
- •Unit 1.1. Early History of Flight Text 1.
- •Unit 1.2. International Civil Aviation Organisation (icao) Text 1
- •The history of the International Civil Aviation Organization
- •Foundation of the International Civil Aviation Organization
- •Icao Aims
- •Icao Offices
- •Unit 1.3. World Aviation Companies and Aircraft Manufacturers
- •Text 1. The Boeing Family
- •Boeing 787 Dreamliner Will Provide New Solutions For Airlines, Passengers
Aviation Basics
|
AVIATION BASICS |
Unit 1.1. Early History of Flight Text 1.
Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian.
The discovery of the kite that could fly in the air by the Chinese started humans thinking about flying. Kites were used by the Chinese in religious ceremonies. They built many colorful kites for fun, also. More sophisticated kites were used to test weather conditions. Kites have been important to the invention of flight as they were the forerunner to balloons and gliders.
For many centuries, humans have
tried to fly just like the birds a nd
have studied the flight of birds. Wings made of feathers or light
weight wood have been attached to arms to test their ability to fly.
The results were often disastrous as the muscles of the human arms
are not like a birds and cannot move with the strength of a bird.
nd
have studied the flight of birds. Wings made of feathers or light
weight wood have been attached to arms to test their ability to fly.
The results were often disastrous as the muscles of the human arms
are not like a birds and cannot move with the strength of a bird.
The ancient Greek engineer, Hero
of Alexandria, worked with air pressure and steam to create sources
of power. One experiment that he developed was the aeolipile
which used jets of
steam to create rotary
motion.
Hero mounted a
sphere on top of a water kettle. A fire below the kettle turned the
water into steam, and the gas traveled through pipes to the sphere.
Two L-shaped tubes on opposite sides of the sphere allowed the gas to
escape, which gave a thrust
to the sphere that caused it to rotate. The importance of the
aeolipile is that it marks the start of engine invention - engine
created movement will l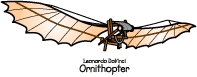 ater
prove essential in the history of flight.
ater
prove essential in the history of flight.
Leonardo da Vinci made the first real studies of flight in the 1480's. He had over 100 drawings that illustrated his theories on bird and mechanical flight. The drawings illustrated the wings and tails of birds, ideas for man carrying machines, and devices for the testing of wings. The Ornithopter flying machine was never actually created. It was a design that Leonardo da Vinci created to show how man could fly. The modern day helicopter is based on this concept. Leonardo da Vinci's notebooks on flight were reexamined in the 19th century by aviation pioneers.
T he
brothers, Joseph
Michel and Jacques Etienne Montgolfier, were inventors of the
first hot air balloon.
They used the smoke from a fire to blow hot air into a silk bag. The
silk bag was attached to a basket. The hot air then rose and allowed
the balloon to be lighter-than-air. In 1783, the first passengers in
the colorful balloon were a sheep, rooster and duck. It climbed to a
height of about 6,000 feet and traveled more than one mile. After
this first success, the brothers began to send men up in hot air
balloons. The first manned flight was on November 21, 1783, the
passengers were Jean-Francois Pilatre de Rozier and Francois
Laurent.
he
brothers, Joseph
Michel and Jacques Etienne Montgolfier, were inventors of the
first hot air balloon.
They used the smoke from a fire to blow hot air into a silk bag. The
silk bag was attached to a basket. The hot air then rose and allowed
the balloon to be lighter-than-air. In 1783, the first passengers in
the colorful balloon were a sheep, rooster and duck. It climbed to a
height of about 6,000 feet and traveled more than one mile. After
this first success, the brothers began to send men up in hot air
balloons. The first manned flight was on November 21, 1783, the
passengers were Jean-Francois Pilatre de Rozier and Francois
Laurent.
S ir
George Cayley is considered the father of aerodynamics.
