
Logic as basis of decision making
Deterministic logic
The deterministic logic clarifies presence at the separate patient set of typical for concrete illness signs. If sign is, it is marked as unit, then it is marked as zero. Then the distribution of zeros and units is compared to the measurement standard for known illnesses. The adequate measurement standard is selected as the more possible diagnosis.
Deterministic logic – the most ancient medical approach to the diagnostics. But it is not most effective. Algorithm of this kind is precise sequence of preset operations and rules. After correct execution of such algorithm the doctor should have ready and unique diagnostic solution, and also the initial scheme of the medical process. In practice the situation looks less optimistically more often: execution of algorithm does not ensure the doctor with ready solutions. It can take place through two groups of reasons:
Errors during execution of algorithm;
Inaccuracy or insufficiency of algorithm.
Such algorithms can not give ideal solution in cases of some diseases combination, in cases of seldom diseases, in cases of genetic syndromes in combination with other diseases and so on.
Correspondingly, the deterministic logic has such disadvantages:
1) High probability of errors in execution of complex algorithms;
2) Impossibility simultaneous spannings of a great many of pathologies.
Attempts of creation of universal algorithms reduce in their qualitative complication to a degree of practical their impracticability on behalf of one doctor.
On the other hand, the deterministic approach has irrefutable advantages:
1) Possibility of emergency diagnostics such as a pathology from bunch of homogeneous illnesses;
2) Possibility of automation of the whole stages of the diagnostic process with release operating time of the doctor.
Logic of phase intervals
The logic of a phase interval is an analysis of parametric coordinates of the patient in multivariate parametric hyperspace of illnesses.
For example, at analysis of patient state a body temperature of the patient forms one-dimensional space of the parameter of a body temperature. We shall assume, that the normal temperature of a human body lays in an interval 36,5-36,7°С (fig. 1):
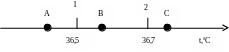
Fig.
1. One-dimensional phase space.
Everything that allocates below a flag 1, is hypothermia, that is a pathology: everything, that is higher than a flag 2, – is a pathological hyperthermia. Only narrow interval between these flags answers norm and is named as zone of health.
B
Fig.
2. A two-dimensional phase space.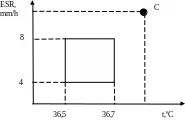 ut
such one-dimensional space in not enough for diagnostic. We must add
other parameters. For example, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
in blood. Normal values of ESR are in limits 4mm/h and 8mm/h. Then
for description of our patient’s state it is necessary to enter one
more coordinate axis ESR (fig. 2).
ut
such one-dimensional space in not enough for diagnostic. We must add
other parameters. For example, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
in blood. Normal values of ESR are in limits 4mm/h and 8mm/h. Then
for description of our patient’s state it is necessary to enter one
more coordinate axis ESR (fig. 2).
Flat square between strait lines limited points 36,5; 36,7 on t axis and 4; 8 on ESR axis on a coordinate plane is a health zone. This figure is planar as the amount of gaugings in this case is equaled to two (n=2) and our space - two-dimensional.
Let's assume, that for the patient C has a hyperthermia and raised ШОЕ (the testimony an inflammation). Diagnostic output now gains more interpreted sort: the inflammatory process which is accompanied by rise of ESR and temperature.
Obviously, as such output very much circumscribed. We shall enter the third metric: eosinophil number in a blood (the testimony allergization of an organism). Space becomes three-dimensional (n=3) (fig. 3).
Health zone gains the form of a volumetric figure – a cube. And if, for example, for the patient С we show rises of eosinophil number (flag С) now the diagnosis is “an inflammation of the allergic nature which is accompanied by a hyperthermia”.
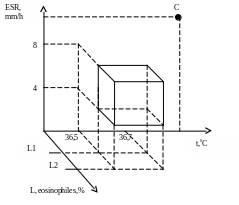
Fig.
3. A three-dimensional phase space
The augmentation of number of researched parameters to three in essence does not raise value of diagnostics. Number of parameters can more exceed three. In that case the space, derived by coordinate axes of parameters (parametric space), is multivariate; it is impossible to map it on a paper. Such space, which dimension exceeds 3, is named as hyperspace. The hyperspace can exist only in the mathematical form, for example, in a computer memory.
Near to healthy zone there is zone of pre-disease, then disease zone circumscribed to the terminator of clinical death (4) outside which zone biological death (5) allocated. Zone biological death– zone with values of parameters not joint with life (for example, a body temperature 100°С).
Different disease zone parts (with various space allocations) correspond to different diseases.
Essence of logic of phase intervals:
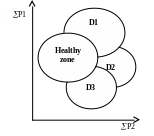
Learning of all possible parameters of a patient organism creates a collection of concrete numbers – current values of these parameters. These numbers are coordinates of a point which answers a current state of an organism and is named as a point of a state in a phase space.
 The
obtained point is compared to a phase space map, in which zones
circumscribed above are posed. On the basis of layout of a point in a
some zone the state of an organism of the patient is unambiguously
determined.
The
obtained point is compared to a phase space map, in which zones
circumscribed above are posed. On the basis of layout of a point in a
some zone the state of an organism of the patient is unambiguously
determined.
L
Fig.4.
A topological map of diagnoses in a phase space (D1, D2, D3 –
zones of three diseases)
1) Simultaneous and interdependent analysis of a great many of parameters;
2) Possibility of automation of great volume of analytical activity in areas, where possibilities of a human brain are limited.
Disadvantages of the approach:
1) Effective system operation of phase diagnostics demands the big empirical experience used as databases and knowledge in the environment of diagnosing programs;
2) Application of logic of phase intervals impossible without computer.
Logic of phase intervals is based on classic formal logic.
