
202___
.pdf
I. Information for study.
Decision Making in Business
Unit 11
I. Information for study.
Decision Making in Business
Text A
Прочитайте следующую информацию и запишите ос- новные термины, связанные с тематикой текста.
Businesses are DECISION MAKING units. The decisions that they make might include:
what to produce;
where to locate the premises;
what method of production to use;
what price should be charged;
what wages should be paid;
and many others.
Why do businesses make decisions? In each case above there are a number of choices a firm may make. For example, the choice might be to locate a new warehouse in Exeter, Plymouth or Torquay. This is an example of a strategic decision because it can affect the profitability and survival of the business. Many of the day-to- day decisions taken by business are called tactical decisions. An example might be when and how much stock to order or the setting of sales targets. These short term control decisions are often repeated on a regular basis. A business may also make longer term control decisions, such as planning to employ extra workers in future to take changes in the economy into account.
Decisions made by firms often involve some risk. Strategic decisions are likely to involve the most risk. For example, the decision to sell a new product in a foreign country involves great risk as there are many factors that can affect its success.
91

Английскийязык.
Лексические основы чтения текстов по экономике
Owners, managers and employees are involved in business activity. They will all make some decisions, although not of equal importance. Major decisions, such as the location of a new plant, will be maid by the owners. Less important decisions, such as the amount of time spent waiting for a delivery before making an enquiry, are likely to be maid by employees.
The size of the business can affect who makes decisions. In a small firm the owner will make most of the decisions because he or she is the person in control. Some decisions might be delegated if the owner trusts the employees. As a small firm expands, the owner might employ a manager to help run the business and take some responsibility for decision making. In very large businesses decisions are made at many different levels, by different people.
Decisions are often classified into three types.
Policy decisions. These are decisions about the general direction and overall policy of the business. They might be the decision to buy another company, the closure of a plant making a loss, or whether or not to launch a new product. These decisions are the responsibility of the board of directors, who control the business on behalf of the shareholders. In small firms policy decisions are made by the owner, although such decisions are likely to be smaller, such as the opening hours of a local store.
Management decisions. Management decisions or executive decisions determine how policy decisions are carried out. An example of such a decision might be deciding the best way to close a loss making branch. For example, should it be closed immediately, gradually, over period of time? Should the closure be negotiated or enforced? Could a management buy-out be considered? Management decisions should ensure that the policy decisions are carried out as efficiently as possible according to the general objectives of the company. Some management decisions might be taken by directors since some directors are also managers in the business.
Administrative decisions. Administrators are often office staff or supervisors, they act according to general company policy and under the direction of management. They will have responsibility for a number of tasks. These may require lower level decisions to be made such as the amount of time allocated to specific tasks or the
92
I. Information for study. Decision Making in Business
choice of equipment. It is sometimes argued that the performance of employees can be improved by letting them become involved in decision making. This is said to improve motivation.
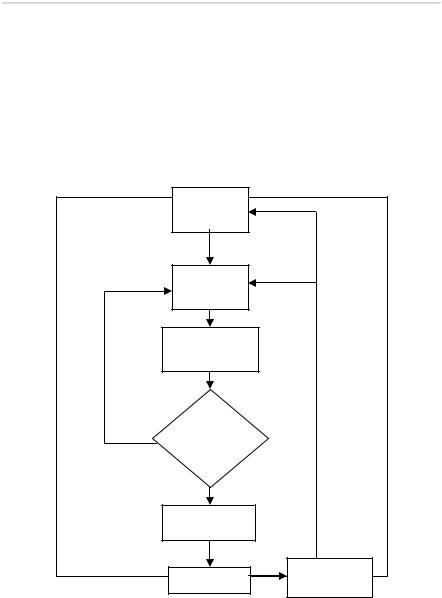
A business makes decisions in order to achieve objectives. For example, it might decide to launch a new product in order to diversify. Decisions are made at all levels in a business and it is useful to have a flexible process which can be followed by all involved. Figure 1 shows the stages in the decision making process.
Figure 1. The decision making process
Identify |
|
objectives |
|
Collect |
|
information |
|
and ideas |
|
Analyse |
|
information |
|
and ideas |
|
Choose a |
|
course of |
|
action |
|
Communicate |
|
and carry out |
|
Outcome |
Evaluate |
and report |
93

