
- •Учебное пособие
- •Часть II 6
- •Часть II
- •From the history of the origin of science
- •A lesson in the history of little things
- •Structure of matter
- •States of matter solids, liquids and gases
- •What is an electron?
- •Gravitation
- •Uses of electricity
- •Solar energy
- •Atomic energy.
- •Peaceful atom
- •The telegraph
- •Modern electronics
- •Cosmonautics
- •Radio-electronics today
- •Astronomy and radio
- •The future of cybernetics
- •Our solar family
- •Life in space
- •The morning star (venus)
- •The moon
- •Why does the moon follow us when we drive.
- •Why is the sky blue?
- •What is the milky way?
- •Comets.
- •Comet in our universe.
- •Eclipse experiment may explain why sun is so hot
- •Man and his environment
- •The environment
- •Pollution
- •Did dragons ever exist?
- •How do we know what dinosaurs were like?
- •How did dinosaurs evolve?
- •Tornadoes
- •Computers.
- •The history of personal computing
- •Masters of invention
- •What's your opinion of computer games?
- •Life in their hands
- •Internet
- •Will the internet affect the practice of medicine?
- •By bill gates
- •Innovation feeds success in the pc industry
- •The checkered flag of the leader
Computers.
A. Hardware

As well as the hardware (=the machines), you also need software (==programs needed to work the machines). These programs are on disks, e.g. the hard disk inside the computer, or floppy disk (small pies of floppy disk) or on CD-ROMs (^Compact Disk Read Only Memory, a CD on which you can put a large amount information).
B. Operating a computer Using the mouse, you can do a number of things by clicking on
different icons (=moving the mouse to point at different pictures at the top of the screen
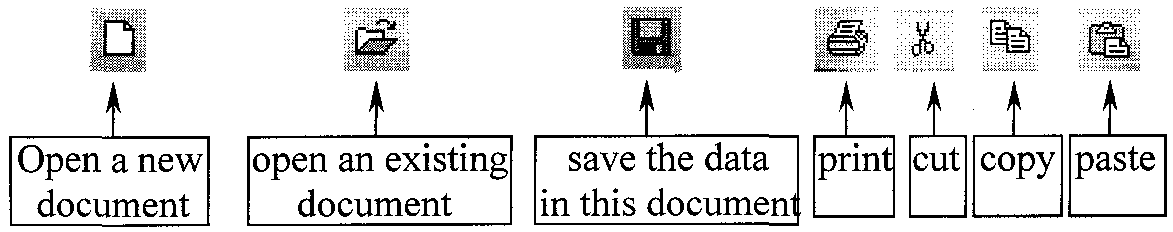
C. What do people use computer for
A word processor is a computers used to prepare documents or letters, or the software that is for this purpose. Many people use their computers for word processing, e.g. writing letters and report. A lot of business people use spreadsheets (=a program which used enter and arrange numbers and financial information) and database (^program which allow you to store, look at or change a large amount of information quickly and easily). Some people also use graphics (= the pictures and symbols a computer program can produce).
D. Important vocabulary
More and more people are becoming computing-literate (=have experience of working with computers and know how to use them) as many programs and machines are so user-friendly (=easy to use).
You can now connect your computers to computers all over the world using the Internet (=a system that allows computers to connect using telephone lines). People send each other e-mail (electronic mail) messages using this system or network. If you computer is slow it may need more memory. It may crash (=stop working) if there is not enough memory or if it has a bug (=software problem; also a virus). Make sure you make a back-up copy of your work (=an extra copy on floppy disk).
The history of personal computing
One of the most important developments leading to the personal computer revolution was the invention of the semiconductor, or transistor, in 1948. This feat was accomplished by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, who were engineers working at Belt Telephone Laboratories. The transistor, nothing more than a solid-stale electronic switch, replaced the much larger vacuum tube and consumed significantly less power in tube's job. Thus, a computer system built with transistors was much smaller and more efficient.
The tube also could act as a switch but was inefficient in this role. A tube consumed a great deal of electrical power and gave off enormous heat.
The switch to transistors began the trend toward miniaturisation that has enabled today's small laptop PC systems, which run on batteries, to have more computing power than many earlier systems that filled rooms and consumed huge amounts of electrical power.
In 1959, engineers at Texas instruments figured out how to put more than one • transistor on the same base material and connect the transistors without wires. Thus, the integrated circuit, or 1C, was born. The first 1C contained only six transistors, but the Intel 80386 in many of today's systems has 280,000. Today, IC can be built with millions of transistors on-board.
In 1969, a company called Intel made waves in the industry by introducing a 1 К— bit memory chip, which was much larger than anything else available at the time. Because of Intel's success in chip manufacturing, the company Japanese-calculator manufacturer called Busicomp and was asked to produce 12 chips for creation of Busicomp's calculator scientific designs. Engineers at Intel took the 12-chtp design and incorporated all the desired functions and capabilities into a single" generic" multipurpose chip. This chip was different from previous designs. The new chip read a variable set of instructions from memory, which Intel already had been producing. The concept was to design what was almost an entire computing device on a single chip. This first microprocessor was the Intel 4004. a 4-bit microprocessor, introduced in 1971. The successor to the 4004 was the 8008 5-bit microprocessor in 1972.
in 1973, some of the first microcomputer kits based on the 8008 chip were developed. In late 1973, Intel introduced the 8080 microprocessor, which was 10 time faster than the earlier 8008 chip and also could have 64 К of memory.
With a cover story In the January 1975 issue of Popular Electronics magazine, a company called MITS introduced the Altair kit, which is generally considered to be the first personal computer- This kit included an 8080 processor, a power supply, a front panel with a great deal of lights, and an enormous 256 bytes ( not kilobytes) of memory. The kit sold for 5395 and had to be assembled. The new processor inspired other companies to write programs, including the CP/M ( Control Program for Microprocessors) operating system and first version of Microsoft basic-now things really started moving. IBM introduced its first" personal computer" in 1975. The Model 5100 had 16K of memory, a built-in BASIC language Interpreter, and a built-in cartridge tape drive for storage. The Mode! 5100 was succeeded by the 5110 and 5120 before IBM introduced the IBM Personal Computer ( which was called the Model 5150).
In 1976, a new company called Apple Computer introduced the Apple I- This system consisted of a main circuit board screwed onto a piece of plywood. A case and power supply were not included; the buyer had to supply them. The Apple I was followed in 1977 by the Apple II. The Apple II, because of its enormous success, helped to set the standards for nearly all the microcomputers , including the IBM PC.
In 1980, the microcomputer world was dominated by two main factions of computers. One faction was the Apple II, which claimed of loyal users and a gigantic software base that was grow at a fantastic rate. Also available were ail the systems that had evolved from the original MITS Altair. These system were compatible with each other and were distinguished by their use of the CP/M operating system and expansion slots that followed the S-100 ( for slot with 100 pins) standard. Although built by a variety of companies and selling under various names, these systems all were able (for the most part) to use the same software and plug-in hardware
