
- •Vocabulary
- •Introduction 8 jobs, people and organizations
- •9 Organizations 2 32
- •[3 The Internet and e-commerce
- •Q] Sales and costs
- •2| Telephoning 3: messages 108
- •Introduction
- •Industry
- •Innovation and invention
- •Innovation and invention
- •McGrew is vice president of (a development/development) and product planning.
- •Electric light was (an invention/invention) which enabled people to stay up later.
- •Indian Rice Research Centre. I’m in charge of research (5)
- •I love (14 technological) , using scientific knowledge (15) improve
- •If he goes on undercutting us, we
- •It’s a terrible place to work. We have to make 30 calls an hour, with few breaks.
- •Invalid entry.
- •6 Volkswagen’s sales rose to 1,058,000 cars from 996,000 a year earlier.
- •The materials used in the boats, and the boatbuilders’ salaries (overhead cost / cogs)
- •Which product has the highest level of profitability as a percentage of its selling price?
- •Years of on investment in Britain’s railways have left them in a very bad state.
- •Planning the concert, they found they had forgotten to the singers,
- •A loan that a company has to repay to a bank over five years is a long-term liability.
- •Don’t want to have the situation where I’ve spent more than I’ve put in.
- •On the savings account, what’s the percentage you pay to savers every year?
- •Peter is 26 and is wondering whether to join his company pension scheme.
- •30 Years ago
- •20 Years ago
- •Petrol prices set to skyrocket
- •Sterling plummets as us dollar weakens
- •Paradiso president axes finance minister /
- •Here the male managers talk about the market as if it was some kind of battlefield.
- •7590 W Charleston Blvd
- •Senior Partner e-mail: kesposito@ace.Com
- •Voicemail
- •That’s strange. Their switchboard isn’t big enough to handle all the calls they get.
- •That’s ridiculous! a company with 500 employees, but no one answers the phone.
- •Switchboard operator: Sorry to keep you waiting. ... I’m putting you through.
- •A: It’s been good talking to you. I’m going to have to go. I’ve got to go to a meeting.
- •It was good to hear from you again. The following pages give details of the latest additions to our range. If you require any further information, please do not hesitate to contact me.
- •I’m pleased to announce another good year for shareholders of this company.
- •I know this sounds crazy, but how about giving away 100,000 free samples?
- •I recommend to shareholders that you accept Megabook’s offer for our company.
- •Off: to show how important and clever they are. The chair should keep things
- •I’ve been asked to chair a meeting about the Christmas office party, but I’m incredibly nervous as I’ve never chaired one before. Is there a secret for success?
- •The combined resources of our two organizations will allow us to achieve great things.
- •It could sound monotonous and boring if you speak from a complete, prepared text.
- •They add visual interest, provide you with support and help the audience follow you.
- •Reforms 4 pressures 6 economy
Which products make a profit?
Which product has the highest level of profitability as a percentage of its selling price?
Which loses money?
Which just breaks even?
Which is the biggest money-spinner or cash cow, in terms of overall profit?
Which product may be a loss leader, to encourage furniture stores to buy other, profitable products?
Complete the sentences using correct forms of expressions from B opposite.
She felt the organization was and wasting money on entertainment and
luxury travel.
UK tobacco companies have an advertising of £50 million a year.
Orson Welles was supposed to make a film version of Heart of Darkness, but he ran , and the project was cancelled.
The repair budget for Windsor Castle after the fire was £40 million. In fact, the repairs were completed six months ahead of schedule and £3 million
Years of on investment in Britain’s railways have left them in a very bad state.
Planning the concert, they found they had forgotten to the singers,
and could only pay the orchestra.
Spending on books is rising as a proportion of total consumer
Match the sentence beginnings (1-3) with the correct endings (a-c). The sentences all contain expressions from C opposite.
There are economies of scale in hospital services; a so cutting unit costs.
Some universities put more students into classes, b but we are learning from our
mistakes.
The learning curve is very steep, c however, they only apply up to about
100-200 beds.
![]()
Over +o tpu
Does your company, or one you would like to work for, have a cash cow or a loss leader? Does your company, or one you would like to work for, benefit from economies of scale?
Getting paid
Shipping and billing
When you ask to buy something, you order it, or place an order for it. When the goods are ready, they are dispatched or shipped to you.
An invoice is a document asking for payment and showing the amount to pay. The activity of producing and sending invoices is invoicing or billing.
Trade credit
Vaclav is talking about his furniture business:
‘Of course, we don’t expect our business customers to pay immediately. They are given trade credit, a period of time before they have to pay, usually 30 or 60 days. If a customer orders a large quantity or pays within a particular time, we give them a discount, a reduction in the amount they have to pay.
But with some customers, especially ones we haven’t dealt with before, we ask them to pay upfront, before they receive the goods.
Like all businesses, we have a credit policy, with payment terms: rules on when and how customers should pay. This is part of controlling cash flow, the timing of payments coming into and going out of a business.’
