
1.Grammar_Book_Intermediate
.pdf
GRAMMAR BOOK
 Intermediate
Intermediate
englishdom.com

Lesson 1 |
R e v i s i o n o f |
t e n s e s |
|
|
2 |
|
Lesson 2 |
P r e s e n t t e n s e s ( S i m p l e , C o n t , S t . v e r b s ) |
3 |
||||
Lesson 3 |
P a s t t e n s e s |
( S i m p l e , P e r f e c t , |
P e r f e c t C ) |
4 |
||
Lesson 4 |
P a s t t e n s e s |
2 |
( C o n t , P e r f e c t , |
P e r f e c t C ) |
5 |
|
Lesson 5 |
F u t u r e f o r m s 1 |
|
|
6 |
||
Lesson 6 |
F u t u r e f o r m s 2 |
|
|
7 |
||
Lesson 7 |
P a s s i v e f o r m s |
|
|
8 |
||
Lesson 8 |
C o n d i t i o n a l s |
p a r t |
1 |
|
9 |
|
Lesson 9 |
C o n d i t i o n a l s |
p a r t |
2 |
|
10 |
|
Lesson 10 |
O t h e r c o n d i t i o n a l |
f o r m s |
|
11 |
||
Lesson 11 |
R e p o r t e d s p e e c h p a r t 1 |
|
12 |
|||
Lesson 12 |
R e p o r t e d s p e e c h / e m b e d d e d q u e s t i o n s |
13 |
||||
Lesson 13 |
G e r u n d s / i n f i n i t i v e s |
|
14 |
|||
Lesson 14 |
M o d a l s i n t h e p a s t |
|
16 |
|||
Lesson 15 |
P h r a s a l v e r b s |
|
|
|
17 |
|
Lesson 16 |
P r e p o s i t i o n a l |
p h r a s e s |
|
18 |
||
Lesson 17 |
I d i o m s |
|
|
|
|
20 |
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free |
2 |
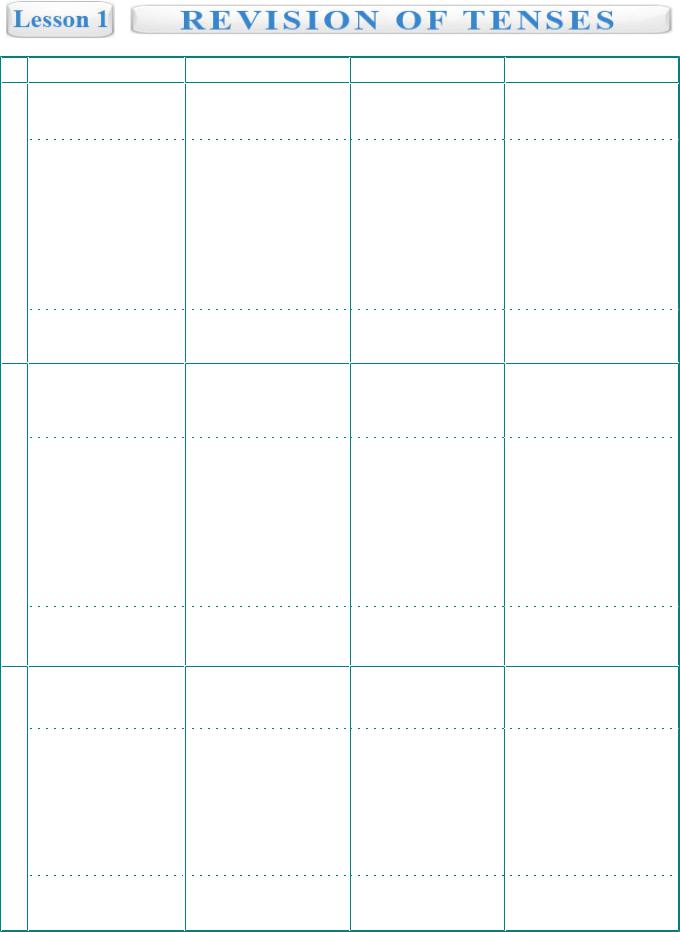
Simple |
Continuous |
Perfect |
Perfect Continuous |
|
1) |
It's happening now |
An action has happened |
An action started in the |
|
A regular action 2) |
Talking about plans |
by now |
past, but have |
|
3) |
Today |
continued till now |
||
|
P
R |
V (s)/1st form (s) |
am / is / are + V ing |
E |
|
|
S |
+ He goes to work |
+ He is going to work |
E |
- He doesn’t go to work |
- He is not going to work |
N ? Does he go to work |
? Is he going to work |
|
T |
|
|
|
Always | usually |
Now | at the moment | |
|
sometimes | every day |
at 5 o'clock | next week | |
|
from time to time |
today |
|
An action finished |
A long action in |
|
at a specific |
the past at a particular |
|
time in the past |
moment |
have(s) + V3 |
have(s) + being + V ing |
+ He has gone to work |
