
- •Qfr £t¶qpht0i 3hpqiptii'ip£khj
- •9Fipbpaoh dH '9b6ndm79f6q ’ ’q :I›‹asxonaj
- •0 Point seven
- •It}]obo1)hhx h85h8'4ohHt
- •If a resistor has a resistance of only 2 ohms but its current-carrying
- •I . A resistor is used a) to measure the resistance.
- •Voltage source is applied b) to the insulator.
- •Current passes through conductor a) easily.
- •Trensformem
- •In a circuit.
- •Incandescence ljnken'desnsl «a×m, «×mוa«×«
- •Incandescent lamp [,inken'desnt lamp] nauna iiaxaniiaaiiii×
- •Translate into Russtsn:
- •Components of Electric Circuits
- •In case the motor, when starte d • ºR³
- •In case the curvature winding is overheated.
- •In case of abnormal motor speed.-
- •In case rotor brushes against Stator.-
- •Protection Against Environmental Pollution
- •2. Grammar Revision
- •20 Twcaty ['twenti]
- •7HB Uarb
- •It was b. Pascal that invented the mechanical computer.
- •Punniuatinn iTlarha
- •3. Materials for Reading and Discussing MaTepnansi gnR vt Hne n o6cyx‹qéHnr LlJorh uiith a Oictionarg
- •3Eyxu azrenudcxoco saszxc
- •2. Civc the title to the text.
- •Voltage Velues
- •Reed tbe text and find in it tbe answers to the questions tbat fotlow iL
- •WJtat is the above article about?
- •Read the text and find in it the answcm to the questions that follow iL
- •Generators and underground transmission lincs can be supcrcoolcd.
- •W’hat ¶as is the space filled with?
- •W’hy should the system be protected?
- •4. What arc the advantages of the device?
- •Contectom Type 370
- •2. W'hIch arc the functions of cach of these parts?
- •2. What did the emission result in?
- •Raaignmenta in lLlriting
- •I) Titles.- Two-phase System; Single-phase System, Three-phase Sys-
- •1. An a.C. Distributing system employing a single
- •2. The transmission of heat from places of higher
- •Direction.
- •4. A device for producing an elecnomotive force
- •Irregular Uarba
- •Ahf'jihhckhii r3hIk
- •Y•ie6niiicii II y•ie6HhIe noco6iiR
- •JlyroBaii a.Ji. AhFaiiiiciciiii r3hIk j(jir ct(tDhTéJIhHhIx cIféttHtt-
- •JlyroBau a.Ji. Coapexieuilhlé c(téJ(ctBlt cBiiiH. Vuc6iioe noco-
In a circuit.
Electric power is trans- a) due to resistors. ferred at a high voltage b) due to capacitors. and reduced to any value c) due to transformers.
A transformer consists of a) coms only.
the primary and the secondary windings.
c) a core and the primary and the secon- dary windings.
The function of the pri- a) to prevent the change of voltage. mary is b) to supply energy.
c) to receive energy.
The function of the sec- a) to receive energy.
ondary is b) to supply energy.
to transfer energy.
to decrease the value of charge.
6. A step-up transformer is a) to step down or decrease the secondary
used voltage.
b) to step up or increase the primary volt-
![]()
7. A step-down transformer a) to step down the secondary voltage. is used b) to step down the primary voltage.
8. A transformer with an a) is used for high-frequency currents. iron core b) is used for low-frequency currents.
A transformer with an air a) for high-frequency currents and for low- core is used frequency currents.
b) for high-bcquency currents only.
In a step-up transformer a) the number of tums of the secondary
winding is greater than the number of tums of the primary.
b) the number of tums of the primary winding is greater than the number of tums of the secondary.
11. A transformer should be a) in casu it has an open in the winding.
substituted b) in case it has a short between the pri- mary and the secondary.
c) in case it has a short between turns.
Complete these sentences using whtle. Follow the model on page 13.
The secondary winding of a nansformer is connected to the load rc-
The primary winding receives energy ..
A step-down transformer decreases the primary voltage ..
An air core transformer is used for high-frequency currents ..
In a step-up transformer the number of turns of the secondary winding
is greater than the number of turns of the primary winding ..
Pair work Put these questions to your groupmate and ask hislher to answer them.
l. What is a tmnsformer used for?
What does a transformer consist of?
What is the function of the primary winding?
What is the function of the secondary winding?
What type of transformer is called a step-up transformer?
What type of transformer is used for high-frequency currents?
What type of transformer is called a step-down transformer?
What type of transformer is used for low-frequency currents?
What is the relation between the number of turns in the windings and the value of current?
What are common troubles in a tmnsformer?
What should be done in case a transformer has a trouble?
![]()
Current Transformers
Current transformers are used for operating ammetcrs, wattmeters, and other measuring devices. They produce in the rectum a current lower than the measured current but proportional to it.
Current transformers also insulate the instrument from the circuit which is being measured. This is necessary for high voltage circuits.
![]()
![]()
a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back Into English.
 alternating l,aJta'neiti9]
alternating l,aJta'neiti9]
di'rect
di'rection
 flow [llou]
flow [llou]
![]()
![]()
![]()
Read the words and write down their Russian equivalents:
['saiklJ cycle Spa 'sekand] per second ltaip] type
Put down the Russian for:
one time five times sixty times
direct voltage source alternating voltage source direction of flow
Types of Current
Current is a flow of electricity through a circuit. Let us consider two main types of current: direct and alternating. A direct current (d.c.) flows through a conducting circuit in one direction only. It flows pro- vided a direct voltage source is applied to the circuit.
