
- •Content
- •Introduction
- •Sillabus
- •1. Data for teachers
- •2. Data on discipline
- •5. Brief description of the discipline
- •6. Content of the discipline 6.1. List of lectures
- •7. Schedule of the tasks and surrender of discipline «Economic theory" for students independent work
- •8. References The laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the Letters (Message) of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Regulations rk
- •Basic literature:
- •Additional literature:
- •9. Course policy
- •10. Information on the assessment of knowledge
- •Scheme of assessment of knowledge on the discipline
- •Tentative map Assessment of the students exam
- •2. Glossary
- •3. A short course of lectures
- •1.1 Economic needs, economic benefits and economic resources.
- •1.2 The subject of economic theory
- •1.3 Methods and functions of economic theory
- •Theme 2. Fundamentals of social production
- •2.1 The bases of social production
- •2.2 Structure of social production
- •2.3 Economic Systems. Types of economic systems
- •1. The traditional economic system
- •2. Command and administration economy system
- •3. Market economic system
- •4. Mixed system
- •3.1 Economic and legal content property
- •The system of property relations
- •Fig. 1. The structure of ownership
- •4.1 The forms of social economy. Commodity economy
- •4.2 The nature and function of the market
- •Invariant category that has general economic features inherent to any commodity production.
- •4.3 Origin, nature and function of money
- •4.4 The essence of entrepreneurship and its feature
- •5.1 Demand. Factors determining the demand. The law of supply
- •5.2 Supply. Factors determining the sentence. The law of Supply
- •5.3 Interaction of supply and demand market equilibrium
- •5.3 Elasticity and its types
- •Elastic demand
- •5.4 The theory of consumer behavior
- •6.1 The essence of competition. The theory of perfect and imperfect competition
- •1. On the market at the same time there are many firms, each of which occupies a small share of the market
- •2. Homogeneity of products
- •3. Freedom of entry and exit from the industry
- •4. There fairness information
- •6.2 Theory of monopoly
- •Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
- •6.3 Antitrust and competition policy
- •7.1 The reproduction process of capital
- •7.2 Basic and working capital
- •Scheme 1. Factors of self-financing
- •Incease in profits
- •7.3 Investment as a source of financing of productive assets
- •Theme 8. Costs and revenues of the enterprise (company)
- •8.1 Nature and types of costs
- •8.2 Revenue and its types
- •8.3 Profit and its role in the development of the company
- •9.1 Peculiarities the demand for resources
- •9.2 Labor market and wage
- •9.3 Capital markets and interest rates
- •Fig. 16. Demand for capital Fig. 17. Supply of capital
- •9.4 The land market. Land rent
- •10.1 The national economy as a system
- •10.2 System of National Accounts
- •10.3 The macroeconomic indicators and methods of calculation
- •Methods of measuring gnp
- •The calculation of gnp expenditure
- •Calculating gnp by revenue
- •The calculation of gnp "value added"
- •Theme 11. Macroeconomic equilibrium
- •11.1 Macroeconomic equilibrium and its characteristics
- •11.2 Model employment resources
- •12.1 Cyclical nature of the market economy
- •12.2 The Economic cycle and its variants
- •12.3 The concept of economic growth the measurement
- •Types and factors of economic growth
- •Theme 13. Unemployment and inflation are both manifestations of economic instability
- •13.1 Essence and basic forms of unemployment
- •13.2 The effect of unemployment rate on the value of gnp. Okun's Law
- •13.3 Inflation and its causes
- •14.1 Concept and types of monetary systems
- •14.2 The demand for money and money supply
- •14.3 The structure of the financial system
- •14.4 State budget and public debt
- •14.5 Principles and forms of taxation
- •14.6 International relations: the nature, form
- •4. Assignments for practical classes and self-study Theme 1. Subject and method of economics (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 2. Fundamentals of social production (1 hour)
- •1. As played wealth?
- •2. The goods are different from the natural product?
- •3. Economic Geography
- •4. Find the right answer
- •5. Graphic problem.
- •6. The concept of "services" and "intangible benefits"
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 3. Property relations and their role in the economy (1 hour)
- •1. Questions about the nature of the property
- •7. What is true and false?
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 4. Foundations of a market economy and business activities (1 hour)
- •1. Gogol about the farm landowners Plyushkin
- •6. Adventures scientist w. Cameron
- •7. Find the right answer
- •8. Function of money
- •9. The design task
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 5. Fundamentals of the theory of supply and demand (2 hours)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 6. Competition and Monopoly (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 7. Circuit and the circulation of capital (funds) of enterprise (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 8. Expenses and income of the company (the company) (1 hour)
- •8. All the profit goes to a businessman?
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 9. Factor markets and formation of factor income (1 hour)
- •Theme 10. The national economy as a system (1 hour)
- •2. The table presents the nominal and real gdp over the period 1999 to 2003
- •3. By the terms of the left hand column find the definition in the right column.
- •4. True-false:
- •5. Does Kazakhstan's gdp this article? If not, why not? If so, then the calculation of expenditure and revenue and in what specific section?
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 11. Macroeconomic equilibrium (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •1. Right - wrong:
- •2. Activation of the human factor
- •4. Types of intensification of production.
- •Theme 13. Unemployment and inflation as a manifestation of economic instability (1 hour)
- •2. Economic challenge.
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 14. The main directions of economic policy (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •5. Questions for the interim control for the subject "Economic Theory"
- •5. 1 Questions for the 1-st interim control
- •5.2 Questions for the 2nd interim control
- •6. Tests to consolidate students' knowledge
- •References
14.1 Concept and types of monetary systems
Monetary system - is an organized form of currency in the country, that is, the movement of money in the domestic turnover of cash and non-cash, serving the sale of goods, the movement of loan capital and fictitious. It includes: currency, the scale of prices, types of money emission system - legally established currency issue, the state apparatus, which regulates the circulation of money.
Money is one of the commodities that are specific property which is the ability to exchange for another commodity. In the economic literature, this property is called liquidity. She's the greatest of money compared to other products that give them the character of a universal equivalent.
In any economic system is currently the main types of money are:
- Notes, i.e. paper money:
- Small change ("change").
This central money, which is responsible for issuing state.
As part of the goods sold is always in debt, under the bill, that any credit money issued by issued by issuing bank.
Banknotes - bank notes issued by issuing banks.
Promissory notes - debt (1 - 3 months), which gives the holder the right to demand payment of this amount by the deadline.
Cheque deposits, checks - a means of transferring ownership of the deposits in banks or other financial institutions. Money is not the write checks, and any demand deposits (deposits) in the bank.
In developed market economies deposits are more important than the paper money - up to 90% of trading is payable by check or by credit card. The use of credit cards ("e-money") requires a high level of computerization of banks, trade and service.
14.2 The demand for money and money supply
Based on the nature of money - their ability to communicate to all other commodities, they are formed by supply and demand.
Demand for money (total) consists of two components:
A) The demand for money for transactions;
B) The demand for money by assets
А . The demand for money for transactions is proportional to nominal GDP.
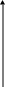
 %
%
Dtr