+ He has been going |
- He hasn’t gone to work |
- He hasn’t been going |
? Has he gone to work |
? Has he been going |
Already | just | never | ever | since | by | yet
Something that happened before another action in the past
For 2 hours | for a long time | since that time | all month
Something started in the past and continued up till another time in the past
P |
Ved/V2 |
was/were + V ing |
had + V3 |
A |
|
|
|
S |
+ He went to work |
+ He was going to work |
+ He had gone to work |
T - He didn’t go to work |
- He wasn’t going to work |
- He hadn’t gone to work |
|
|
? Did he go to work |
? Was he going to work |
? Had he gone to work |
|
Last week | yesterday | |
At 5 o'clock yesterday | |
By last year | before |
|
month ago | long time |
while | when | at that |
another action | by 3 |
|
ago | from time to time |
moment |
o'clock yesterday |
|
An action that will |
A long action at a |
An action that will |
|
happen sometime in the |
particular moment |
happen by a particular |
|
future |
in the future |
moment or time |
had+ been+ V ing
+He had been going
-He hadn’t been going
?Had he been going
For a long time | since last year | till/until | all the month
A long action before some point in the future
F |
will+ V1 |
U |
|
T |
+ He will go to work |
U |
|
R |
- He won’t go to work |
E |
? Will he go to work |
|
Always | usually | sometimes | next summer | tomorrow
will be + V ing |
will+ have+ V3 |
+ He will be going to |
+ He will have gone to |
- He won’t be going to |
- He won’t have gone to |
? Will he be going to |
? Will he gone to |
At 5 o'clock tomorrow | |
By next year | before |
when | while | at that |
another action | by 3 |
moment |
o'clock tomorrow |
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free
will + have + been +V ing
+He will have been going
-He won’t have been going ? Will he have been going
For a few months | for 2 weeks | till next year
3
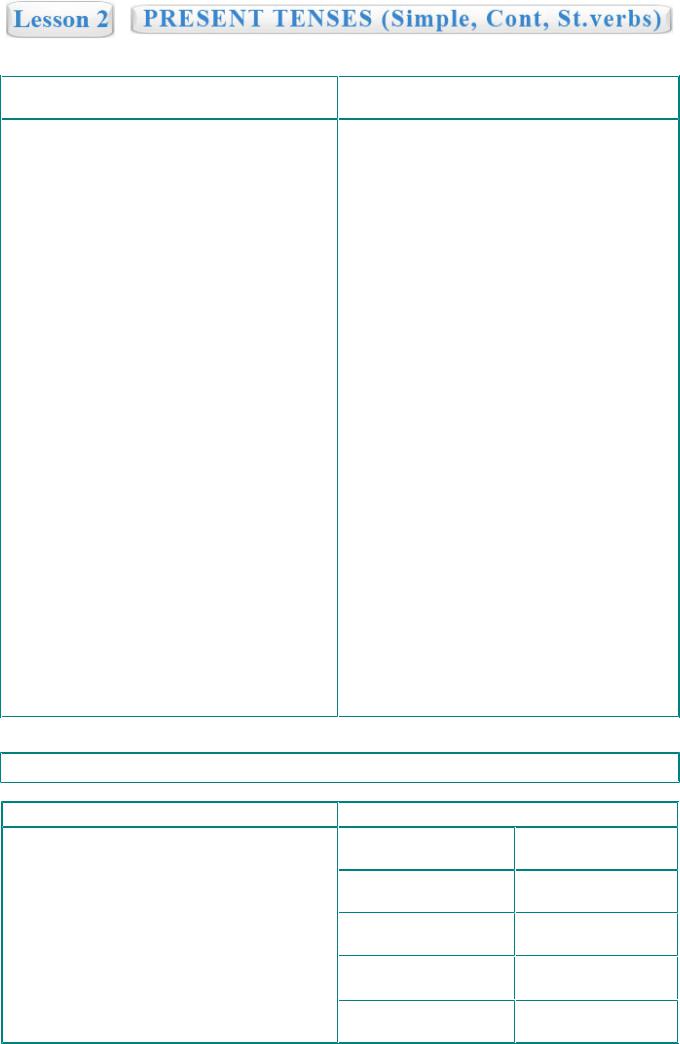
Present Simple
(V/1st form)
This tense is used for regular actions:
-He goes to work every day.