An alternating current (a.c.) is a current that changes its direction of flow through a circuit. It flows provided an alternating voltage source is applied to the circuit. Alternating current flows in cycles. The number of cycles per second is called the frequency of the current. In a 60-cycle alternating current circuit the current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
It is easy to transform a.c. power from one voltage to another by a transformer. Transformers are also used to step down the voltage at the receiving point of the line to the low values that are necessary for use.
When necessary a.c. can be changed into d.c. but this is seldom nec-
essary.
![]()
. D.c. is a current that a) changes its direction of flow.
b) flows in one direction.
2. A.c. flows provided a) a direct voltage source is applied.
b) an alternating voltage source is applied.
3. In an alternating cur- a) current flows in one direction 60 times per rent circuit second.
b) current flows in one direction 60 times and in the other direction 60 times per second.
4. A.c.
can be changed into d.c.
cannot be changed into d.c.
Complete tbcsc sentences using x›hffc. Follow the model on psgc 13.
An alternating current changes its direction of flow ..
A direct current flows provided a direct voltage source is applied .
Answer the following questions:
What types of current do you know?
When does a direct current flow?
What type of current is called an alternating current?
What type of current is called a direct current?
What is called the frequency of current?
What device is used to transform cc. power kom one voltage to another?
Is it men necessary to change a.c. into d.c.?
7. Read about frequency, snswcr the question that follows.
Frequency
The number of cycles per second is the frequency of an alternating cur- rent. There are two frequencies: the standard for Europe is 50 cycles per second while the standard for the USA is 60 cycles per sucond. A standard frequency has a great advantage since different systems can be intercon- nected.
What is tbc advantage of a standard frcqucacy7
 a)
Cover
the
rlght
column
and
read
the
English
words.
Translate
a)
Cover
the
rlght
column
and
read
the
English
words.
Translate
them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
 in'ductancu
in'ductancu ![]()

![]()
![]()
to provide [pra'vaid]
to touch ltatJl
to bring
that is
definite ['definitJ
![]()
x8c8zscs
npxxocirrs, no/tnocn s
3o ecu»
onpe/tenenusiR
Translate into Russian and put down the Russian equivalents. Then
translate them beck into English (orelly).
definite value primary coil wire coil
mutual inductance
varying current one ampere per second
I . Coils of wire are called inductor.
Two coils are brought close together.
A source of current is applied to one of the coils.
Mutual inductance is measured in henries.
![]()
resistor, resist, resistance; induce, induction, inductor, inductance;
conductor, conduct, conductance ; compute, computer
Inductance and Mutual Inductance
Any conductor has some definite value of inductance. The induc- tance of a conductor shows how well it can provide induced voltage.
Elements of a circuit with a definite value of inductance are coils of
wire called inductors. The inductance of a coil depends upon its size and material. The greater the number of turns of a coil, the higher is its inductance. An iron core also increases the value of inductance. Coils of this type are used for low-frequency currents while coils with an air core are used for high-frequency currents.
Two coils A and B are brought close together and a source of vary- ing current is applied to coil A. If a measuring device is connected
across the terminals of coil B it will be found that a voltage is induced in this coil though the two coils do not touch. The secondary voltage, that is the voltage in coil B, is called induced voltage and energy from one coil to the other transfers by induction. The coil across which the

![]()
Thus, when a ante of change of one ampere per second in the primary
coil
will
produce
one
volt
in
the
sec-
![]() ondary
coil,
the
two
coils
have
one
ondary
coil,
the
two
coils
have
one
henry of mutual inductance.
It should be taken into consideration that induction by a varying cur-
 rent
results
from
the
change
in
current
not
rent
results
from
the
change
in
current
not
faster the current changes, the higher the induced voltage.
velue. The
![]()
1. Any conductor has a) sonic definite value of resistance.
b) some definite value of inductance.
![]() Any
conductor
can
provide a)
electric
power.
Any
conductor
can
provide a)
electric
power.
induced voltage.
3. Elements with a definite value a) are called inductors.
of inductance b) are called coils.
am called sources.
4. The inductance of a coil de- a) its size.
pends upon b) its core.
its material.
its number of tums.
![]() An iron
core
An iron
core
increases the value of inductance.
decreases the value of inductance.
6. The value of mutual induc- a) in watts. tance is measured b) in henries.
7. Induction by a varying current a) results from the change in currant.
b) results from the change in the cur-
rent value.
![]() The
faster
the
current
changes, a)
the
lower
is
the
induced
voltage.
The
faster
the
current
changes, a)
the
lower
is
the
induced
voltage.
b) the higher is the induced voltage.
Complete these sentences using w8ffe. Follow the model on pgg j3.
I . An alr core decreases the value of inductance ..
An iron core is used for low-frequency currents
The coil in which voltage is induced is called the secondary ..
![]()
What value of inductance do conductors have?
What is the function of inductors?
What are elements with a definite value of inductance called?
What does the inductance of a coil depend upon?
How does the indUGtance of a coil depend upon the material of its
core?