Английскийязык.
Лексические основы чтения текстов по экономике
II.Practice
1.Переведите текст на русский язык, используя словарь в конце урока.
2.Найдите в тексте ответы на поставленные вопросы и за- пишите их.
1)Why do businesses make decisions?
2)What is the difference between strategic and tactical decisions?
3)Who makes major decisions in business?
4)What kind of decisions are usually made by employees?
5)What kind of decisions are called policy decisions?
6)Give an example of a management decision. By whom is it taken?
7)Who may take administrative decisions?
8)Enumerate the stages of the decision making process.
3.К выделенным жирным шрифтом словам в тексте под- берите слова, противоположные по значению, из следующего списка:
profitable, rigid, failure, to agree, long term, to neglect, to dismiss, strategic, minor, specific, employee
4. Найдите в тексте предложения, соответствующие по смыслу данным ниже, и запишите их.
1)Решение продавать новую продукцию в зарубежные странысвязаносбольшимриском.
2)Стратегические решения влияют на рентабельность предприятия.
3)В маленькой компании большинство решений обыч- но принимает владелец.
4)При расширении фирмы владелец иногда нанимает управляющего, который принимает на себя ответст- венность за принятие решений.
94

I. Information for study.
Decision Making in Business
5)Политические решения принимает совет директоров, который руководит предприятием от имени акцио- неров.
6)Управленческие решения должны обеспечивать как можно более эффективное выполнение политических решений в соответствии с общими целями компании.
7)Иногда говорят, что служащие будут лучше работать, если дать им возможность участвовать в принятии решений.
8)Решения принимаются на всех уровнях компании.
9)Повседневные решения, которые принимаются на предприятии, называются тактическими решениями.
10)Самые важные решения, например, решение о раз- мещении нового завода, принимаются владельцем.
5.Образуйте существительные от данных глаголов. Пере- ведите их.
to produce, to locate, to survive, to employ, to direct, to close, to execute, to motivate, to supervise, to own
6. Образуйте наречия от данных прилагательных. Переве- дите их.
immediate, gradual, efficient, equal, general, large, short, local
7. Изложите краткое содержание текста А на английском языке в письменном виде.
III. Vocabulary to Text A
to argue
board of directors branch
buyout to carry out closure
--оспаривать, возражать
--совет директоров
--филиал
--выкуп доли в предприятии
--выполнять
--закрытие
95

Английскийязык.
Лексические основы чтения текстов по экономике
dayto- day |
-- |
повседневный |
decision making |
-- |
принятие решений |
to delegate |
-- |
поручить, передать полномочия |
delivery |
-- |
доставка |
to diversify |
-- |
разнообразить |
to employ |
-- |
принять на работу, нанять |
employee |
-- |
служащий |
to enforce |
-- |
принудить, заставить |
enquiry |
-- |
запрос |
executive |
-- |
руководитель |
to expand |
-- |
расширяться |
extra |
-- |
дополнительный |
flexible |
-- |
гибкий |
gradually |
-- |
постепенно |
to launch |
-- |
запустить в производство |
level |
-- |
уровень |
likely |
-- |
вероятный |
to locate |
-- |
разместить |
location |
-- |
местоположение, размещение |
long term |
-- |
долгосрочный |
loss |
-- |
убыток |
management |
-- |
управление, руководство |
to negotiate |
-- |
вести переговоры |
objective |
-- |
цель |
official staff |
-- |
конторский персонал |
performance |
-- |
работа, производительность труда |
policy |
-- |
политика |
premises |
-- |
производственные помещения |
profitability |
-- |
рентабельность |
responsibility |
-- |
ответственность |
shareholder |
-- |
акционер |
stage |
-- |
стадия, этап |
stock |
-- |
запас |
supervisor |
-- |
контролер |
survival |
-- |
выживание |
to take into |
-- |
принимать в расчет |
account |
|
доверять |
to trust |
-- |
96
I. Information for study. Decision Making in Business
IV. Test
1. Выберите из колонки справа по смыслу слова, пропу- щенные в предложениях.
1) |
The choice might be to … a new warehouse |
a) |
behalf |
|
in Exeter, Plymouth or Torquay. |
b) |
decisions |
2) |
It might decide to … a new product in or- |
c) |
launch |
|
der to diversify. |
d) |
locate |
3) |
The size of the business can affect who |
e) |
profit |
|
makes … . |
f) |
performance |
4) |
An example of such a decision might be |
g) |
policy |
|
deciding the best way to close a … making |
h) |
management |
|
branch. |
i) |
survival |
5) |
A strategic decision can affect the profitabil- |
j) |
loss |
|
ity and … of the business. |
k) |
expands |
6)As a small firm …, the owner might employ a manager.
7)The board of directors controls the business on … of the shareholders.
8)In small firms … decisions are made by the owner.
9)Some … decisions might be taken by directors who are also managers in the business.
10)The … of employees can be improved by letting them become involved in decision making.
2.Выберите существительные, которые по смыслу могут следовать за данными глаголами.
1) to employ |
a) owners |
|
2) to locate |
a) products |
|
||||
|
b) workers |
|
|
b) profits |
|
c) shareholders |
|
|
c) premises |
3) to carry out |
a) decision |
|
4) to launch |
a) a product |
|
b) discussion |
|
|
b) a process |
|
c) depreciation |
|
|
c) a price |
5) to improve |
a) preference |
|
|
|
|
b) performance |
|
|
|
|
c) consequence |
|
|
|
97
Английскийязык.
Лексические основы чтения текстов по экономике
3. Выберите из приведенного списка термины, соответст- вующие данным определениям.
1) |
waste resulting from losing |
a) |
to buy out |
2) |
a decision between alternative goods |
b) |
to charge |
3) |
a course of action adopted by govern- |
c) |
to employ |
|
ment, party, etc |
d) |
choice |
4) |
a person employed for wages |
e) |
loss |
5) |
body of persons carrying on work under |
f) |
policy |
|
manager |
g) |
staff |
6) |
to confer with view to compromise or |
h) |
to negotiate |
|
agreement |
i) |
employee |
7)to demand a price for a good or a service
8)to keep a person in one's service
9)to pay a person to give up his or her property
98