-She cleans her flat at the weekend.
-I go to English class every Monday.
For general truths:
-Children grow quickly.
-It snows in Alaska.
-People in America eat a lot.
For telling stories:
- A man goes to the doctor and says: “I have trouble falling asleep...”
For describing or commenting:
-Ronaldo takes the ball and scores!
-Mary sits near Pedro and starts talking...
For headlines in newspapers or magazines:
-The President decides to get married.
-A black lady gives birth to a white child!
To talk about future events in a schedule:
-The theatre opens on the 1st of September.
-The new show airs on Sunday.
After relative pronouns:
-The lady who sits next to me is my wife.
-I don't know why he likes his pink shirt.
With state verbs:
- An orange tastes awesome.
Present Simple Continuous
(am / is / are + V ing)
This tense is used for activities which are in progress at the moment:
-I'm waiting for you.
-He's still sleeping.
Something is in progress this week, month, year:
-Claire is taking Chinese courses this year.
-John is visiting the dentist this month.
For changing situations:
-It's getting colder.
-You're getting drunk.
For talking about appointed plans:
-I'm meeting Jeff after my classes.
-Mary is coming back on Tuesday.
With words such as "always" or "constantly" showing emphasis:
-He's always wearing this suit. I'm tired of it!
-Irina is constantly complaining about her boss!
With two or more actions which are happening at the same time:
- The sun is shining and the birds are singing, while I'm lying on the beach.
With some state verbs which mean actions:
- We're having lunch at the moment.
NO TA BENE
STATE VERBS
Appearance: appear, resemble, seem Composition: consist of, contain, have Connection: come from, concern, cost, fit, suit
Existence: be, exist
Knowledge: forget, know, realize, understand Likes and dislikes: dislike, hate, like, love, prefer Needs and wants: need, want, wish
Opinion: believe, doubt, imagine, suppose, think Possession: belong to, have, own, owe, posses Senses: feel, hear, notice, see, smell, sound, taste
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free
EXAMPLE
I have a car.
This cake smells tasty.
It feels cold today.
Your Mexican food tastes good.
He looks good in this shirt.
We’re having delicious barbecue now.
I’m smelling a new perfume.
Sam isn’t feeling good today.
We’re tasting a new dessert now.
We’re looking at him because he looks good.