![]()
What is the relation between the current changes and the value of in- duced voltage?
What is the unit of resistance?
What is the unit of potential difference?
For what type of current is an air core used?
12.
What is the relation between the number of tums of a coil and its in-
ductance value?
7. Psir work T’cll your groupmatc about mutual inductsncw £.et him/bcr
put the questions of Exercise 6 to you and answer them.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
device field loose tight
 self-inductance
self-inductance
[di'vais] ![]()
 [Ii:Id]
[Ii:Id]
Jlusl [tait]
to couple l'kxpl]
![]()

![]()
therefore l'0caJo:I
![]() Put
down
the
words
with
the
opposite
referring
end
translate
them
into
Russian.
Put
down
the
words
with
the
opposite
referring
end
translate
them
into
Russian.
![]()
 incompetent
—
incorrect
—
indirect
—
indefinite
-
incompetent
—
incorrect
—
indirect
—
indefinite
-
![]() Put
down
Russian
equivalents
of
these
word
coaibinetions.
Then
Put
down
Russian
equivalents
of
these
word
coaibinetions.
Then
trensletc them beck into English.
loose coupling — tight coupling - transformer coupling - elecDomagnetic fields -
When circuits are indirect-inductively coupled energy is transferred from one circuit to another using electromagnetic field of the induc- tance through which a varying current is flowing. The coupling device is a transformer. It is not in series with the elements of the circuit, therefore the coupling is indirect. The transformer consists of two windings: the primary and the secondary. The primary circuit is con- nected to the voltage source, the secondary — to the load circuit.
The coupling may be tight and loose. In case the coils of the coup- ling element are close together, the coupling is tight. In case the coils are repainted the coupling is loose. In the loose coupling the mutual in- ductance is small compared with the self-inductance.
![]()
The circuit connected to the a) the secondary circuit. voltage source is called 6) the primary circuit.
The circuit receiving its en- a) the primary circuit. crgy through a coupling is 6) the secondary circuit.
The function of a coupling a) to sepamte the circuits. element is b) to transfer energy.
c) to prevent a short between the circuits.
When the coupling is tight a) the coils are separated.
b) the coils are close together.
Whefl the coils fifé close to- 0) the coupling is loose. gether b) the coupling is tight.
The circuits are indirectly a) the coupling element is common to
Coupled when both circuits and is in series with their other elements.
the coupling element is not common to the circuits and is not in series with their other elements.
Complete these sentences using in/Ie. Follow the model on page 13.
The circuit receiving energy is the secondary circuit
The coupling is loose when the coils are separated
When the coupling element is not common to the circuits and not in se- ries with their elements, the circuits arc indirectly coupled .
Answer the following questions:
l. What type of circuit is called the primary?
What type of circuit is called the secondary?
What is the function of a coupling element?
What type of coupling is called loose?
What type of coupling is called tight?
In what case are the circuits directly coupled?
In what case are the circuits indirectly coupled?
What is the difference between a tight and loose coupling?
In what case should a coupling element be substituted?
7. Pair work Drew s scbcmc of 1) a loose coupling, 2) a tigbt coupling.
Describe the schemes to your groupmate.
![]()
1. a) Cover the right column end reed the English words. Translate them into Russian end check your trensletion.

![]()
Ftltcr bypass ckokc
[’fitta] [baipos] [t{ouk]
high-pass ['haipo»l
low-pass [louposJ
to oppose [a'pouzJ
on the other hand choke coil
bypass coil bypass condenser high-pass filter
low-pass filter opposing coils opposed current

 ££JtbT(3
BC]9XHBX
98C7DT
££JtbT(3
BC]9XHBX
98C7DT
Filters
 This
filter
is
used
to
separate
direct
cur-
rent
from
alternating
current.
It
consists
of
a
capacitor
and
a
choke
coil.
Direct
current
cannot
flow
through
the
capacitor
since
its
This
filter
is
used
to
separate
direct
cur-
rent
from
alternating
current.
It
consists
of
a
capacitor
and
a
choke
coil.
Direct
current
cannot
flow
through
the
capacitor
since
its
p, p¿ insulator oppose the flow of direct cur-
rent. Therefore, it flows through the choke coil. Its windings easily pass direct current
Fig. J3
through them. Alternating current, on the
other hand, passes through the capacitor,
since it cannot easily pass through the choke coil. In this way the direct
and the alternating currents are separated.
A high-pass filter is used to pass high frequencies and to prevent the flow of low frequencies. It consists of a condenser and an inductance coil. The condenser passes currents of high frequencies and opposes the flow of low frequency currents. Low frequencies must be returned to the soume and the inductance coil is used for a bypass.
A low-pass filter is used to pass low frequencies and to prevent the flow of high frequencies. It consists of an inductance coil and a con- denser. The inductance coil passes low frequencies and opposes the flow of high frequencies. To return the high frequencies back to the source, a condenser is used for a bypass. Its capacity opposes the flow of low fre- quencies through it.
Complete the sentences using the correct variant
A filter is used in order a) to sepamte d.c. from a.c.
6) to transfer energy from the primary to
2. A fiher consists of
Direct current easily passes
Alternating current easily
passes
5. A low-pass filter is used
![]()
7. In a high-pass filter
to separate low frequencies from high frequencies.
a) a resistor and a transformer.