Cayley experimented with wing design, distinguished between lift
and drag,
formulated the concepts of vertical
tail surfaces,
steering rudders,
rear elevators,
and air screws.
George Cayley worked to discover a way that man could fly. Cayley
designed many different versions of gliders that used the movements
of the body to control. A young boy, whose name is not known, was the
first to fly one of Cayley's gliders, the first glider capable of
carrying a human.
ir
George Cayley is considered the father of aerodynamics.
Cayley experimented with wing design, distinguished between lift
and drag,
formulated the concepts of vertical
tail surfaces,
steering rudders,
rear elevators,
and air screws.
George Cayley worked to discover a way that man could fly. Cayley
designed many different versions of gliders that used the movements
of the body to control. A young boy, whose name is not known, was the
first to fly one of Cayley's gliders, the first glider capable of
carrying a human.
F or
over 50 years, George Cayley made improvements to his gliders. Cayley
c
or
over 50 years, George Cayley made improvements to his gliders. Cayley
c hanged
the shape of the wings so that the air would flow over the wings
correctly. Cayley designed a tail for the gliders to help with the
stability. He tried a biplane
design to add strength to the glider. George Cayley also recognized
that there would be a need for machine power if the flight was to be
in the air for a long time.
hanged
the shape of the wings so that the air would flow over the wings
correctly. Cayley designed a tail for the gliders to help with the
stability. He tried a biplane
design to add strength to the glider. George Cayley also recognized
that there would be a need for machine power if the flight was to be
in the air for a long time.
George Cayley wrote "On Ariel Navigation" that showed that a fixed wing aircraft with a power system for propulsion, and a tail to assist in the control of the airplane, would be the best way to allow man to fly.
G erman
engineer, Otto Lilienthal, studied aerodynamics and worked to design
a glider that would fly. Otto Lilienthal was the first person to
design a glider that could fly a person and was able to
fly long distances.
Otto Lilienthal was fascinated by the idea of flight. Based on his
studies of birds and how they fly, he wrote a book on aerodynamics
that was published in 1889 and this text was used by the Wright
Brothers as the basis for their designs. After more than 2,500
flights, Otto Lilienthal was killed when he lost control because of a
sudden strong wind and crashed into the ground.
erman
engineer, Otto Lilienthal, studied aerodynamics and worked to design
a glider that would fly. Otto Lilienthal was the first person to
design a glider that could fly a person and was able to
fly long distances.
Otto Lilienthal was fascinated by the idea of flight. Based on his
studies of birds and how they fly, he wrote a book on aerodynamics
that was published in 1889 and this text was used by the Wright
Brothers as the basis for their designs. After more than 2,500
flights, Otto Lilienthal was killed when he lost control because of a
sudden strong wind and crashed into the ground.
S amuel
Langley
was physicist and astronomer who realized that power was needed t
amuel
Langley
was physicist and astronomer who realized that power was needed t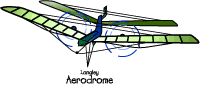 o
help man fly. Langley conducted experiments using whirling arms and
steam motors. He built a model of a plane, which he called an
aerodrome,
that included a steam-powered
engine. In 1891,
his model flew for 3/4s of a mile before running out of fuel.
o
help man fly. Langley conducted experiments using whirling arms and
steam motors. He built a model of a plane, which he called an
aerodrome,
that included a steam-powered
engine. In 1891,
his model flew for 3/4s of a mile before running out of fuel.
Samuel Langley received a $50,000 grant to build a full sized aerodrome. It was too heavy to fly and it crashed. He was very disappointed. He gave up trying to fly. His major contributions to flight involved attempts at adding a power plant to a glider. He was also well known as the director of the Smithsonian Institute in Washington, DC.
Octave
Chanute was a successful engineer who undertook the invention of
airplanes as a hobby, after being inspired by Otto
Lilienthal. Chanute designed several aircraft, the Herring –
Chanute biplane was his most successful design and formed the basis
of the Wright biplane design.
