
- •Accounting
- •Accounting
- •The Accounting Process (The Accounting Cycle)
- •Balance sheet
- •Reporting profitability
- •Reporting financial position
- •Reporting cash flow
- •Types of cash flow
- •Accruals accounting
- •Types of Accounting
- •Managerial Accounting
- •Financial Accounting
- •Tax accounting
- •Other types of Accounting
- •Bookkeeping
- •Bookkeeping process
- •Bookkeeping systems
- •Single-entry system
- •Double-entry bookkeeping system
- •Debits and Credits
- •Financial statement
- •Annual Report
Financial Accounting
Financial accounting provides information to decision makers who are external to the business. To understand the role of financial accounting, consider a large corporation such as IBM. The owners of corporations are called shareholders, and IBM has more than 600,000 shareholders. Obviously, each shareholder cannot participate directly in the running of IBM, and because IBM needs to maintain various trade secrets, its many thousands of shareholders are not permitted access to much of the firm’s information. Because of this, shareholders delegate most of their decision making power to the corporation’s board of directors and officers. Figure 1.2 contains an organizational chart for a typical corporation. Shareholders, however, need information to evaluate (1) the performance of the business and (2) the advisability of retaining their investment in the business. Financial accounting provides some of the information for this purpose; such information is also used by potential shareholders who are considering an investment in the business.
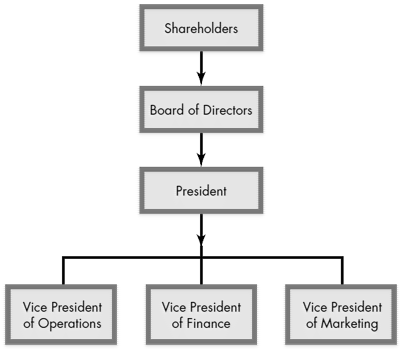
Figure 1.2 - Organizational Chart of a Typical Corporation
Creditors and potential creditors are also served by financial accounting. Firms often seek loans from banks, insurance companies, and other lenders. Although creditors are not internal parties of those firms, they need information about them so that funds are loaned only to credit-worthy organizations. Financial accounting will usually provide at least some of the information needed by these decision makers.
Tax accounting
Tax accounting encompasses two related functions: tax compliance and tax planning. Tax compliance refers to the calculation of a firm’s tax liability. This process entails the completion of sometimes lengthy and complex tax forms. Tax compliance takes place after a year’s transactions have been completed. In contrast, tax planning takes place before the fact. A business transaction can be structured in a variety of ways; a car can be purchased by securing a loan, for example, or it can be leased from the dealer. The structure of a transaction determines its tax consequences. A major responsibility of tax accountants is to provide advice about the tax effects of a transaction’s various forms. Although this activity may seem to bean element of managerial accounting, it is separately classified due to the necessary specialized tax knowledge.
Other types of Accounting
A few additional types of accounting exist. Accounting information systems are the processes and procedures required to generate accounting information. These include identifying the information desired by the ultimate user, developing the documents (such as sales invoices) to record the necessary data, assigning responsibilities to specific positions in the firm, and applying computer technology to summarize the recorded data.
Another type of accounting deals with non-business (not for profit) organisations. These organizations do not attempt to earn a profit and have no owners. They exist to fulfill the needs of certain groups of individuals. Non-business organisations include hospitals, colleges and universities, churches, the federal, state, and local governments, many other organizations such as museums, volunteer fire departments, and disaster relief agencies.
Nonbusiness organizations have a need for all the types of accounting we have just reviewed. For example, a volunteer fire department might need to borrow money to purchase a new fire truck. Its banker would then require financial accounting information to make the lending decision.
Nonbusiness organizations are fundamentally different from profit-oriented firms: They have no owners and they do not attempt to earn a profit. Because of this, the analysis of the financial performance of business and nonbusiness organizations is considerably different. This text addresses only business organizations. Most colleges and universities offer an entire course devoted to the accounting requirements of nonbusiness organizations.