6) B Choke Gmt and 8 capacitor.
c) an inductance coil and a capacitor.
a) through a choke coil.
through a capacitor.
through a capacitor.
through a choke coil.
to pass high frequencies and to prevent
the flow of low bcquencies.
to pass low frequencies and to prevent the flow of high frequencies.
a capacitor is used as a bypass.
an inductance coil is used as a bypass.
an inductance coil is used as a bypass.
a capacitor is used as a bypass.
![]()
Model.- Direct current passes through the choke coil of a filter; alternating current, on i6e other hand, passes through the capacitor.
A low-pass filter is used to pass low frequencies ..
2. In a hlgh-pass filter an Inductance coil is used as a bypass ..
A htgh-pass filter is used to prevent the flow of low frequencies ..
Alternating current passes through a cepecltor ..
![]()
What is a filter used for?
What does a filter consist of7
What is the function of a low-pass filter?
What is the function of a high-pass filter?
What is the difference between a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter?
What elements are used as a bypass?
What is the function of a choke coil?
What is the function of an inductance coil?
![]()
scribe the schemes end the function of the filtcm.
6. Read the text and answer tbe question tbst follows it.
Choke Input Filter end Cepecity Input L•ilter
recti ['rektifai] sbinpsuurs eliminate [I1imineit] ycrpaxxrb
A choke input filter and a capacity input filter are used in mctifiers. Filters of this kind are connected to mctifiers in order to eliminate pulsa- tions produced in rectified current.
l) Choke input filter is a low-pass filter. A choke coil is in series with the rectifier output.
2) Capacity input filter is a high-pass filter. A capacitor is connected
directly across or in pamllel with the rectifier output.
Whet is the diNcrence between e choke input filter end e capacity in-
put filter?
1. e) Cover the right column end reed the English words. Tmnslete
them into Russian end check your trnnsletion.
Cover the left column end trensletc the Russian words beck Into
English.

![]()
![]()
to contain lkan'teinl
to
collect [kalekt] ![]()
to
emit li'mit] ![]()
 to
suppress [sa'pres]
to
suppress [sa'pres]
connol circuit comet grid screw grid
![]()
![]() suppressor
grid
suppressor
grid
 counter
flow
counter
flow
oscillatory circuit
![]()
Model.’ to heat — heattr

![]()
![]()
![]() Distribute
the
words
below
into
the
three
columns.
Distribute
the
words
below
into
the
three
columns.
-
Model.- ection
process
door
emit
emission
emitter
collector, heat, collection, suppress, collect, suppressor, suppression, con-
tain, reaction, container, react, heater, reactor, computer, compute, oscil- late, oscillating, oscillator
![]()
diode [daiad] oiodc |traiad]
![]()
![]()
oscillator ['as‹le‹ta!
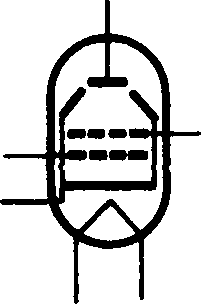
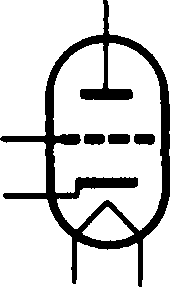
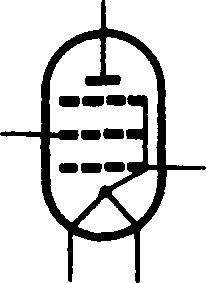
Electron Tubes
Let us consider elecoon tubes. Among the electron tubes in use nowadays there are a diode, a triode, a tetrode and a pentode. The main parts of electron tubes are electrodes. Electrodes are placed into a glass or metal bulb.
![]()
A diode contains the cathode and the plate. When a diode operates the cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them.
A triode contains the cathode, the plate and the control grid. When
the tube operates the cathode emits electrons, the plate collects them
and the grid controls the flow of electrons. Therefore, the grid is called
a control gi•id.
A tetrode contains the cathode, the plate, the control grid and the
screen grid.
When a tube operates it may oscillate. The function of the screen grid is to eliminate oscillations. Therefore it is called a screen grid.
A pentode contains two electrodes and three grids: the control grid, the screen grid and the suppressor grid. When a pentode opemtes the suppressor grid eliminates the secondary emission.
Common troubles in tubes are an open heater and low emission. These roubles result from constant use or from some other reason.
In case a tube has a trouble it stops opemting or operates badly. A tube with a trouble should be replaced by another one.
Complete tbe sentences usisg the correct variant:
t. A pentodc contains a) the cathode, the plate, two'scrccn grids
and the suppressor grid.
![]() the
cathode,
the
plate,
the
comet
grids, the screen
grid
and
the
suppressor
grid.
the
cathode,
the
plate,
the
comet
grids, the screen
grid
and
the
suppressor
grid.
A tcoodc contains
A biodc contains
![]() the
cathode,
the
plate,
the
suppressor
grid
the
cathode,
the
plate,
the
suppressor
grid
and the screen grid.
![]() the
cathode,
the
plate,
the
screen
grid
and
the
control
grid.
the
cathode,
the
plate,
the
screen
grid
and
the
control
grid.
![]()
the cathode, the plate and the control grid.
4. The function of the a) to collect elecnons.
cathode is 6) to eliminate the secondary emission.