The most often used affixes
The most often used affixes
(Список наиболее употребительных аффиксов)
|
Суффиксы |
|
|
Префиксы |
|
||
сущест- |
прила- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
витель- |
гатель- |
глаголов |
наре- |
|
|
|
|
ных |
ных |
|
чий |
|
|
|
|
er |
ic |
ate |
ly |
be |
con |
contra |
in |
or |
ical |
ise |
ward |
de |
in |
ultra |
un |
|
|
( ize) |
|
|
|
|
|
ist |
able |
fy |
|
re |
en |
super |
non |
ment |
ible |
en |
|
pre |
sub |
over |
dis |
ent |
ory |
|
|
se |
ob |
under |
mis |
ance |
ary |
|
|
per |
dis |
counter |
|
ence |
ent |
|
|
pro |
ex |
multi |
|
ity |
ant |
|
|
for |
abs |
inter |
|
age |
ous |
|
|
|
trans |
macro |
|
ion |
ive |
|
|
|
|
micro |
|
ure |
ful |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ness |
less |
|
|
|
|
|
|
th |
ed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ing |
ing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
99

Английскийязык.
Лексические основы чтения текстов по экономике
Tapescripts
(тексты, записанные на кассете)
Unit 1
Text B
This morning we're going to start looking at the second of the three economic issues I mentioned last week. The first you have already read something about, so let's turn to the second. That is the question of income. By that I mean income distribution, the way in which income – that's what people earn – is distributed or shared around.
Let's look at income more closely. You, and your family, have an income. You have an annual income, that is what you earn in a year. This income allows you to enjoy various goods and services. It means you have a certain standard of living. Your standard of living, of course, includes what you think of as necessary to your life, things like food, water, somewhere to live, health and education. But your income doesn't just cover the necessities of life. It also includes recreation, whether that's sport or TV, or a holiday. Now, as you know, your income will be less than that of some of your neighbours, but it will be more than that of some of your other neighbours. By your neighbours, I mean not just people living in your own country, but also people living in other countries.
Now, just as you and your family have an income, so nations, different countries, also have an income – the national income, it's often called. Now a national income is not the money the government gets. The national income is the sum total of the incomes of all the people living in that country, in other words, everyone's income added together. In the same way we can think of world income as the total of all the incomes earned by all the people in the world.
I want now to look at the distribution of world income, and of national income. Then we can ask the questions: who, in the world, gets what share of these incomes? The distribution of income, either in the world or in a country, tells us how income is
100