4
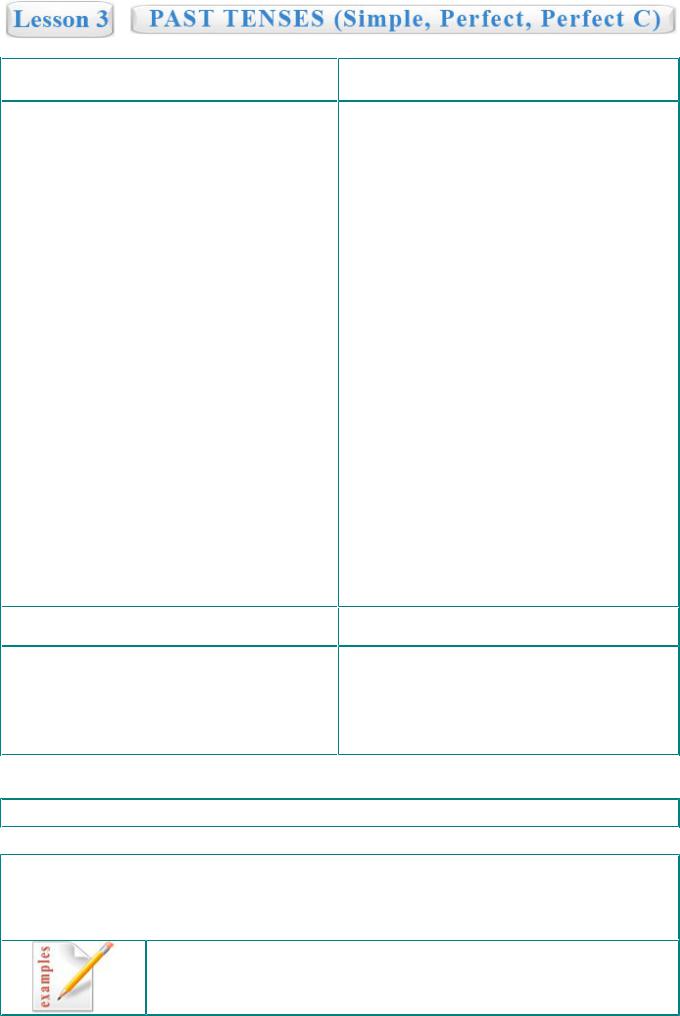
Past Simple |
Present Perfect |
(ed/V2) |
(have/has + V3) |
We use the Past Simple for repeated actions or past habits:
-I read the newspaper every morning.
-I liked to dance ballet when I was a little boy.
-We went to the zoo a long time ago.
We use the Past Simple to list a series of completed actions in the past:
- I went to McDonalds, ate my meal, and then I went to the cinema with my girlfriend.
With a period of time which has finished:
-I played baseball this morning. (It's evening now)
-We went to school in the afternoon. (It's night now)
With short actions using "when":
-I got up when my mom yelled at me.
-When we called Sally, she didn't pick up her
phone.
- I saw Peter when he broke his phone.
With a sub-clause in the same tense:
-As soon as I heard strange noise, I woke up.
-From the first time we met, I knew you were a
doctor.
Used to
To describe past habits which are not present anymore we also use "used to":
+We used to play basketball in the yard when we were kids.
- We didn’t use to play basketball in the yard … ? Did we use to play basketball in the yard …
We use the Present Perfect to say that an action happened at an unspecified time before now:
-I've been to London three times.
-My friend has changed his location ten times.
For periods of time which have not finished yet:
-I haven't seen his new baby yet.
-We've already visited three states in the USA. (We're still there)
-Jeff has done a lot today. (It is still today)
When the result is obvious now:
-Look, you've broken my new TV!
-Oh God, she's gotten so fat!
-The cook has put too much salt in this meal.
To talk about the change that has happened over a period of time:
-You've lost weight since I saw you the last time.
-She's divorced twice since we last met.
We often use the Present Perfect to list the accomplishments of individuals and humanity:
-Kristen has received her degree in Biology.
-Gary has been chosen as the new store manager.
Present Perfect Continuous
(have/has + been + V ing)
We use this tense to describe an action which is continuing up to the present:
-We've been choosing a present for Mary all day and we still can't decide what to get. (till now)
-Oh God, you look exhausted! - I’ve been running around the city all day! (till now)
NO TA BENE
The difference between the Past Simple and the Present Perfect:
The Present Perfect expresses the idea that something has happened by now and has links with the present. The Past Simple expresses the idea of an action which happened some time ago and doesn't have any connection with the present moment.
They liked to travel with their parents as they were children. (but not now) They have travelled a lot for the past couple of years. (till now)
Bill didn't ride a horse last year. (last year is over)
Bill hasn't ridden a horse yet. (never tried, but he still can)
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free |
5 |

Bill has been riding a horse all day. (he’s still riding)
Past Continuous |
Past Perfect |
(was/were + V ing) |
(had + V3) |
When both actions were happening at the same time
-I was working while they were eating.
-She was singing a song while waiting for him.
-Sam was having a party while Ann was waiting
for his call.