º to emit electrons.
The function oftkc a) to eliminate oscillations. plate is 6) to emit electrons.
![]() to
collect
elecnons.
to
collect
elecnons.
The function of the a) to emit electrons.
connol grid is 6) to conool the clccoon flow.
to eliminate secondary emission.
The function of the a) to collect electrons. screen grid is b) to reduce the capacity.
º) to eliminate oscillations.
8. The function of the a) to comet the electron flow. suppressor grid is b) to eliminate secondary emission.
to eliminate oscillations.
9. Constant use of a tube a) high emission. results in b) low emission.
c) an open heater.
![]() Answer
the
following
questions:
Answer
the
following
questions:
What types of electron tubes are used nowadays?
How many electrodes does a diode (a triode, a tetrode, a pentodc) contain?
What is the function of the cathode (the plate, the control grid, the
screen grid, the suppressor grid)?
What does the constant use of a tube resu,1t in?
What d‹›«s low emission result from?
When must a tube be replaced?
Peir work. Think of five questions covering the article given below. Put these questions to your groupinetc end esk hislher to enswer thcia.
Pentode
When in an operating tube the screen-grid voltage is high, secondary emission does not return to the plate and passes to the screen grid. This rc- sults in a counter flow of elecnons. To eliminate this counter flow, a third grid was placed between the plate and the screen grid and connected to the cathode. This grid is called a suppressor grid. Since the suppressor grid has a negative potential it returns the secondary emission back to the plate and thus eliminates it in the tube. The tube containing elecnodes -the cathode, the plate, the connol grid, the scrcen grid and the suppressor grid — is called a pentode. The cathodc emits electrons, the plate collccts them, the comet grid controls the flow of elecnons, the screen grid helps the plate to collect electrons and reduces the capacity between the control grid and the plate, the suppressor grid eliminates the secondary emission.
![]()

Cover the right column end read the English words. Translate
theia into Russian end check your translation.
Cover the left column end trenslete the Russian words beck into
English.
half
to rectify
[ho:I]
![]()
![]()
-
to amplify
['nmplilai]
ycuiiuBBTh
to convert
by means of
[kan'va:t]
rrpeo6p83osusazs, o6paut8 s
nocpencraou, c nououiaio
that is why
soT ££ovcuy
to put into opemtion npuaonwix a neftciaue, 3aiiycxaTs
2. Read tbe words and put down tbcir Russian equivalcau:
pulse lpxlsJ electron [iJektr3n] cycle l'saikl] indie l'reidiou l
3. Distribute the words below into the three columns:
action process doer
[ju:sJ use, [ju:z] use, rectifier, rectification, amplifier, amplify, convert, user, converter, application, apply, pulse, pulsation, opemte, operator
4. Trenslete these word combinations into Russian:
e. half-wave
half-cycle
half-wave rectifier positive half-cycles
electron tube application
negative half-cycles
by means of a filter
b. by means oftke suppressor grid tubes used as rcctificrs tubes used as oscillators
Use of Electron Tubes
Let us consider some cases of electron tube application. Tubes are common elements of radio and electronic devices. Tubes are used
as rectifies — to convert a.c. into d.c.,
as oscilletom — to produce oscillating waves and
as emplifiem — to amplify the input voltage and current.
Half-Wevc Rectifier
Alternating current is converted into direct current by means of a
rectifier.
A half-wave rectifier consists of a diode in series with a resistance. In order to put a rectifier into operation, a source of a.c. should be ap-
plied to it. When an a.c. source is applied the diode begins to conduct. The rectifier passes currents during positive half-cycles of the applied voltage. That is why it is called a half-wave rectifier. When the device operates d.c.'flows in the same direction. It is a pulsating current. Since pulsations should be eliminated, a filter is applied. Pulsations are elimi- nated by means of this filter.
Complete the sentences using the correct variant:
Electron tubes are used a) as amplifies only.
6) as oscillator only.
c) as rectifiers, amplifies and oscillator.
A.c. is converted into d.c.
A half-wave rectifier consists of
In order to put a rectifier into operation
A half-wave rectifier
![]()
Rectified current is
Pulsations are eliminated
by means of a rectifier.
by means of an amplifier.
a) a diode in series with a transformer.
a diode in series with a resistor.
d. c. is applied.
a.c. is applied.
during positive and negative half-cycles.
during positive half-cycles of the ap•
![]()
![]()
by means of a choke coil.
by means eta filter.
How are elecnon tubes used?
What type of device is called a rectifier?
By what means is alternating current rectified into direct current2
4. What elements does a half-wave rectifier consist of?
S. What current should be applied to put a half-wave rectifier into opem-
tion?
6. When does a half-wave rectifier pass current?
7. By what means are pulsations eliminated?
7. Draw a scheme of a half-wave rectifier and describe its operation.
-49-
I. a) Cover tbc right column and reed the English words. Tresslstc tbcm iato Russias and cbcck your traastattoa.
b) Cover the left columa aad translate tbc Russtaa words back iato
end ![]()
filament lower upper secondary
end capacity
end coils filament battery filament current
secondary circuit
secondary resistance
[lilamant]
![]()
![]()
![]()
 J'sekandariJ
J'sekandariJ
![]()
 2.
Read
the
words
aad
put
dowa
tbcir
Russias
equivalents.
