
"The system of English phonemes"
There are two main classes traditionally distinguished by phoneticians of any language. They are called consonants and vowels.
Consonants are pronounced with noise and voice combined, vowels are pronounced with voice only. The difference is in different work of organs of speech. In the case of vowels no obstruction is made. In the case of consonants different obstructions are made.
So consonants are characterized by the so-called close articulation (the blockage of can be complete, partial and intermittent). The blockage is made by organs of speech so consonants are always characterized by noise.
Consonants
On the articulatory level every consonant can be characterized by 2 facts:
in what articulatory position are organs of speech while pronouncing this consonant;
where in the mouth this consonant is formed.
Also a lot of other factors can influence the pronunciation of this consonant, for example:
by what organ of speech the obstruction is made;
in what position are "vocal cords" (голосовые связки);
with what power this consonant is pronounced and so on …
All consonants can be classified in different ways.
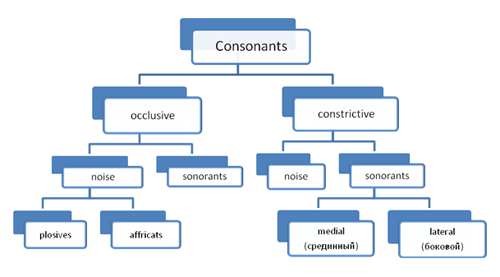
Classification of Vassilyev
There are 2 main factors according to which all consonants can be classified:
the type of obstruction
the manner of production of noise
There are 2 classes of consonants:
occlusive (смычные), in the production of which a complete obstruction is made;
constrictive (щелевые), in the production of which an incomplete obstruction is made.
occlusive |
constrictive |
tea |
sea |
seed |
seas |
pull |
full |
boat |
vote |
Each of these 2 classes is subdivided into noise consonant and sonorant. The factors of dividing these sounds is prevailing of noise or tone (голоса) in characteristics of a sound. In their turn noise consonants are divided into plosive (взрывные) [d] [t] and affricates [ʤ] [ʧ].
Classification of Sokolova and Tikhonov
The factor of their classification is the degree of noise. There are 2 classes of consonants:
noise
sonorants
Sonorants are the most debated consonants. The point is that they are pronounced differently from all other consonants. There air passage between organs of speech is very wide, much wider than in the production of other consonants. As a result we hear not noise but tone so sonorants sound more like vowels than consonants. Some British phoneticians refer them to the class of semivowels [w] [j] [r]. Soviet and Russian phoneticians think that these are consonants.

Resume
There are 2 factors that are most important in classification of sounds
degree of noise
manner of articulation
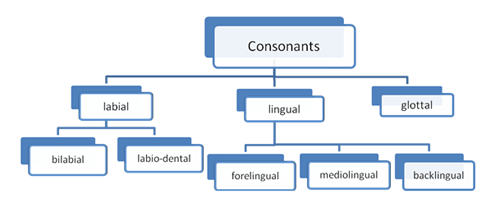
The place of articulation is another very important characteristic of English consonants. According to it all English consonant can be classified into:
labial (губные)
lingual (смычные)
glottal (гортанные)
Labial can be subdivided into:
bilabial
labio-dental
Lingual are subdivided into:
forelingual (передне-язычный)
mediolingual
backlingual
Examples:
pan – tan |
(bilabial – forelingual) |
why – lie |
(bilabial – forelingual) |
weil – yale |
(bilabial – mediolingual) |
pick – kick |
(bilabial – backlingual) |
less – yes |
(forelingual – mediolingual) |
day – gay |
(forelingual – backlingual) |
sigh – high |
(forelingual – glottal) |
feet – seat |
(labio-dental – forelingual) |
Our next point should be made in connection with another sound property, that is voiced and voiceless characteristic which depends on the work of vocal cords. It has been long believed that from the articulatory point of view there is a distinction on the absence or presence of vibrations of vocal cords between such pairs of sounds as: p-b; k-g; t-d; v-f; s-z; ʃ-ʒ; ʧ-ʤ, but this not the only difference between them. It is obvious that there is also energy difference.
All voiced consonants are weak, all voiceless consonants are strong.
There is one more articulatory characteristic according to which English consonants can also be classified, that is the position of the soft palate (мягкое небо). According to it consonants can be oral (ротовые) and nasal(носовые). Only some consonants demand the lowed position of the soft palate. They are nasal occlusive sonorants. They differ from oral plosives in which the soft palate is lowed (опущен) or risen (приподнят).
In the English system of consonants there is a problem of affricates. That is their status and number. There are two debated questions:
are the English sounds [ʧ] [ʤ] monophonemic or biphonemic combinations?
if they are monophonemic then how many phonemes of this kind exist in the system of English consonants and can such combinations [tr] [dr] [ts] [dz] [tƟ] [dð] be considered as affricates?
One thing is clear: that is all these sounds are complexes because articulatorily and acoustically we can distinguish two elements. The articulatory difference between [ʧ] and [ʤ] on the one hand and [t] [d] on the other hand is based on the speed of releasing the obstruction. When [ʧ] and [ʤ] are pronounced the obstruction is released slower than in case of [t] [d]. But it isn’t the only difference between affricates and plosives. There is no synchrony in releasing the obstruction by the central part of the tongue and its sides.
Considering phonetic duality of affricates it is necessary to analyze the relation of affricates to other consonants. Traditionally it is the type of obstruction that serves the bases for comparison.
There are 2 types of obstruction: complete and incomplete. According to this it is impossible to refer affricates to any group because they consist of 2 types of obstructions: complete and incomplete. So they are singled out (выделяются) in a separate group – affricates or occlusive / constrictive consonants.
The problem of affricates is a debated problem among phoneticians. According to Russian phoneticians there are 2 affricates - [ʧ] and [ʤ].
An English phonetician D. Jones says there are six affricates: [ʧ] [ʤ] [tr] [dr] [ts] [dz].
An English phonetician A. Gimson increases their number to eight adding two more affricates: [tƟ] [dð].
To understand if they are affricates or not we must define their articulatory indivisibility. This procedure is usually fulfilled according to principles of Trubetskoy. According to his point of view a sound complex can be considered monophonemic if:
its elements belong to one syllable;
they are produced by one articulatory effort;
its duration doesn’t exceed normal duration of its both elements.
