is on the vertical axis. Convex indifference
curves get flatter as you move to the right along the horizontal axis
and steeper as you move upward along the vertical axis because of
diminishing
marginal utility:
a
consumer requires more and more units of R to substitute for a
forgone unit of M as the amount of R consumed rises relative to the
amount of M consumed.
The tangency condition between the indifference curve and the budget line holds when the indifference curve and the budget line just touch. This condition determines the optimal consumption bundle when the indifference curves have the typical convex shape.
The relative price rule says that at the optimal consumption bundle, the marginal rate of substitution between two goods is equal to their relative price. At the optimal consumption bundle:−MUR /MUM = − PR /PM. Optimal consumption rule: MUR / PR= MUM /PM
