
- •Content
- •Introduction
- •Sillabus
- •1. Data for teachers
- •2. Data on discipline
- •5. Brief description of the discipline
- •6. Content of the discipline 6.1. List of lectures
- •7. Schedule of the tasks and surrender of discipline «Economic theory" for students independent work
- •8. References The laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the Letters (Message) of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Regulations rk
- •Basic literature:
- •Additional literature:
- •9. Course policy
- •10. Information on the assessment of knowledge
- •Scheme of assessment of knowledge on the discipline
- •Tentative map Assessment of the students exam
- •2. Glossary
- •3. A short course of lectures
- •1.1 Economic needs, economic benefits and economic resources.
- •1.2 The subject of economic theory
- •1.3 Methods and functions of economic theory
- •Theme 2. Fundamentals of social production
- •2.1 The bases of social production
- •2.2 Structure of social production
- •2.3 Economic Systems. Types of economic systems
- •1. The traditional economic system
- •2. Command and administration economy system
- •3. Market economic system
- •4. Mixed system
- •3.1 Economic and legal content property
- •The system of property relations
- •Fig. 1. The structure of ownership
- •4.1 The forms of social economy. Commodity economy
- •4.2 The nature and function of the market
- •Invariant category that has general economic features inherent to any commodity production.
- •4.3 Origin, nature and function of money
- •4.4 The essence of entrepreneurship and its feature
- •5.1 Demand. Factors determining the demand. The law of supply
- •5.2 Supply. Factors determining the sentence. The law of Supply
- •5.3 Interaction of supply and demand market equilibrium
- •5.3 Elasticity and its types
- •Elastic demand
- •5.4 The theory of consumer behavior
- •6.1 The essence of competition. The theory of perfect and imperfect competition
- •1. On the market at the same time there are many firms, each of which occupies a small share of the market
- •2. Homogeneity of products
- •3. Freedom of entry and exit from the industry
- •4. There fairness information
- •6.2 Theory of monopoly
- •Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
- •6.3 Antitrust and competition policy
- •7.1 The reproduction process of capital
- •7.2 Basic and working capital
- •Scheme 1. Factors of self-financing
- •Incease in profits
- •7.3 Investment as a source of financing of productive assets
- •Theme 8. Costs and revenues of the enterprise (company)
- •8.1 Nature and types of costs
- •8.2 Revenue and its types
- •8.3 Profit and its role in the development of the company
- •9.1 Peculiarities the demand for resources
- •9.2 Labor market and wage
- •9.3 Capital markets and interest rates
- •Fig. 16. Demand for capital Fig. 17. Supply of capital
- •9.4 The land market. Land rent
- •10.1 The national economy as a system
- •10.2 System of National Accounts
- •10.3 The macroeconomic indicators and methods of calculation
- •Methods of measuring gnp
- •The calculation of gnp expenditure
- •Calculating gnp by revenue
- •The calculation of gnp "value added"
- •Theme 11. Macroeconomic equilibrium
- •11.1 Macroeconomic equilibrium and its characteristics
- •11.2 Model employment resources
- •12.1 Cyclical nature of the market economy
- •12.2 The Economic cycle and its variants
- •12.3 The concept of economic growth the measurement
- •Types and factors of economic growth
- •Theme 13. Unemployment and inflation are both manifestations of economic instability
- •13.1 Essence and basic forms of unemployment
- •13.2 The effect of unemployment rate on the value of gnp. Okun's Law
- •13.3 Inflation and its causes
- •14.1 Concept and types of monetary systems
- •14.2 The demand for money and money supply
- •14.3 The structure of the financial system
- •14.4 State budget and public debt
- •14.5 Principles and forms of taxation
- •14.6 International relations: the nature, form
- •4. Assignments for practical classes and self-study Theme 1. Subject and method of economics (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 2. Fundamentals of social production (1 hour)
- •1. As played wealth?
- •2. The goods are different from the natural product?
- •3. Economic Geography
- •4. Find the right answer
- •5. Graphic problem.
- •6. The concept of "services" and "intangible benefits"
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 3. Property relations and their role in the economy (1 hour)
- •1. Questions about the nature of the property
- •7. What is true and false?
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 4. Foundations of a market economy and business activities (1 hour)
- •1. Gogol about the farm landowners Plyushkin
- •6. Adventures scientist w. Cameron
- •7. Find the right answer
- •8. Function of money
- •9. The design task
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 5. Fundamentals of the theory of supply and demand (2 hours)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 6. Competition and Monopoly (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 7. Circuit and the circulation of capital (funds) of enterprise (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 8. Expenses and income of the company (the company) (1 hour)
- •8. All the profit goes to a businessman?
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 9. Factor markets and formation of factor income (1 hour)
- •Theme 10. The national economy as a system (1 hour)
- •2. The table presents the nominal and real gdp over the period 1999 to 2003
- •3. By the terms of the left hand column find the definition in the right column.
- •4. True-false:
- •5. Does Kazakhstan's gdp this article? If not, why not? If so, then the calculation of expenditure and revenue and in what specific section?
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 11. Macroeconomic equilibrium (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •1. Right - wrong:
- •2. Activation of the human factor
- •4. Types of intensification of production.
- •Theme 13. Unemployment and inflation as a manifestation of economic instability (1 hour)
- •2. Economic challenge.
- •Independent work of the student
- •Theme 14. The main directions of economic policy (1 hour)
- •Independent work of the student
- •5. Questions for the interim control for the subject "Economic Theory"
- •5. 1 Questions for the 1-st interim control
- •5.2 Questions for the 2nd interim control
- •6. Tests to consolidate students' knowledge
- •References
Theme 8. Costs and revenues of the enterprise (company)
8.1 Nature and types of costs
Costs of production of the company (cost) - all of the cost of the company for the production and sale of products. This includes the cost of materials and supplies, depreciation, wages and other types of costs.
Modern economic theory for a different approach to the treatment costs. It comes from the limitations of resources and their possible alternative uses. Limited resources mean that it is always necessary to choose, and the choice means giving up one in favor of another.
Production costs can be divided into external (explicit) and internal (implicit).
External (explicit) or accounting related to the fact that the firm pays employees, fuel, spare parts, ie all that it does not produce itself to create the product. Depending on the specialization of the value of external costs for the production of the same product range. Thus, the assembly plant the proportion of external costs more.
Internal costs (implicit) - owner of your own company or store does not pay himself salary, does not receive the rent for the building, which houses the shop. If he puts money in the trade, you will not get those interest that he had put them in the bank. Explicit costs are sometimes called accounting costs, and the amount of implicit and explicit call economic costs.
Costs are divided into independent of size and depending on the volume of products produced by the company, called the fixed and variable costs of production.
Fixed costs of production FC firm is independent of the volume of production. It is the costs of the Company, payment of interest on loans, taxes, depreciation and payroll costs management personnel. They will not change their output.
VC variable costs change with production volume. They represent the firm's costs for raw materials, wages, energy and transport. Division of costs into fixed and variable is applied to the short-term period of operation of the firm. In the short run, fixed costs remain the same, and the firm can change the amount of products just by changing the value of variable costs. In the long run all costs become variable, ie it is quite a long time interval for firm could change its production capacity.
Total cost TC is the sum of fixed and variable costs. Their size varies as a rule, with changes in the variable costs of production. Total costs are different from the variables only fixed costs.
C

