
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary Tasks
- •I. Study the following words and phrases. Recall the sentences in which they are used in the text. Use them in sentences of your own.
- •II. Replace the Ukrainian words and phrases by appropriate English equivalents. Translate the sentences.
- •III. Change the noun form into the verb and adjective forms. You may want to use a dictionary.
- •IV. For each word or phrase, write one which means the opposite.
- •V. Match these words as they occur in the text. Translate the phrases.
- •VII. Find words and phrases in the text which mean:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks with prepositions.
- •II. Mark these statements t (true) or f (false) according to the information in the text. Find the part of the text that gives the correct information.
- •I. Write sentences with the following words.
- •II. Write questions to the following answers.
- •Text b. Financial Plan
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and Speaking Tasks
- •I. Make up questions covering the content of the text and le your fellow students answer them.
- •II. Having read the text, what you can now say about:
- •III. Work with a partner who read the text to produce a summary of the text. You need only mention the important points. Lesson 2. Firm's finances Text a: Short-Term and Long-Term Expenditures
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary Tasks
- •I. Study the following words and phrases. Recall the sentences in which they are used in the text. Use them in sentences of your own.
- •II. Replace the Ukrainian words and phrases by appropriate English equivalents. Translate the sentences.
- •III. Change the noun form into the verb and adjective forms. You may want to use a dictionary.
- •IV. For each word or phrase, write one which means the opposite.
- •VII. Find words and phrases in the text which mean:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks with prepositions.
- •II. Mark these statements t (true) or f (false) according to the information in the text. Find the part of the text that gives the correct information.
- •III. Without looking back at the next, exchange its content with someone who read the text too.
- •I. Write sentences with the following words.
- •Part II. Sources of Long-Term Funds
- •Vocabulary
- •Vocabulary Tasks
- •I. Study the following words and phrases. Recall the sentences in which they are used in the text. Use them in sentences of your own.
- •II. Replace the Ukrainian words and phrases by appropriate English equivalents. Translate the sentences.
- •III. Change the noun form into the verb and adjective forms. You may want to use a dictionary.
- •IV. For each word or phrase, write one which means the opposite.
- •VII. Find words and phrases in the text which mean:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks with prepositions.
- •Inventory Loans
- •Reading Tasks
- •I. Answer the questions using the information from the text.
- •II. Mark these statements t (true) or f (false) according to the information in the text. Find the part of the text that gives the correct information.
- •III. Without looking back at the next, exchange its content with someone who read the text too. Writing and Speaking Tasks
- •I. Write sentences with the following words.
- •III. Identify five sources of short-term financing for businesses.
- •Text b: Financial Management for Small Businesses
- •Venture Capital As a Source of Funds
- •Vocabulary
- •Reading and Speaking Tasks
III. Change the noun form into the verb and adjective forms. You may want to use a dictionary.
Example: term (n) - term (v) - terminable (adj)
Force, edge, dissolution, expenditure, receiver, delay, prediction, obligation, adjustment, competitor, finish, shipment, merchandise, cover.
IV. For each word or phrase, write one which means the opposite.
Dissolution, revenues, accounts payable, paid bill, amount undue, permanently, deny credit, considerably, work-in-process inventory, current assets, crucial, unacceptable.
V. Match these words as they occur in the text. Translate the phrases.
1. raw materials 2. long-term (capital) 3. repayment 4. finished 5. accounts 6. dissolution of the 7. unpaid 8. credit 9. incentive 10. amounts 11. grave 12. payment |
a) products b) terms c) buyers d) inventory e) policy f) histories g) receivable h) expenditures i) consequences j)firm k) due 1) bills |
VI. Choose the explanation for each of these words and phrases.
1. short-term (operating) expenditures 2. inventory 3. accounts payable 4. long-term (capital) expenditures 5. raw materials inventory 6. accounts receivable 7. finished-goods inventory 8. work-in-process inventory |
a) unpaid bills to suppliers b) the supplies of farm and natural products purchased by a firm for use in its production process c) expenditures incurred regularly in a firm's everyday business activities d) amounts due from customers who have purchased goods on credit e) expenditures on fixed assets f) materials and goods that are held by a company but will be sold within one year g) the portion of a firm's inventory consisting of goods part-way through the production process h) the portion of a firm's inventory consisting of completed goods ready for sale |
VII. Find words and phrases in the text which mean:
1. to refuse to pay until some point of time
2. a person or firm supplying goods, materials, etc
3. someone who buys and sells a particular product
4. the conditions under which you agree to pay for something
5. a person, team, company etc. that is competing with another
6. the rules governing the extention of credit to customers
7. assets that have long-term use or value, such as land, buildings and equipment
8. use pressure or influence to get or do something
9. very serious and worrying
10. extremely large
11. reduction in the cost of goods or services
12. something that happens as a result of a particular action or set of conditions.