Octave Chanute published "Progress in Flying Machines" in
1894. It gathered and analyzed all the technical knowledge that h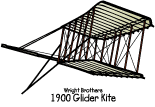 e
could find about aviation accomplishments. It included all of the
world's aviation pioneers. The Wright Brothers used this book as a
basis for much of their experiments. Chanute was also in contact with
the Wright Brothers and often commented on their technical progress.
e
could find about aviation accomplishments. It included all of the
world's aviation pioneers. The Wright Brothers used this book as a
basis for much of their experiments. Chanute was also in contact with
the Wright Brothers and often commented on their technical progress.
O rville
Wright and Wilbur Wright were very deliberate in their quest
for flight. First,
they spent many years learning about all the early developments of
flight. They completed detailed research of what other early
inventors had done. They read all the literature that was published
up to that time. Then, they began to test the early theories with
balloons and kites. They learned about how the wind would help with
the flight and how it could affect the surfaces once up in the air.
rville
Wright and Wilbur Wright were very deliberate in their quest
for flight. First,
they spent many years learning about all the early developments of
flight. They completed detailed research of what other early
inventors had done. They read all the literature that was published
up to that time. Then, they began to test the early theories with
balloons and kites. They learned about how the wind would help with
the flight and how it could affect the surfaces once up in the air.
The next step was to test the shapes of gliders much like George Cayley did when he was testing the many different shapes that would fly. They spent much time testing and learning about how gliders could be controlled.
The Wright Brothers designed and
used a wind tunnel
to test the shapes of the wings and the tails of the gliders. A fter
they found a glider shape that consistently would fly in the tests in
the North Carolina Outer Banks dunes, then they turned their
attention to how to create a propulsion
system that would
create the lift needed to fly. The early engine that they used
generated almost 12 horsepower.
fter
they found a glider shape that consistently would fly in the tests in
the North Carolina Outer Banks dunes, then they turned their
attention to how to create a propulsion
system that would
create the lift needed to fly. The early engine that they used
generated almost 12 horsepower.
T he
"Flyer" lifted from level ground to the north of Big Kill
Devil Hill, at 10:35 a.m., on December 17, 1903. Orville piloted the
plane which weighed six hundred and five pounds. The first
heavier-than-air flight traveled one hundred twenty feet in twelve
seconds. The two brothers took turns during the test
flights. It was
Orville's turn to test the plane, so he is the brother that is
credited with the first flight.
he
"Flyer" lifted from level ground to the north of Big Kill
Devil Hill, at 10:35 a.m., on December 17, 1903. Orville piloted the
plane which weighed six hundred and five pounds. The first
heavier-than-air flight traveled one hundred twenty feet in twelve
seconds. The two brothers took turns during the test
flights. It was
Orville's turn to test the plane, so he is the brother that is
credited with the first flight.
Humankind was now able to fly! During the next century, many new airplanes and engines were developed to help transport people, luggage, cargo, military personnel and weapons. The 20th century's advances were all based on this first flight at Kitty Hawk by the American Brothers from Ohio.
From www.ueet.nasa.gov
Exercise 1. Find the definition of the following words and word combinations and translate them into Ukrainian.
Kite, balloon, glider, aeolipile, ornithopter, hot air balloon, biplane, langley aerodrome, power plant
Exercise 2. Finish the sentences
1. The discovery of the kite …
2. Kites have been important to the invention of flight …
3. For many centuries, humans have tried to fly just like the birds …
4. The ancient Greek engineer, Hero of Alexandria, …
5. One experiment that he developed was …
6. The importance of the aeolipile is that it marks the start of …
7. Leonardo da Vinci's notebooks on flight were reexamined …
8. In 1783, the first passengers …
9. Cayley experimented with wing design …
10. Cayley changed the shape of the wings …
11. George Cayley wrote "On Ariel Navigation" that showed that …
12. Otto Lilienthal was the first person to design a glider …
13. He built a model of a plane, which he called an aerodrome …
14. It gathered and analyzed all the technical knowledge that …
15. They learned about how the wind would help with …
16. The next step was to test …
17. The "Flyer" lifted from level ground …
18. During the next century, many new airplanes and engines were developed …
Exercise 3. Answer the questions:
1. What was the Chinese contribution to the development of flight?
2. What do you know about Greek engineer, Hero of Alexandria?
3. What do Leonardo da Vinci’s drawings illustrate?
4. Explain the principle of hot air balloon operation.
5. Who is the founder of aerodynamics and what were his inventions?
5. Did Otto Lilienthal achieve success in his studies?
6. Who was the first to realize that the power was needed to help man to fly and what did he do?
7. Name the biplane that formed the basis of the Wright biplane design
8. Whom do we consider the inventor of flight?
9. What was the contribution of the Wrigth brothers into aviation?
10. What steps were taken by the Wright brothers to achieve success?
11. What is “Flyer”?
12. What do you know about the first flight made by the Wright brothers?
13. State the books that were published on the threshold of flight invention.
14. Name the scientists who made the contribution into the development of flight. What was their contribution?
Exercise 4. Match the word to the most appropriate translation.
|
to crash engine horsepower (hp). flight steam wing tails drag lift tubes weapons to climb to rotate thrust surfaces luggage cargo |
потік повітря труба обертати тяга (двигуна, гвинта) крило хвіст (хвостове оперення) лобовий опір підйомна сила розбивати політ поверхня (крила) двигун кінські сили багаж вантаж зброя набирати висоту |
Exercise 5. Match the word in column A with those in column B in order to make an appropriate word combination, as in the example and provide a translation. Example: sources of power – джерела живлення
|
A |
B |
|
propulsion military to run out of power steering vertical wing whirling steam steam-powered rear air sources rotary wind air |
pressure of power motion tail surfaces rudders elevators screws shape arms motor engine fuel plant tunnel system personnel |
Exercise 6. Offer your ways of translation. What types of transformations are possible?
1. More sophisticated kites were used to test weather conditions.
2. The results were often disastrous as the muscles of the human arms are not like a birds and cannot move with the strength of a bird.
3. Two L-shaped tubes on opposite sides of the sphere allowed the gas to escape, which gave a thrust to the sphere that caused it to rotate.
4. Leonardo da Vinci's notebooks on flight were reexamined in the 19th century by aviation pioneers.
5. Cayley experimented with wing design, distinguished between lift and drag, formulated the concepts of vertical tail surfaces, steering rudders, rear elevators, and air screws.
6. Based on his studies of birds and how they fly, he wrote a book on aerodynamics that was published in 1889 and this text was used by the Wright Brothers as the basis for their designs.
7. Langley conducted experiments using whirling arms and steam motors. He built a model of a plane, which he called an aerodrome, that included a steam-powered engine.
8. Chanute designed several aircraft, the Herring - Chanute biplane was his most successful design and formed the basis of the Wright biplane design.
9. The Wright Brothers designed and used a wind tunnel to test the shapes of the wings and the tails of the gliders.
10. Orville piloted the plane which weighed six hundred and five pounds.
Exercise 7. Fill in the blanks with a suitable word or phrase from the box below.
|
flight, kites, gliders, supersonic, spaceflights, wings, control surfaces, hor air balloon wood fire, steerable, wind tunnel, lift, drag |
1. Aviation history refers to the history of development of mechanical _________from the earliest attempts in ___________ and ______________to powered heavier-than-air, _______________ and _________________.
2. Some six centuries after Ibn Firnas, Leonardo da Vinci developed a hang glider design in which the inner parts of the __________ are fixed, and some ___________________ are provided towards the tips
3. The first generally recognized human flight took place in Paris in 1783. Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier and François Laurent d'Arlandes went 8 km (5 miles) in a ____________________
4. The balloon was powered by a _________________, and was not _______________: that is, it flew wherever the wind took it.
