
Mini-course 1 Decision Analysis (Dr. Mariya Sodenkamp) / Class 5 / ITB_L5_ 2015_04_27
.pdf
Step 3: Calculate local priorities
Initial Comparison Matrix:
C1
C2
A = ...
Ci
...
Cn
Given:
C1 |
C2 |
... |
Cj ... |
a11 |
a12 |
... |
a1 j ... |
a21 |
a22 |
... |
a2 j ... |
... ... ... ... ...
ai1 ai 2 ... aij ...
... ... ... ... ...
an1 an 2 ... anj ...
|
|
|
|
Cn |
|
|
|
C1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
a1n |
|
|
|
a |
|
C2 |
|
|
2n |
|
|
... = ... |
|||
|
|
|
Ci |
ain |
|
||
... |
|
... |
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
nn |
|
|
|
|
Cn |
|
C1 C2 w1 w1
w1 w2 w2 w2
w1 w2
... ...
wi wi
w1 w2
... ...
wn wn
w1 w2
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
Cj
w1
wj w2
wj
...
wi
wj
...
wn
wj
A - matrix of pairwise comparisons; Ci − compared
... Cn
... w1 wn
... w2 wn
... ...
... wi wn
... ...
... wn wn
elements;
|
aij = |
wi |
− pairwise comparison |
values (i, j = 1,2,...n) |
|
|
|||
|
|
w j |
|
|
Find: |
wi '−normalized priorities of |
the elements Ci |
||
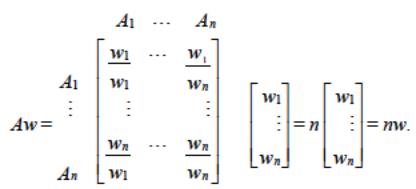
Eigenvector (priority vector)
In the judgment matrix A, instead of assigning two numbers wi and wj and forming the ra3o wi/wj we assign a single number drawn from the Fundamental Scale. The general eigenvalue formula3on is obtained by perturba3on of the following consistent formula3on:
where A has been mul3plied on the right by the transpose of the vector of weights w=(w1,...,wn). The result of this mul3plica3on is nw.
Thus, to recover the scale from the matrix of ra3os, we must solve the problem Aw=nw. This is a system of homogenous linear equa3ons. It has a nontrivial solu3on if and only if n is eigenvalue of A.
of the Eigenvector (approximated method I)
I. An |
|
an approximation to the priorities is to |
|||
|
|
means of the rows: |
|||
1) |
|
w1 |
|
C1 |
W − vector of priorities |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
w2 |
C2 |
wi − priority of the element Ci |
|
|
|
... |
|
... |
|
|
|
W = |
|
|
|
|
|
wi |
Ci |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
... |
... |
|
|
|
|
w |
Cn |
|
|
|
|
n |
|
|
|
wi ' = nwi
∑wi
i=1
w1 ' C1w2 ' C2
... ...
W ' =
wi ' Ci
... ...
wn ' Cn
W '− normalized vector of priorities (Eigenvector)
wi '−normalized priority of the element Ci

Derivation of the Eigenvector
(approximated method II)
II. Second way to obtain an approximation is by normalizing the elements
in each column of the judgment matrix and then averaging values over each row.
1) Matrix normalized in columns:
|
C1 |
C2 ... |
Cj ... |
Cn |
||||||||||
|
a11 ' |
a12 ' ... |
a1 j ' ... |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
C1 |
a1n ' |
|||||||||||||
C2 |
a |
21 |
' |
a |
22 |
' ... |
a |
2 j |
' ... |
a |
|
' |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2n |
|
|||||
A' = ... |
... |
|
... ... |
... ... |
... |
|
|
|||||||
Ci |
a |
' |
a |
' ... |
a ' ... |
a |
' |
|
||||||
|
|
i1 |
|
|
i 2 |
|
|
|
ij |
|
|
in |
|
|
... |
... |
|
... ... |
... ... |
... |
|
|
|||||||
|
a |
|
' |
a |
|
' ... |
a |
|
' ... |
a |
|
|
|
|
Cn |
n1 |
n2 |
nj |
|
' |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nn |
|
||||
aij ' = naij ∑aij i=1
2) Normalized eigenvector:
w1 ' C1w2 ' C2
... ...