Traaslstc
2.
Read
the
words
aad
put
dowa
tbcir
Russias
equivalents.
Traaslstc
tbcm back isto Eaglisb (orally).
[kam'pounant] component
![]()
‘['minimaml
![]()
3. Put dows tbc Russian For:
low voltage winding tube plate filament winding
£'uII-wave Rectt£›er
In a full-wave rectifier two diodes are used. They are connected to a common load resistance. The secondary of the transformers has a cuntrc tap to which the load is connected. Current flows through the tubes
from their plates to their cathodes. When the upper end of the high-
VOlt8QG WlRdlRQ IS JlOSltlVfl, GuiTent floWs through the UppGp tube.
During the opposite half cycle the lower end of the high voltage
![]()
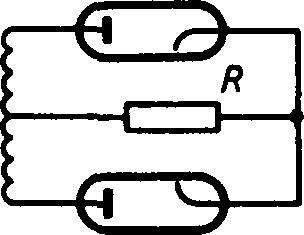
lower tube conducts current. Cur- R
rent flows through the filament winding to its centre tap, then through the load to the centre tap of the high-voltage winding and to the
tube
plate
which
is
positive.
![]()
Complete the sentences uslng the correct verlent:
A full-wave rectifier contains a) one diode.
6) two diodes.
The load is connected to
the centre tap of the primary.
6) the ccnae tap of the secondary.
Current flows through the tubes a) from the plates to the cathodes.
from the cathodes to the plates.
When the upper end of the high- a) current flows through the upper voltage winding is positive tube.
b) current flows through the lower
During the negative half-cycle a) the plate of the lower tube be-
comes posiave.
![]()
6. During the positive half-cycle a) the lower tube conducts current.
6) the upper tube conducts current.
5. Complete the sentences using whtle. Follow the model on pegc 13.
l. A hell-wave rectifier contains one diode
2. When the uppur end of the high-voltage winding is positlvc, current
flows through the upper tube ..
3. During the negative half-cycle the lower tube conducts current ..
Pair work. Put these questions to your groupmatc aad let bim/bcr an-
I . How many diodes docs a full-wave rectifier contain?
What clement is the load connected to?
What is the direction of current in the tubes?
During which cycle docs the plate become negative?
When docs the lower tube conduct current?
When does the upper tube conduct current?
What is the difference between a half-wave and a full-wave rectifier?
What is the difference in their construction?
In what way docs a full-wave rectifier operate?
In what way doea a half-wave rectifier opcmtc?
I l . What are the main pans of a half-wave rectifier?
12. What arc the main parts of a full-wave rectifier?
![]()
1. a) Cover the right column and reed the English words. Translate
them iato Russias asd cbcck your trsssJation.
b) Cover the left colums end translate the Russias words beck iato English.
to feed (fed)
![]()
to remain
![]()
push-pull
push-pull amplifier push-pull circuit
push-pull nansformcr feedback
feedback amplifier feedback coil feeding transformer
 [in'klu:d]
[in'klu:d]
IlHTfiTh
GO,QGJ9 IBTh, 3BKJIIO•IBTb (» c«6e)
OCT8BBTbGR TOJlEBTh
TE b
nyuinyn, nyuinynsiibiR nayxiaxriii›iR ycitiiwrens nayxrarriiaa cxcsia nyuinyiisiisifl ipaiici]iopiiaiop
(IBTH88 CB113h
pereiicpa itaiisift ycwiuieiis saiyuisa obpaTiioh cassii citnoaott ipaiici]iopiiaTop
Put down tbe Russias for:
plate currant supply alternating current components maximum grid voltage transformer secondary winding
Push-pull Amplifier
An amplifier is used to produce the output voltage greater than the input voltage. A push-pull amplifier includes two tubes. Their control grids are connected to the opposite ends of the input transformer secon- dary winding. The centre of this winding is connected to the tube cath- odes. When maximum grid voltage is produced in one tube, minimum grid voltage is produced in the other tube. Thus, the sum of the plate
t currents remains constant.
The plate currents are fed
 ‹› Tr
‹› Tr
![]()
Fig. 16
into the opposite ends of the
![]()
Complete these sentences, using the correct variant:
l . An amplifier is used a) to separate a.c. from d.c.
b) to change the value of the input voltage.
2. The input voltage is increased a) by means of a rectifier.
b) by means of an amplifier.
3. A push-pull amplifier includes a) only one tube.
b) two tubes.
4. When maximum grid voltage a) maximum grid voltage is produced is produced in one tube in the other tube.
b) minimum grid voltage is produced
in the other tube.
5. The sum of the plate currents a) changes.
b) remains constant.
D.c. components
A.c. components
arc eliminated.
add in the circuit.
add in the circuit.
are eliminated.
![]() Complete
the
sentences
using
whtle.
Follow
the
model
on
page
13:
Complete
the
sentences
using
whtle.
Follow
the
model
on
page
13:
I . An amplifier is used to increase the value of the input voltage ..
When maximum grid voltage is produced in one tube ..
Dlrcct current plate components are eliminated .
![]()
![]()
What is an amplifier used for?
By what means is a greater output voltage produced?
What arc the main parts of a push-pull amplifier?
In what way arc the tubes and the transformer connected?
Why does the sum of the plate currents remain constant?
