
- •Bioinformatics
- •We all know that elephants only give birth to little elephants, giraffes to
- •Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA
- •DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with
- •The DNA strand is made of letters ATGCTGGAATAAATGTCAATTTGA
- •The complete DNA instruction book, or genome, for a human contains about 3
- •Gene
- •Proteins
- •Ribonucleic acid, RNA
- •The journey from gene to protein is complex and tightly controlled within each
- •Make Research. Be successfull
- •Major research areas
- •Sequence analysis
- •Genome annotation
- •Literature analysis (data mining)
- •Analysis of gene expression
- •Analysis of regulation
- •Analysis of protein expression
- •Analysis of mutations in cancer
- •Comparative genomics
- •Modeling biological systems
- •High-throughput image analysis
- •Do not do this!!!
- •References

 Lecture #1
Lecture #1

Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is conceptualizing biology in terms of molecules and then applying “informatics” techniques (derived from disciplines such as applied math, Computer Science and statistics) to understand and organize the information associated with these molecules, on a large scale
It generates new knowledge that is useful in such fields as drug design, genome, cancer e.t.c.

We all know that elephants only give birth to little elephants, giraffes to giraffes, dogs to dogs and so on for every type of living creature. But why is this so?
Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary (passed by inheritance) material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA.
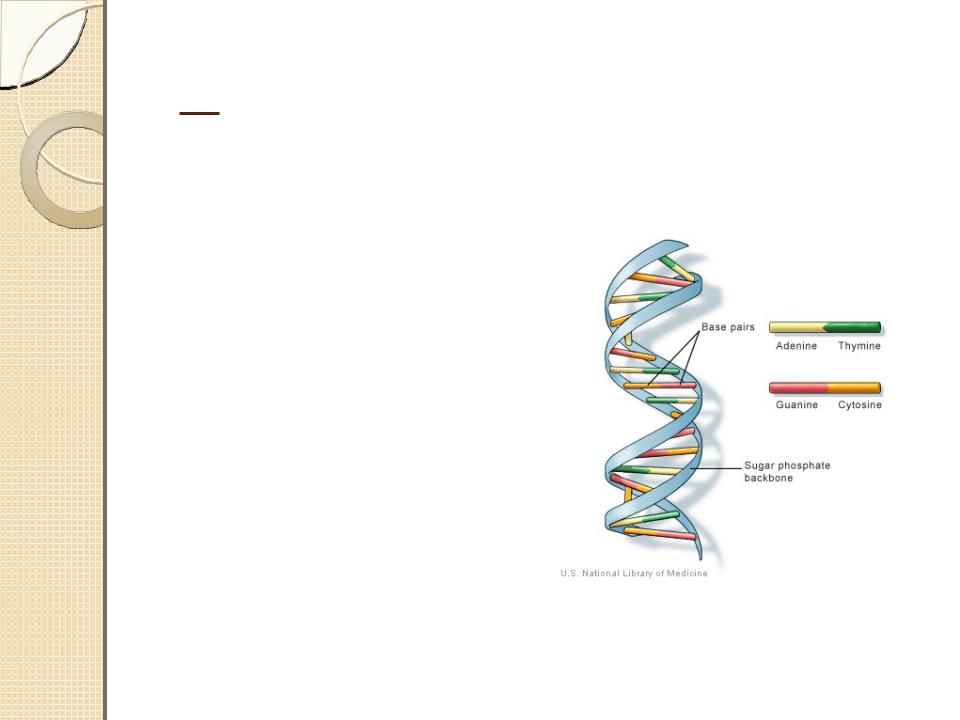
The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C),
and thymine (T).

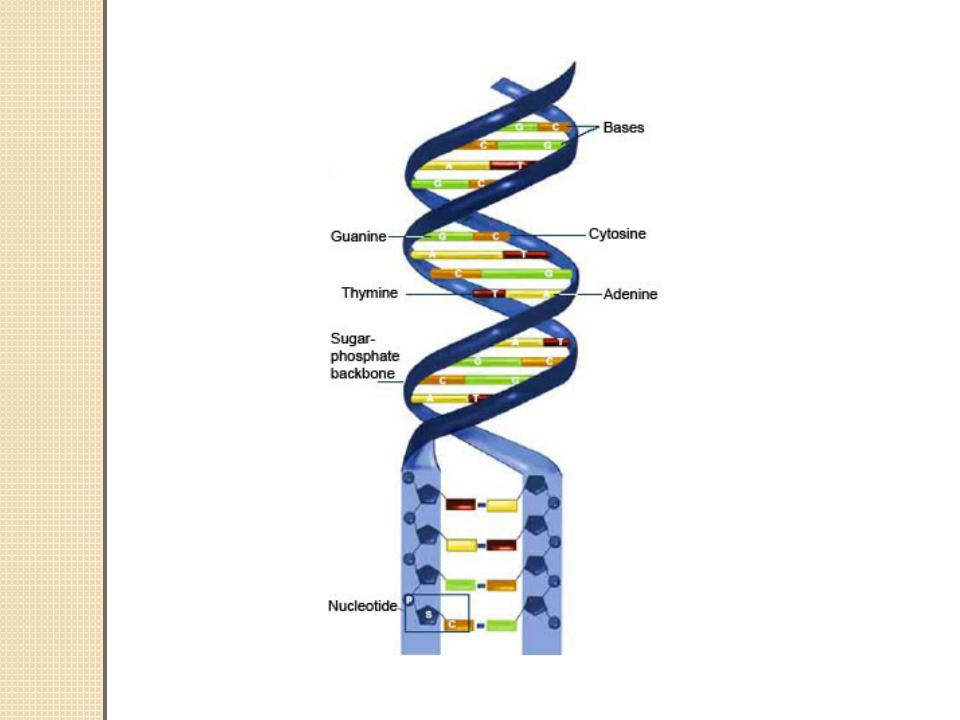
DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Together, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide.
Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a
spiral called a double helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat like a ladder, with the base pairs forming the ladder’s rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder.
An important property of DNA is that it can replicate, or make copies of itself. Each strand of DNA in the double helix can serve as a pattern for duplicating the sequence of bases. This is critical when cells divide because each new cell needs to have an exact copy of the DNA present
in the old cell.