W ' =
wi ' Ci
... ...
wn ' Cn
n
∑ aij '
wi ' = j =1n
aij '− normalized pairwise comparison values

Car Selection Example
Derive criteria priorities (importance weights)
First, add up the values in columns
|
Price |
Maintenance |
Horse-power |
Fuel consump3on |
|
|
|
|
|
Price |
1 |
5 |
7 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
Maintenance |
1/5 |
1 |
2 |
1/2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Horse-power |
1/7 |
1/2 |
1 |
1/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel consump3on |
1/3 |
2 |
4 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sum of Column |
176 /105 |
17/2 |
14 |
19/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
Second, divide each element of comparison matrix by its Sum of Column.
|
Price |
Maintenance |
Horse-power |
Fuel consump3on |
|
|
|
|
|
Price |
105/176 |
10/17 |
7/14 |
12/19 |
|
|
|
|
|
Maintenance |
21/176 |
2/17 |
2/14 |
2/19 |
|
|
|
|
|
Horse-power |
15/176 |
1/17 |
1/14 |
1/19 |
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel consump3on |
35/176 |
4/17 |
4/14 |
4/19 |
|
|
|
|
|
Now sum of elements in each column is 1.
The matrix is normalized (distributive normalization).
Third, calculate arithmetic mean in each column (we use approximated method II, see Slide 25)
|
Price |
Maintenance |
Horse-power |
Fuel consump3on |
Priority Vector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Price |
0.59 |
0.59 |
0.50 |
0.63 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maintenance |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.14 |
0.11 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Horse-power |
0.09 |
0.06 |
0.07 |
0.05 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel consump3on |
0.20 |
0.23 |
0.29 |
0.21 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
With respect to the goal, Price is the most important criterion with importance 58%, Fuel consumption is the second important factor with importance 23%, it is followed by Maintenance with 12%, and the least important criterion
is Horse power with 7%.
Sum of all elements of the priority vector is 1.
Fuel |
Car A |
Car B |
Car C |
Priority |
cons. |
|
|
|
Vector |
|
|
|
|
|
Car A |
1 |
1/4 |
1/7 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
|
|
Car B |
4 |
1 |
1/3 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
|
|
Car C |
7 |
3 |
1 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise: Outsourcing Partner Selection
|
Vendor A |
Vendor B |
Vendor C |
|
|
|
|
Supplier's |
130 |
150 |
110 |
suggested price, |
|
|
|
euro |
|
|
|
Distance, km |
12,000 |
3,500 |
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
Organizational |
good |
excellent |
satisfactory |
behavior |
|
|
|
Adaption with |
complete |
partial |
complete |
the purchaser‘s |
|
|
|
procedures |
|
|
|
Based on the information above, which vendor is the most preferred (using the AHP)?
Step 3: Calculate local priorities…
Step 4: Estimate inconsistency of provided judgments
An important step in the AHP is to measure consistency of judgments that the decision maker provided during his/her pairwise comparisons.
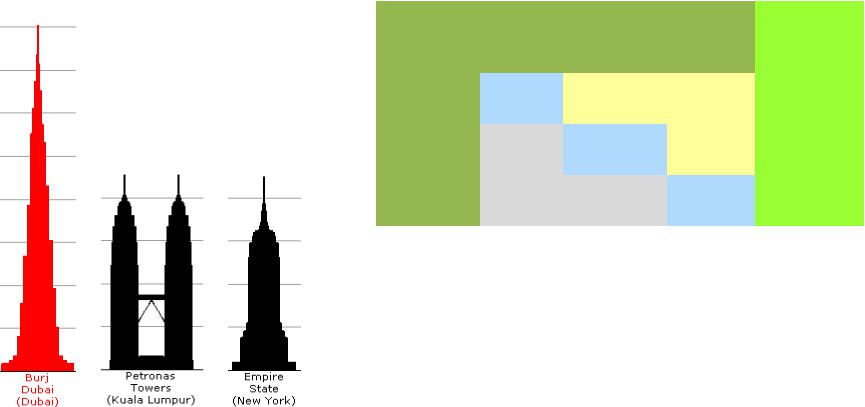
Example: Inconsistent comparison of tower heights
|
Burj |
Petronas |
Empire |
Priority |
Height |
Dubai |
Towers |
State |
Vector |
|
|
|
|
|
Burj Dubai |
1 |
2 |
2 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
|
|
Petronas |
1/2 |
1 |
4 |
0.38 |
Towers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Empire State |
1/2 |
1/4 |
1 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
Consistency Ratio = 0.19
Consistency Ratio exceeding 0.1 indicates inconsistent judgments. In such cases, the decision maker should revise his/her judgment values in the comparison matrix.