VIII. Fill in the blanks with prepositions.
Why Organizations Need Funds
Organization require funds for dozen .... reasons. Some funds must be held .... the form of cash to meet day-to-day requirements. If the firm permits customers to make credit purchases, funds must be available to prevent cash deficiencies .... the time between the sale and the receipt of payment.
Inventory used in producing goods and services or stocked .... a retail store cost money. This money will not be recovered until the finished output is sold or the raw materials are converted .... finished products and sold. Other funds requirements include making interest payments .... loans; paying dividends to stockholders, and purchasing land, facilities, and equipment. The financial plan identifies the firm's specific cash needs and when they will be needed. Comparing these needs .... expected cash inflows from product sales, payments made by credit purchasers, and other sources will help the financial manager determine precisely what additional funds must be obtained .... any given time. If inflows exceed cash needs, the financial manager will invest the surplus to earn interest. On the other hand, if inflows do not meet cash needs, the financial manager will seek additional sources .... funds. The following chart illustrates this process.
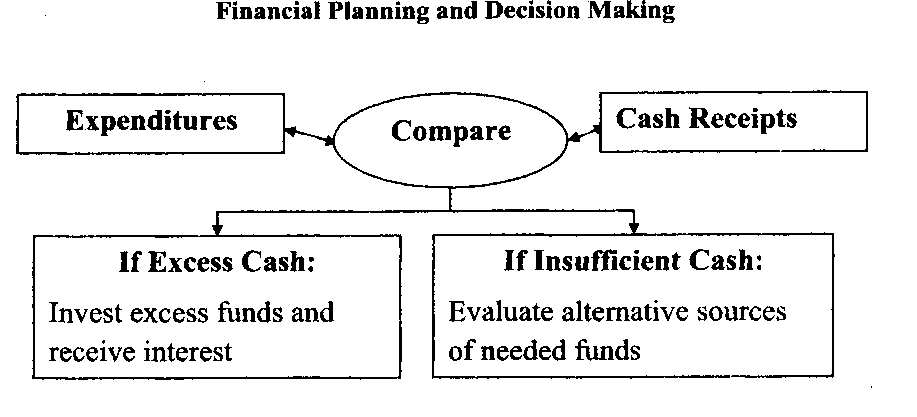
IX. Fill in the blanks with the most appropriate words from the list.
1. efficient 2. bills 3. funds 4. computers 5. finances |
6. interest 7. outstanding 8. cash 9. dividends 10. payments |
Financial Managers try to minimize the amount of .... held in the form of cash since it does not earn interest. However, some funds must be available each day in the firm's checking account to pay .... and to meet the payroll. Periodically, larger amounts of cash must be available to pay taxes, provide stockholders with .... (if the firm is a corporation), or make interest payments due on loans or mortgages. While the typical firm will use an interest-earning checking account for these funds, such accounts typically earn less .... than other investments.
The general principle underlying cash management is to minimize the amount of ... .required for businesses operations so that more can be used in interest-producing investments. In order to minimize the firm's cash needs, the financial manager should pay bills as late as possible and collect money owed to the firm as quickly as possible. These actions lead to .... cash management - as long as they do not damage the firm's credit rating or cost more than they save.
One of the least expensive ways for firms to manage .... themselves is by finding out where and how their cash is working for them. Banks are now selling desktop .... to larger companies, giving financial managers access to balances on bank accounts throughout the world. Excess funds that are not earning interest can be instantly moved elsewhere. Midsize companies use lock-boxes, which are essentially local addresses where customers can make.....Companies that receive large numbers of small checks can bypass banking delays caused by mailing this way. Still another new method of managing cash is the controlled disbursement account, a system that lets a firm know how many checks and in what amounts will clear what banks at what time. Firms can then keep funds invested until the minute .... checks clear.
Reading Tasks
I. Answer the questions using the information from the text.
1. Why does a company need money?
2. What can lead to bankruptcy and dissolution of the firm?
3. What are two different kinds of financial outlays?
4. What are short-term (operating) expenditures?
5. What are accounts payable?
6. Why is it the firm's interest to withhold payment as long as it can?
7. What are accounts receivable?
8. What is a credit policy?
9. In what cases do financial managers deny credit to firms?
10. What do payment terms determine?
11. What is inventory?
12. What is raw materials inventory?
13. What is work-in-process inventory?
14. What is finished-goods inventory?
15. What financial consequences can failure to manage inventory lead to?
16. What are long-term (capital) expenditures?
17. What are fixed assets?
18. Why do long-term expenditures pose special problems for the financial manager?