Where arc the plate currents fed?
What type of current is amplified by a push-pull amplifier?
What is the difference between a rectifier and an amplifier?
![]()
![]() a}
Cover
the
rlgbt
columa
aad
read
tbc
Eaglisb
words.
Translate
tbcm
iato
Russian
aad
check
your
translation.
a}
Cover
the
rlgbt
columa
aad
read
tbc
Eaglisb
words.
Translate
tbcm
iato
Russian
aad
check
your
translation.
6) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words back into English.
![]() ['batas] nonou«×ress«oe
(c›ieuiaiouiec)
['batas] nonou«×ress«oe
(c›ieuiaiouiec)
![]()
to follow
stage of amplification
grid bias
grid bias battery
grid plate capacitance
['faloul

 ciynciis
(xacxag)
ycitiiciiiis
ciynciis
(xacxag)
ycitiiciiiis
ciixoc s aiioniioii ccrxii
![]()
the main‘parts of the device
the following change of voltage the main components of the plate voltage
plate voltage supply grid bias
voltage variations
![]()
 Amplifiers
in
use
nowadays
contain
several
stages.
Sometimes
their
number
is
very
great.
Let
us
consider
an
amplifier
including
three
stages.
Its
circuit
uses
three
triodes
connected
in
series.
The
circuit
has
a
resistance
as
the
plate
load.
A
common
plate
voltage
supply
and
a
common
grid
bias
are
employed.
The
grid
of
each
tube
is
insulated
from
the
direct
current
component
of
the
plate
voltage
by
means
of
a
capacitor.
When
the
amplifier
operates
the
voltage
operation
of
the
load
of
one
tube
is
applied
to
the
grid
of
the
next
tube.
The
voltage
variation
is
transferred
to
the
grid
of
the
following
tube
through
a
capacitor.
Amplifiers
in
use
nowadays
contain
several
stages.
Sometimes
their
number
is
very
great.
Let
us
consider
an
amplifier
including
three
stages.
Its
circuit
uses
three
triodes
connected
in
series.
The
circuit
has
a
resistance
as
the
plate
load.
A
common
plate
voltage
supply
and
a
common
grid
bias
are
employed.
The
grid
of
each
tube
is
insulated
from
the
direct
current
component
of
the
plate
voltage
by
means
of
a
capacitor.
When
the
amplifier
operates
the
voltage
operation
of
the
load
of
one
tube
is
applied
to
the
grid
of
the
next
tube.
The
voltage
variation
is
transferred
to
the
grid
of
the
following
tube
through
a
capacitor.
![]()
A change of voltage on the first grid Circuit results in an amplifiGd
plate current in the third stage.
3. complete these sentences, using tbc correct variant:
I . Amplifiers in use nowa- a) include only one stage.
days b) lRGlUde several stages.
2. A three-stage amplifier a) three triodes connected in parallel. uses 6) three triodes connected in series.
The grid of each tube is in- a) by means of a coil.
sulatud 6) by means of a capacitor.
4. The voltage variation is a) through a tube.
transferred 6) through a capacitor.
5. The circuit uses a) a different grid bias.
6) a common grid bias.
Answer the following questions:
How many stages do amplifies include?
What are the main parts of a three-stage amplifier?
By what means are the grids of the tubes insulated?
What type of grid bias is employed?
In what way is the voltage variation transferred?
1. a) Cover the right column end rcsd the English words. Translate
them Into Russian and check your translation.
 b)
Cover
the
left
column
end
translate
the
Russian
words
beck
into
b)
Cover
the
left
column
end
translate
the
Russian
words
beck
into
-
to close
[klouz]
aasisixais, aaxpsiaais
close to
l'klous t•l
6•••×o x (OT)
to switch on to switch off various
l'vcarias]
axiiio•iais asixiiio•iais
paniiieiusifi, pasiioo6pasiisik
2. Reed tbc words asd put dowa tbcir Russias equivalents. Tbca treas- lxtc them back iato English (orelly).
[rilei] relay [$ektrou'mxg»‹!l «I•ctromagnct ['o:rnatja] annaturc [1‹»ntxkt] contact
![]()
-
['sistim]
system
[,o:ta'mmtik I
automatic
['panlJ
panel

![]() into
adverbs
by
adding
-fj'.
Put down
their Rus-
into
adverbs
by
adding
-fj'.
Put down
their Rus-
Model.’ automatic — automatically
unprogrcssive —
![]()
Put down the Russian for:
to start flowing to start moving to start operating to start powering the motor
various branches of industry small cross-section relay’s primary circuit
Electromagnetic Reley
Electromagnetic devices called relays no widely used in various
branches of industry.
The main parts of a relay are an electromagnet, a spring and an ar- mature. When a current starts flowing in the electromagnet winding, the armature moves and the spring closes the contacts. The primary circuit of a relay is its electromagnet circuit and the secondary circuit is the one closed by the contacts.
When there is no current in the rulay’s primary circuit, the spring
pulls the armature and the contacts open.
Fig. 18 shows how a relay is used to control the work of an electric motor. The relay is placed close to the motor which is connected to its secondary circuit. The armature closes the contacts of the secondary
circuit, and the motor starts operating; it will stop when the relay opens.