The DNA strand is made of letters ATGCTGGAATAAATGTCAATTTGA
The letters make words
ATG CTC GAA TAA ATG TCA ATT TGA ATT TGA
The words make sentences
<ATG CTG GAA TAA> <ATG TCA ATT TGA>
These “sentences” are called genes. Genes tell the cell to make other molecules called proteins. Proteins enable a cell to perform special functions, such as working with other groups to make walking e.t.c

The complete DNA instruction book, or genome, for a human contains about 3 billion bases and about 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes.
The importance of DNA became clear in 1953 thanks to the work of James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. By studying X-ray diffraction patterns and building models, the scientists figured out the double helix structure of DNA - a structure that enables it to carry biological information from one generation to the next.
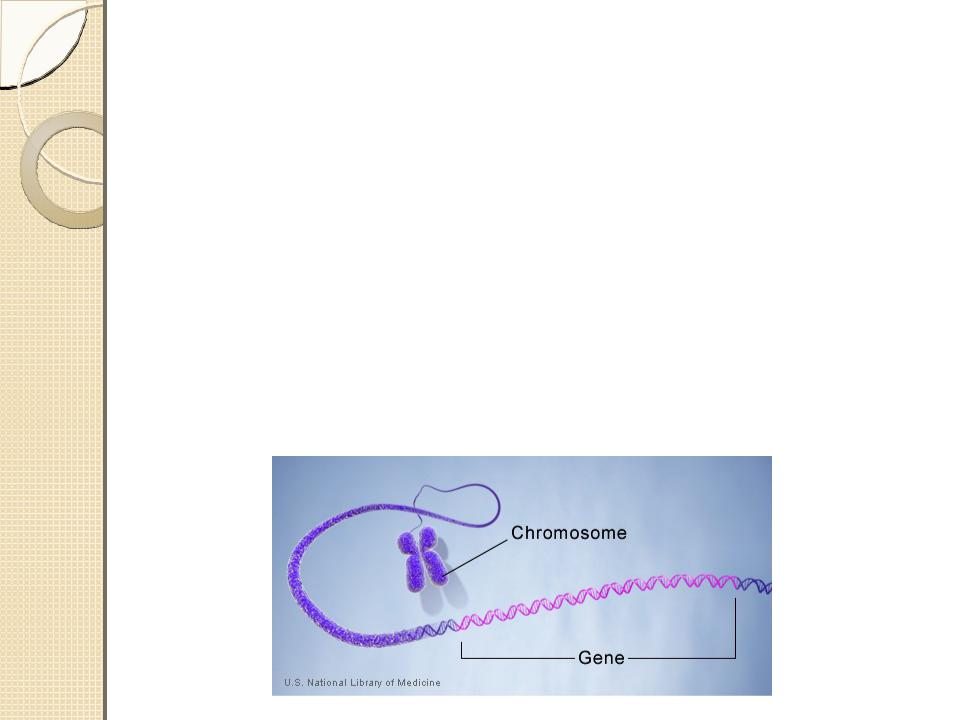
Gene
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredityGenes, which are made up of DNA.
Genes act as instructions to make molecules called proteins.
The Human Genome Project has estimated that humans have between 20,000 and 25,000 genes.
Every person has two copies of each gene.
Most genes are the same in all people, but a small number of genes are slightly different between people.

Proteins
Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body.
They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs.
Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains.
There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a protein.

Ribonucleic acid, RNA
RNA, which stands for ribonucleic acid, is also a long-chain molecule. The function of RNA is to translate the genetic material stored in DNA, into protein structures. RNA essentially carries out the instructions of DNA.
It differs from DNA in that it consists of a single chain of nucleotides. Another difference is that the sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose found in DNA. The bases in RNA are the same as in DNA except that the thymine (T), which appears in DNA, is replaced by another base called uracil (U), which links only to adenine (A).