 TC
C
MC AC
TC
C
MC AC

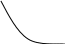 AVC
AVC
VC
FC
AFC

Q Q
Figure 10. Fixed, variable and Fig.11. Average and marginal
total costs of the company costs of firm
Us to know the value of costs per unit of output. Therefore, average the cost of production. Distinguish three types of average costs (Figure 11):
1) The average fixed cost AFC. They are fixed costs, divided by the volume of production. Since fixed costs do not change, then the AFC decreases as the volume of production:
AFC = FC
Q
2) The average variable cost AVC. They are variable costs divided by the volume of production:
AVC = VC
Q
3) The average total cost ATC. They represent the total cost divided by the volume of production ATS has costs per unit of output:
АТС =ТС
Q
They represent a link between the cost of production and its price. Comparing them with the price of the item, you can determine profitability or excessive production.
The company always strives to obtain maximum profit. To do this, it increases the volume of production, there is the additional cost of production. As far as they are effective, to judge the category of marginal costs of production.
The marginal cost МС (sometimes called incremental, marginal) costs are gains from the production of one additional unit of output:
М С=
ТС
С=
ТС
Q
Marginal costs are determined by the growth of only the variable costs of production as a result of an additional unit of output. They show. How much will my company increase its total output by one unit.
Opportunity cost (or opportunity costs) - costs of which the company refuses, when it uses its resources and is not lost due to the use of these resources in the best way. These costs represent the best use of resources of the firm. These costs are called opportunity costs.
The company is the so-called transaction costs. They are related to the fact that the company constantly makes contracts, carries out transactions with partners. So it is constantly necessary to negotiate, establish connections, negotiating conditions, gather the information you need to notify their future partners, i.e. exercise of market transactions. All this requires costs or transaction costs.