Accounts
Jennifer and Kathleen are businesswomen. Jennifer has her own company in Britain and Kathleen owns one in the US.
I’m
waiting to be paid by some of my customers. These are my debtors.
They owe me money.
'
The suppliers and other organizations that I owe money to are my
creditors.
I
must remember to pay tax to v the Inland Revenue on time!
There
are some companies that owe Jennifer
me
money, but I get the feeling I’m never going to get paid: they’re
bad V
debts
and I’ve written them off.
The
customers that I’m waiting to be paid by are my accounts
receivable or receivables.
The
suppliers and other organizations that I owe me to are my accounts
payable payables. I must remember pay tax to the Inland Revet
Service on time!
Kathleen
Messco dispatched the goods to Superinc.
Superinc ordered goods from Messco.
Superinc eventually settled the invoice.
Superinc did not pay the invoice on time.
Two weeks later, Superinc had still not received an invoice, making them think Messco’s invoicing was not very efficient.
Someone in accounts at Messco chased the invoice by phoning the accounts department at Superinc.
When the goods arrived, Superinc noticed there was no invoice and asked Messco to issue one.
Messco’s accounts department raised an invoice and sent it to Superinc.
29.2
is a constant problem. I get materials from suppliers on a
30-day payment basis, but I’m supplying large companies who pay me on a 60- day payment term.
With some types of new wine, you can pay a special price and wait
for it to be delivered in about ten months’ time.
Small businesses complain that larger companies abuse by
paying invoices too slowly.
We offer a two per cent for payment within ten days.
We have a very strict : our are that
everyone pays within 30 days.
29.3
What
are the normal payment terms in your company or the company you are
interested in?
Do
small companies have problems getting paid in your country? Do some
businesses offer discounts to the public?
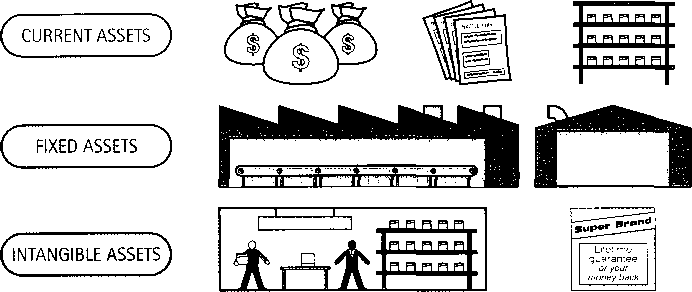
Assets,
liabilities and the balance sheet
Assets
current assets: money in the bank, investments that can easily be turned into money, money that customers owe, stocks of goods that are going to be sold.
fixed assets: equipment, machinery, buildings and land.
intangible assets: things which you cannot see. For example, goodwill: a company’s good reputation with existing customers, and brands (See Unit 22): established brands have the power to earn money.
If a company is sold as a going concern, it has value as a profit-making operation, or one that could make a profit.
Depreciation
Joanna Cassidy is head of IT (Information Technology) in a publishing company:
‘Assets such as machinery and equipment lose value over time because they wear out, or are no longer up-to-date. This is called depreciation or amortization. For example, when we buy new computers, we depreciate them or amortize them over a very short period, usually three years, and a charge for this is shown in the financial records: the value of the equipment is written down each year and written off completely at the end.
The value of an asset at any one time is its book value. This isn’t necessarily the amount that it could be sold for at that time. For example, land or buildings may be worth more than shown in the accounts, because they have increased in value. But computers could only be sold for less than book value.’
Liabilities
Liabilities are a company’s debts to suppliers, lenders, the tax authorities, etc. Debts that have to be paid within a year are current liabilities, and those payable in more than a year are long-term liabilities, for example bank loans.
Balance sheet
A company’s balance sheet gives a picture of its assets and liabilities at the end of a particular period, usually the 12-month period of its financial year. This is not necessarily January to December.
Look at A opposite. What kind of asset is each of the following? Which three are not assets?
Vans which a delivery company owns and uses to deliver goods.
Vans for sale in a showroom.
A showroom owned by a company that sells vans.
A showroom rented by a company that sells cars.
Money which customers owe, that will definitely be paid in the next 60 days.
Money which a bankrupt customer owes, that will certainly never be paid.
The client list of a successful training company, all of which are successful businesses.
The client list of a training company, with names of clients that have all gone bankrupt.
Use the correct forms of words in brackets from B opposite to complete these sentences.
The bank had lent too much and was left with a mountain of bad debts: £4.3 billion was (write off / wrote off / written off) last year.
Most highway building programs in the US are (amortization / amortize /
amortized) over 30 years or more.
The company reported a record income of $251.2 million, after a $118 million
(charge / charged / charges) for reduction in the (book value / books value /
booked value) of its oil and gas properties.
Under the new law, businesses face five different (depreciate / depreciation /
depreciations) rules for different types of equipment.
The company reported a loss of $12.8 million, partly due to a special charge of $1.5
million to (write down / wrote down / written down) the value of its spare
parts inventory.
Look at C and D opposite and say if these statements are true or false.