The Past Continuous is used to show that a longer action in the past was interrupted:
-She was cooking a dinner when he came.
-You were sleeping when I spoke to you.
-She was dancing when I saw her.
With a particular moment in the past:
-I was preparing for my exam at midnight.
-Chet was having a lection at 5 yesterday.
With temporary situations in the past:
-At that time I was studying at school.
-She was planning to enter the college.
For background information in a story:
- It was raining hard and people were getting home after work.
For annoying habits in the past:
-As a kid Jane was always teething me.
-As I remember her, she was always eating.
Changing and developing situations in the past:
-I was getting angry with my Internet so I decided to change it soon.
-Ben was getting fatter and fatter, nobody could control it.
Completed actions before the moment in the past:
-Mary had done a lot before she left her work.
-This movie had already become old when we finally decided to watch it.
We use the Past Perfect to describe situations which happened before the past:
-I had bought a nice laptop before you gave me your old one.
-Had you finished your work before we picked you up?
With series of actions before the moment in the past:
- Before Adam moved to a new house he had gotten married, had changed his job and had earned a lot of money.
Completed actions in the past which have results now:
-I adore this game because I had played it with my parents as a child.
-Tom is professional in poker; he had spent all his life for doing this.
Past Perfect Continuous
(had + been + V ing)
We use this tense to describe actions continuing up to the moment in the past:
-Gary had been moving all his life until he found his perfect place to live.
-He had been struggling with this game before
he finally won.
NOTA BENE: The Past Perfect emphasizes completion (or the result of a completed action) while the Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes the duration or activity of an action.
Jeff had been searching the Internet until he realized it's time to sleep. (not completed action)
He had done a lot before he went to bed. (completed action)
Mike had been working for five years before the new boss came. (not completed action, maybe he still works)
Mike had progressed in his career before the new boss came. (completed action)
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free |
6 |
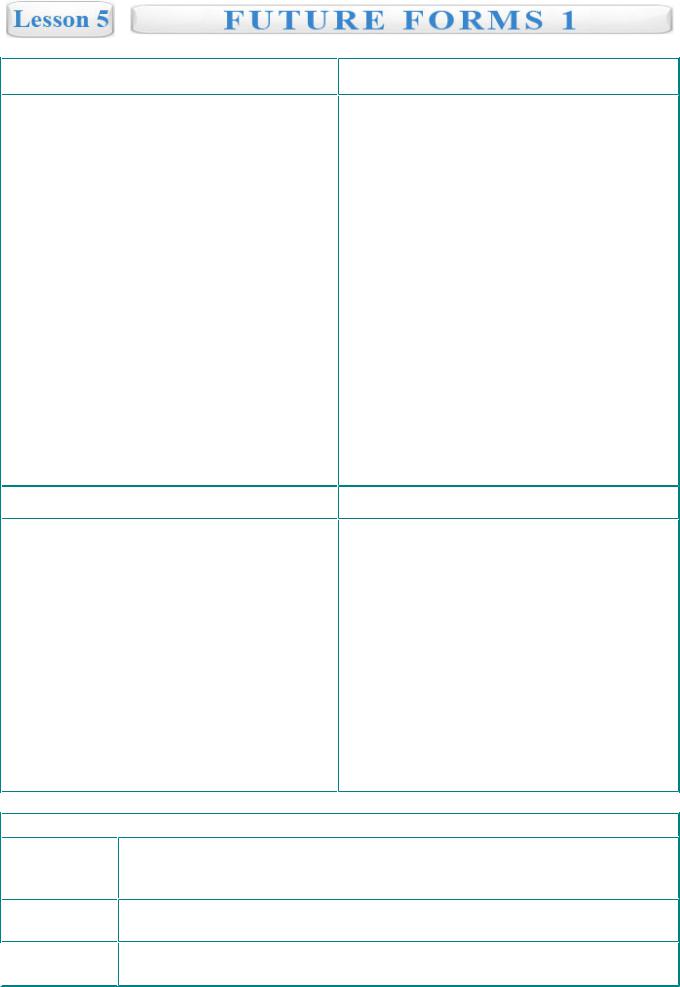
Future Simple |
Present | Future Continuous |
We use will in the Future Simple with general predictions:
-If you eat so much chocolate you will feel sick.