Without a relay, conductors with a large cross-section would have to
be brought to the motor. This would be very uneconomical. The current
in a relay is tuns and even thousands of times smaller than that used to power the motor. Thurufore, the connecting wires can have small cross- sections.

Fi$. 18
In many systems the relay primary circuit operates automatically. Every evening and morning street lights are switched on and off from the main control panel by means of a gruat number of rulays.
Complete the sentences using the correct varlent:
The main parts of a rc- a) an electromagnet, a capacitor, and a spring.
lay are 6) an clccoomagnct, an armature, and a spring.
When current starts a) the spring opens the contacts.
flowing b) the spring closes the contacts.
The spring pulls the a) when there is current in the primary circuit.
armaturc 6) when there is no current in the primary cir- cuit.
The wires connecting a) have a large cross-section.
the panel with the relay b) have a small cross-section.
5. Strcut lights are a) by means of relays. switched on and off 6) by means of electric motors.
6. Complete tbesc scatcsccs usiag wiIte. F'ollow tbc model on psgc 13:
l. The primary circuit of a relay is its electromagnetic circuit ..
2. When there is no current in the relay’s primary circuit the contacts
3. Without a relay conductors with a large cross-section should be used
4. Every cvcnlng street lights arc switched on ..
![]()
What arc the main parts of a mlay7
How is a relay put into operation?
When does the spring pull the aiinature?
![]()
What wires connect the panel with the relay?
By what means are street lights switched on and off7
8• Pair work. a) Metch the questions end the enswem. b) Ask the ques-
tlons end let your groupmate enswer them.
In what position does a) Switches are used to open and close the circuits. the switch have high b) Closed is the on-position; open is the off-posi- (low) resistance? tion.
What arc the func- c) The switch is connected in series with the loan tions of the switch? d) In the on-position the closed switch has a very
In what position is the low rmistance, which results in maximum cur-
switch open? closed? rent in the load with zcm voltage loss across the
In what way is the switch. When the switch is off it has a very high switch connected to resistance and no current flows through the cir- the circuit? cuit.
1. a) Cover the right column and read the English words. Translate them into Russian and check your translation.
b) Cover the left column and translate the Russian words beck Into
fuse [fjuz]
link !ligk]
fault [fo:IU
faulty
 equipment [i'kwipmantJ
equipment [i'kwipmantJ
![]()
 o6opynoaaiiae
o6opynoaaiiae
ycraiioaxa; RI. coopyueiiiis
38fZ{£tJJTBTb, £I]3C,8,OX[36Jt9Tb
HCfTOJtb3OB8Tb
o6opyaosazs, cnapx›xazs
![]()
![]()
![]()
2. Read tbc words and put dowa tbclr Russias cquivslcsts Tbca trsns-
 Istc
tbcm
back
iato
EaglJsb
{orslly).
Istc
tbcm
back
iato
EaglJsb
{orslly).
principle
![]()
faulty protection device
Model. charge — overcharge - neperpysxa
connect — disconnect — passeaioi×rs
 heat - —
heat - —
 4.
Form
tbc
nouns
from
tbc
given
verbs
according
to
tbc
model.
Translate
4.
Form
tbc
nouns
from
tbc
given
verbs
according
to
tbc
model.
Translate
Model. to protect — protection -mamma
to utilize - - tO StEtl — — toreducc — —
to connect — —

![]()
utilizer, utilize, installation, displace, overheated, displacement, overpro-
duction, starter, equip, protection, disorganize
Trsnslstc into Russian. Mtnd 6or6 ... ond, Nr c«sa, up fo:
Both solid and gaseous insulators are highly in use.
In case a fuse gets faulty it should be replaced by a new one.
Capacitor of very high capacity - up to 1000 and more iaF - are util-
ized in modem installations.
Fuses are widely used nowadays as protection devices. They are utilized in various circuits, electrical equipment and installations..Fuses serve to protect them against overcurrents and short-cimuits.
- 6G -
There are different types of fuses in use nowadays. Of them, quartz- sand fuses serve for voltages up to 500 volts; fuses tit this kind are pro- duced with current ratings of IS to 60 amp and of 100 to 350 amp.
Fuses are commonly used in low-voltage industrial installations
rated up to 1,000 V.
Fuse protection is based on a very simple principle: in case of a short-circuit or overcurrent, when the maximum value of current has been exceeded, the fusible link of a fuse is heated to its melting point. This opens the circuit and disconnects the circuit from the power source. In case of a fault, one should replace the faulty fusible element by a new one.
Fuses are used both in direct current (d.c.) and alternating current (a.c.) circuits.
![]()
I . A fuse serves a) as a load.
b) as a protection.
2. Fuses are used
3. In case of a fault
for d.c. only.
for both a.c. and d.c.
the whole fuse should be replaced.
the faulty link should be replaced.
4. Fuse protection is based on a) a simple principle.
b) a complex principle.
![]() Memorize
tbe
questions.
Use
tbcm
in
s
talk
with
your
¿roupmste:
Memorize
tbe
questions.
Use
tbcm
in
s
talk
with
your
¿roupmste:
I . What does a fuse serve for?
For what type of current are fuses used?
What should be done in case of a faulty fuse?
What principle is fuse protection based on?
![]()
tbem into Russian end cbcck your translation.
b) Cover tbe left column and trsnslstc tbe Russian words back into
English.
