
- •Часть 3
- •Вопрос 10: Why is the Queen the fifth longest serving British monarch?
- •Вопрос 11: How often does the Queen have audience with the Prime Minister? How many and what Prime Ministers has she given regular audiences over the reign?
- •Вопрос 12: What do you know about the succession to the throne and the Ceremony of Coronation?
- •Вопрос 13: What do you know about the Royal family?
- •Вопрос 14: What is 'Civil List'? What is the Royal Household?
- •Вопрос 15:. Who will be the next King or Queen?
- •Вопрос 16: The Legislature: general survey (1) законодательная власть; законодательные учреждения)
- •Вопрос 17: What are the devolved national legislatures of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland?
- •Вопрос 18: The Parliament of the u.K.: general survey.
- •Вопрос 19: The House of Commons: composition, main functions, traditions.
- •Вопрос 20: What does parliamentary work of an mp consist of?
- •Вопрос 21: What are the functions of the Speaker?
- •Вопрос 22: The House of Lords: composition, main functions, traditions.
- •Вопрос 23: Who presides over the House of Lords? What functions does he fulfil?
- •Вопрос 24: Legislation: general survey. (1) законодательство; законодательная деятельность 2) закон; законопроект)
- •Вопрос 25: What is a Bill? What are the main classes of Parliamentary Bills?
Вопрос 24: Legislation: general survey. (1) законодательство; законодательная деятельность 2) закон; законопроект)
The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law.
United Kingdom legislation derives from a number of different sources. The United Kingdom does not have a single body of legislation, but is divided into three jurisdictions, each with its own laws and legal system: England and Wales (English law), Scotland (Scots law), and Northern Ireland (Northern Ireland law).
An act of Parliament[1] in the United Kingdom is a type of legislation called primary legislation. These acts are passed by the UK parliament in Westminster or the devolved administration in Scotland. A draft piece of legislation is called a bill, when this is passed by parliament it becomes an act and part of statute law.
Вопрос 25: What is a Bill? What are the main classes of Parliamentary Bills?
A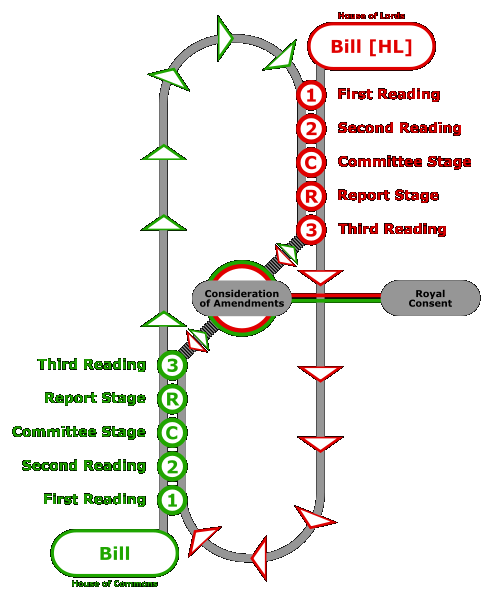 draft piece of legislation is called a
bill. A bill is a proposed law under
consideration by a legislature.
draft piece of legislation is called a
bill. A bill is a proposed law under
consideration by a legislature.
A bill does not become law until it is passed by the legislature and, in most cases, approved by the executive. Once a bill has been enacted into law, it is called an act or a statute. The term bill is primarily used in the United States and the Commonwealth. In the United Kingdom, the subparts of a bill are known as clauses while the subparts of an act are known as sections. Bills may start their passage in either the House of Commons or House of Lords, although bills which are mainly or entirely financial will start in the Commons
There are several types of bills and acts. Although public, private, and hybrid bills are mutually exclusive.
Public acts are the largest category of legislation, affecting the public general law which applies to everyone in the UK. Acts apply to the whole of the UK or sometimes to a number of its constituent countries - England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Private acts are local and personal in their effect, applying to a specific (real or legal) person differently from others. Private bills are "usually promoted by organisations, like local authorities or private companies, to give themselves powers beyond, or in conflict with, the general law.
Private bills only change the law as it applies to specific individuals or organisations, rather than the general public.
It is important not to confuse private bills with private members' bills, which are public bills designed to affect a general change in the law. The only difference from regular public bills is that they are brought forward by a private member (a backbencher) rather than by the government
Financial bills raise revenue and authorise how money is spent. The most well known such piece of legislation is the annual Finance Bill introduced by the Chancellor of the Exchequer at the budget.
Housekeeping bills This type of bill is designed to keep the business of government and public affairs up to date.