-You will miss the play if you don't hurry up.
With an immediate decision:
-I will finish my work and call you.
-By the way, she will stay with us tonight.
For making promises:
-I'll pick you up, don't worry.
-Will you marry me?
In combination with time clauses:
-When I arrive I will give you a call.
-She will make you a sandwich after you clean your room.
To be going to
"To be going to" is used with a personal intention:
-I'm going to go out tonight.
-My friends are going to move soon.
With distant future intentions:
-Ben is going to study French sometime.
-Hazel is going to be a good mother in a future.
For future predictions based on physical (usually visual) evidence:
-Look! The clouds are grey. It is going to be rain.
-Be careful! You're going to spill your tea on my new laptop!
We use the Present Continuous for planned or personally scheduled events:
-We're having a party tomorrow at 7 o'clock.
-She is meeting her lawyer after work.
We use the Future Continuous with an action in a progress some time in a future:
-I'll be sleeping all day tomorrow.
-Gary will be playing cards all evening tonight.
With an action which will be happening during a period of time in the future:
-Kate will be cleaning her flat until she gets tired.
-Mike will be searching the internet before his mom comes back home.
An action which will happen because it's regular or decided:
- We'll be seeing John tomorrow as usually and will thank him for the present.
To be | due to | about to
With official order or arrangement we use
"to be + infinitive":
-We're to start the ceremony tonight.
-He's to be given a bonus.
-You're to stay here until you apologize.
With a short time we use due to or about to:
-Sonya is about to cry, she's very disappointed.
-I'll call you back, I'm about to leave my home.
-We're due to meet in 30 minutes.
When + will
If + will

 Will = please
Will = please
englishdom.com |
NO TA BENE
We don't use will after time clauses as when, as soon as, before...
Example: When I will see you – incorrect! When I see you I will give you a present. - correct
In conditional clauses we use will in second clause without if:
Example: If he will come – incorrect! If he comes we will be very glad. - correct
In this case will means to be willing to:
Example: If you will hold my bag, I can open the door. (Can you hold my bag, please?)
feel english & feel free |
7 |
Future Continuous |
Future Perfect |
(will+ to be + V ing) |
(will + have + V 3) |
The Future Continuous is used for actions which will happen because they are decided:
-I'll be doing yoga tomorrow at the same time.
-Sam will be visiting her dance class all year.
-Karen will be visiting the hairdresser next Tuesday as usually.
An activity which will happen during some period of time in the future:
-We'll be studying here for six months.
-Jane will be cleaning her room all day.
-Mike will be playing games while you'll be cooking dinner.
With an action at some particular moment in progress in the future:
-Don't call me at this time. I'll be taking a nap.
-We'll be playing baseball when you finish work.
-I'll be sunbathing in the Maldives when you call me.
Habits or repeated actions in the future:
-I think more and more people will be doing Internet shopping in the future.
-Sally will be studying more and more every year.
-Children will be getting fatter eating fast food all the time.
We use the Future Perfect with an event which will happen before a specified time in the future:
-I'll have finished doing my homework by the time you come back home.
-Jack will have lost his job by the end of this week.
Continuing situations up to a certain time:
-This time next year I'll have worked here for 10 years.
-By 2050 Gary and Mary will have been married for 50 years!
-We'll have eaten all of the food by the time they come here.
We use the Future Perfect Continuous in the same situations, but when we want to emphasize the duration:
-By 2050 Mary and Gary will have been living together for 50 years.
-This time next year I'll have been working here for 10 years.
-I'll have been teaching for twenty years this summer.
NOTA BENE!
With time words such "as when, as soon as, once" we use the Present Perfect (Continuous):
-I'll give you a pay raise as soon as you have proved that you're a hard-worker.
-I won't give you a pay raise until you've been working here for two years.
-When you have finished your report, I'll let you go.