5. The Wrights constructed their own _______________ and created a number of sophisticated devices to measure __________and _________ on the 200 wing designs they tested.
Exercise 8. Write the correct form of the word in brackets.
In the mid-1770s, Joseph and Etienne Montgolfier, brothers who (work) in their father’s paper factory in Annonay in South-Eastern France, (note) that paper rose in the updrafts of the factory’s chimney, and occasionally a sheet would fold into a dome and continue rising even after leaving the immediate area of the chimney. They (conduct) some simple experiments with silk bags and soon became convinced that a large bag with heated air inside would rise. In actuality, this effect (have) already demonstrated nearly seventy-five years earlier by the Brazilian priest C Bartolomeu de Guasmao, who (conducte) a spectacular demonstration in the court of King John V in Lisbon, Portugal. But the Montgolfiers (know) nothing of this demonstration, and they (know) little about the reason their balloon (rise) into the air. They (believe) that the balloon was filled with a gas they called “Montgolfier gas” that (have) a special property they called “levity.” They did not even associate heated air with Montgolfier gas—they believed that the levity was contained in the smoke. Still, the Montgolfiers conducted their experiments and trials with care and (learn) much from each trial run.
Exercise 9. State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements.
1. Kites initially were made for scientific purpose.
2. Aeolipile is an archaic word that has the meaning - engine.
3. Ornithopter flying machine is considered to be an ancestor of a modern helicopter.
4. The first animals that travelled by air were sheep and rooster.
5. The Wright brothers’ flight lasted longer than George Cayley’s flight.
6. The stability of the gliders partially depends on its tail.
7. Samuel Langley tried to add a power plant to a glider.
8. Wright brothers used the previous experience and added their own ideas.
9. A wind tunnel was used to learn about the nature of wind.
10. The Wright brothers made the first powered airplane flight at Kitty Hawk.
Exercise 10. Translate into English.
Авіація почала розвиватися на початку ХХ століття. Першими в історії авіації були такі літальні апарати, як планер О. Лілієнталя ( середина 90-х років 19 ст.); літак О.Ф. Можайського ( 1882 р.); літак К. Адера ( 1890 р.); літак братів Райт (1903 р.).Перший успішний політ на літаку з двигуном внутрішнього згоряння здійснили 17 грудня 1903 р. американські механіки брати Вільбер і Орвілл Райт. Вони відкрили нову еру - еру підкорення відстаней з нечуваними швидкостями, еру неймовірних рекордів дальності і висоти польоту, еру героїчних льотчиків і допитливих конструкторів. Дальність першого пілотованого польоту на моторному аероплані «Флайер-1», братів Орвілл і Уїлбер Райт, складала 37 метрів, а продовжувався він 12 секунд. Але цей коротенький політ відкрив нову еру в історії людства.
Exercise 11. Have a look at the following text. It contains a number of mistakes and inaccuracies. Act as a proofreader and rewrite the sentences in accord with the rules of style, grammar and word combinability.