10 20 30 M
Fig. 22. The demand for money
for transactions
Households need a certain amount of money for the purchase of essential goods, and businesses - to pay wages and electricity costs, materials, etc.
B. The demand for money from the assets - a consequence of the functionality of the savings. The level of demand depends on the price (interest rate level) in cash assets.

Dа


M
Fig. 23. The demand for money from the assets.
Companies and individuals can keep their assets in various forms - stocks, bonds, money. Each of them has its pros and cons.
Money - the liquid, but do not give a percentage of income. Shares carry a dividend, but not have the ability to access funds.
The answer to the question: how many financial assets to keep the money, and how much in bonds? - Is the value of the interest rate (the relationship is inverse).
The total demand for money is: Dо = Dtr + Dа

% D2 D0 D1
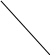
10

М
Fig. 24. The total demand for money
If growing GNP, all other things being equal, demand schedule for money (D1) will move to the right, if GNP will decline, the D2 moves to the left.
What determines the supply of money?
The main sources are:
1. Central (national) bank directly controls a large part of the money supply. Because of certain political decisions, he controls the issuance of money.
2. Commercial banks. Providing loans to businesses and households for purchases, accelerating the movement of commodities, money, which, in turn, re-fit on the new bank account? Addition of money commercial banks provides the ability to issue more loans.
3. National Bank may affect the money supply through the purchase - sale of securities.
4. Currency movement abroad and because of her. The higher the interest rate in the country compared to the surrounding countries, the greater the flow of money from abroad. Likewise, the low interest rate leads to a reduction in leakage rates and the money supply.
Of what elements is the proposal?
Are the following:
M1 - cash
M1 - cash in circulation plus deposits of funds to non-urgent.
Urgent checking accounts can be transferred to the investor call non-urgent and used as non-cash.
Most appropriate at the present time is "near money" - M2:
M2 = M1
+ demon
checking
savings
accounts + small (no more than 100 thousands U.S.) term
deposits.
М3
= М2
+ крупные ср. вклады
The third official definition M3 assumes the company owned by large (up to 100 thousands U.S or more) in the form of bank deposits of certificates that can easily apply to the checking deposits.
M3
=
M2
+
large
time
deposits
In the presence of demand and supply forms the money market.
Money market - a market where the quality of the product are the money as cash and non-cash.
Consider the money market and to determine the equilibrium interest rate - (%).
excess
Е
%
4
3
2
Dм
Sm1
Sm
Sm2








deficit
10
15 20
М
Fig. 26. Restoring the balance in the money market
Price is the equilibrium interest rate (%) at E.
Sm - the money supply as the total amount of M1.
1) Assume that the amount of money supply decreased from 15 to 10 billion dollars more than the number required by the proposed $ 5 billion under the previous% = 3.
To adapt to the lack of money, people will sell part of the financial assets at a higher price (example - 4%), which will lead to the equality of supply and demand.
Conclusion: The decrease in the price of the bond will increase the interest rate.
2) Assume the market increases the money supply from 15 to 20 billion dollars in the same% = 3.
People are encouraged to get rid of money, buying bonds, increasing the demand for them, thus increasing and price.
Conclusion: The increase in bond prices will lower the interest rate.
So, considering the money market, we see that the demand and supply of money are in constant motion, the balancing is provided only to a certain structure of the financial system.