We'll be doing laundry at the same time tomorrow. (Future Continuous)
He'll be working tomorrow anyway, so don't even invite him out. (Future Cont.) Sam will have repaired his car by the time we cook a dinner. (Future Perfect) We'll have been married for ten years by 2020. (Future Perfect)
I'll praise you as soon as you will have your homework done. (Future Perfect)
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free |
8 |
Usage of passive forms
In passive sentences the subject is not the agent (doer) of the verb:
Somebody stole my purse. (Active) My purse was stolen. (Passive)
Normally the doer is not included in a passive sentence because it's not important:
Several people were injured in the explosion. The documents were lost.
The passive is used with a -by phrase only if it's important who performs an action:
Othello was written by Shakespeare.
This picture was drawn by my grandfather. The pizza was delivered by the delivery man.
Nota bene: If we know who performs the action we usually use the active:
Rose made such a wonderful house. Skipper gave me the nicest present!
The passive infinitives are often used after modal verbs:
It could be done by anyone.
He really should be given another opportunity.
General statements:
English can't be learnt without practice.
The house can't be sold without his permission.
To make the statement impersonal:
This work can't be completed by this evening. This request wasn't made by me.
The contract wasn't signed by any of us.
Passive forms
The Present Simple:
Active: I help my mother.
Passive: My mother is helped by me.
The Past Simple:
Active: I wrote this book.
Passive: This book was written by me.
The Future Simple:
Active: We'll finish the project next week. Passive: The project will be finished next week.
The Present Continuous:
Active: I'm writing the report.
Passive: The report is being written by me.
The Past Continuous:
Active: We were opening the door. Passive: The door was being opened by us.
The Present Perfect:
Active: I have done my work for today. Passive: My work for today has been done.
The Past Perfect:
Active: I had done my work before he came. Passive: My work had been done before he came.
The Future Perfect:
Active: I will have done my work. Passive: My work will have been done.
To be going to:
Active: They are going to change the title soon. Passive: The title is going to be changed soon.
Modal verbs:
Active: You must do homework tonight. Passive: The homework must be done tonight.
NO TA BENE
The Perfect The road will have been being built by the end of the month. – incorrect Continuous The road will have been built by the end of the month. – correct
The Future I'll be washing my car at 6 o'clock tonight. – common Continuous: My car will be being washed at 6 o'clock tomorrow. – not used often
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free |
9 |
Conditional 0 |
Conditional 2 |
(If + Present Simple) |
(If + Past Simple + would + V1) |
We use zero conditional to express general truth:
Water freezes if the temperature is 0.
If you don't sleep enough, you feel tired all day. If you want to travel abroad, you need an international passport.
For habitual activities or repeated situations:
If I don't have breakfast, I'm starving all morning. If she is not ready, she skips the lessons.
We get home late if we miss the bus.
Conditional 1
(If + Future Simple)
We use the first conditional to express a possible/real situation in the future:
If I see him, I'll tell him hello.
If it rains outside, we won't go to the cinema. If I miss my train, I'll give you a call.
Normally we don't use "if +will" together:
If it will rain we'll stay at home. – incorrect If it rains we'll stay at home. – correct
If I'll see him I will ask his e-mail. – incorrect If I see him I'll ask his e-mail. – correct
Exception: we use "if + will" with polite requests:
If you'll help with my homework, I'll cook dinner for you.
If she'll pick up our laundry, we'll be really thankful. If you'll carry my bag, I'll walk quicker.
We use the second conditional to talk about unreal situations in future:
If I were taller, I would become a model.(But I'm not) If he had money, he would go abroad.(But he doesn't) If he lost his wife, he would be sad.
We use the structure "if I were you" to give advice:
If I were you, I would change this hairdo. If I were you, I wouldn't move anywhere. If I were you, I would get revenge.
After expressions suggesting doubts or uncertainty:
I would be surprised if he didn't marry her.
It would be strange if they forgot about our meeting. It wouldn't be strange if they lost their key again.
I wouldn't be surprised if he was late again.
Nota bene:
Notice that in unreal situations we say "if I were" instead of "if I was"
Conditional 3
(If + had + V3, would have + V3)
To talk about unreal situations in the past:
If he hadn't ridden his bike, he wouldn't have broken his arm that night.
If you hadn't worked all night, you wouldn't have overslept!
If I had known this, I wouldn't have called you.
englishdom.com | feel english & feel free |
10 |