|
Від планера до літака – один крок
Як збільшити тривалість польоту на планері? Над цим питанням билися всі розробники літальних конструкцій. Пошуки відповіді не могли не підштовхнути до ідеї поставити на планер двигун. Але відзначимо відразу наступне: Роль мотора спочатку полягала лише в допомозі планеристи перелітати з одного повітряного потоку на інший. Зліт ж повинен був відбуватися за усталеною схемою - розгін проти вітру з височини. Перші планерних двигуни аж ніяк не забезпечувалися традиційним в нашому розумінні гвинтом. Якщо двигун на планері потрібен лише на час, то при зупинці його пропелера будуть погіршуватися, на думку конструктора, планують властивості апарату. Тому двигун в розробках Отто Лілієнталя використовувався для створення імпульсу махає крила - все-таки німець був затятим прихильником польоту за подобою птиці. У 1893 р. він запатентував і побудував моноплан з одноциліндровим вуглекислотним двигуном, який підвішувався на груди льотчику. На думку конструктора, рух штока передавалося крил за допомогою ланцюгової передачі, крило, повертаючись під тиском повітря навколо своєї осі при русі його вниз, повинна збільшувати аеродинамічну силу, спрямовану вперед. Але проблема, з якою зіткнувся, творець планерів, полягала в двигуні. Вуглекислотний двигун разом з резервуарами вуглекислоти був важкий (важив 20 кг), потужність його була 2 л. с. Працювати він повинен був мінімум 2 хв. Але надійності його роботи домогтися не вдалося. Тоді конструктор намагався придбати легкий бензиновий двигун, але це теж зробити не вдалося. Нарешті, інженеру П. Шауер надійшло прохання сконструювати вуглекислотний двигун, який мав би два циліндра. Їх передбачалося розмістити на центроплані крила. У 1896 р. планер з двигуном навіть помахав крилами на землі, але не більше того. У цьому ж році Лілієнталь прийшов до ідеї створення планера з нерухомим крилом - центроплана - і махають закінцівками. Сам апарат був вже майже створено, але загибель конструктора завадила довести розпочату справу до кінця. Втім, фахівці сумніваються в тому, що спроби злетіти на орнітоптер (а по суті, це був саме орнітоптер) були б вдалими, навіть якби залишився Лілієнталь живим. |
From the airframe to the aircraft - one step
How to increase the duration of the flight on a glider? Fought over this issue, all developers of aircraft structures. The search for answers could not push the idea to put on the airframe engine. But we note immediately following: The role of the motor initially consisted only of assistance gliders fly from one air stream to another. Take off the same should happen to an established scheme - the dispersal of the wind with height. The first glider motors are not supplied with a tradition in our understanding of the screw. If the engine on the airframe is needed only for a while, then stopping his propeller will worsen, according to the designer, planning unit properties. Because engine designs of Otto Lilienthal used to create the momentum flapping wing - still a German was a staunch supporter of the flight in the likeness of a bird. In 1893,. he patented and built a monoplane with a carbon dioxide-cylinder engine, which was suspended on his chest pilot. In the opinion of the designer, the motion passed stem wings through the chain of transmission, fender, turning the pressure of air around its axis when it moves downward, should increase the aerodynamic force directed forward. But the problem faced by the creator of gliders, was in the engine. Carbon dioxide engine together with reservoirs of carbon dioxide was heavy (weighing 20 kg), its power was 2 liters. with. Work he had at least 2 min. But the reliability of his work not been achieved. Then the designer was trying to buy small gasoline engines, but it also failed to do. Finally, the engineer II. Schauer was asked to design a carbon dioxide engine, which would have two cylinders. They are supposed to be placed on the center section of the wing. In 1896, a glider with an engine even waved the wings on the ground, but no more. In the same year Lilienthal came to the idea of a glider with fixed-wing - center section - and flapping wingtips. The unit itself was almost created, but death prevented the designer started to bring the matter to an end. However, experts doubt that the attempt to fly to the ornithopter (a matter of fact, this was the ornithopter) would be successful, even Lilienthal stay alive. |
Exercise 12. Write a short summary of the Text 1 using the aviation terminology. In the summary you should reconstruct aviation timeline and major achievements of the scientists.
Exercise 13. Role play
Student A:
Imagine you are Orville Wright who has just landed after his first flight. You are giving an interview in which you have to mention about the work done, designing process, theory of flight, experimental results and about your impressions, etc.
Student B:
Imagine you are an interview, who has just seen a technological breakthrough. Your task is to question a pilot and to get to know all the detail: how could he achieve it, what are his impressions, what are his plans for the future, etc.
