
Chapter09
.pdf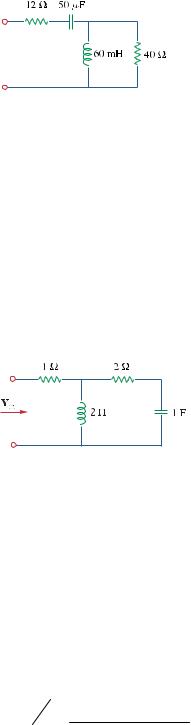
Chapter 9, Problem 56.
At ω = 377 rad/s, find the input impedance of the circuit shown in Fig. 9.63.
Figure 9.63
For Prob. 9.56.
Chapter 9, Solution 56. |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
50µF |
→ |
= |
= − j53.05 |
|||
jωC |
j377x50x10−6 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
60mH |
→ |
jωL = j377x60x10−3 = j22.62 |
||||
Zin =12 − j53.05 + j22.62 // 40 = 21.692 − j35.91 Ω |
|
|||||
Chapter 9, Problem 57.
At ω = 1 rad/s, obtain the input admittance in the circuit of Fig. 9.64.
Figure 9.64
For Prob. 9.57.
Chapter 9, Solution 57. |
|
|||||||
2H |
→ |
jωL = j2 |
|
|||||
1F |
→ |
1 |
= − j |
|
||||
jωC |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Z =1+ j2 //(2 − j) =1+ |
j2(2 − j) |
|
= 2.6 + j1.2 |
|||||
j2 + 2 − j |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Y = 1 |
Z |
= 0.3171− j0.1463 S |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
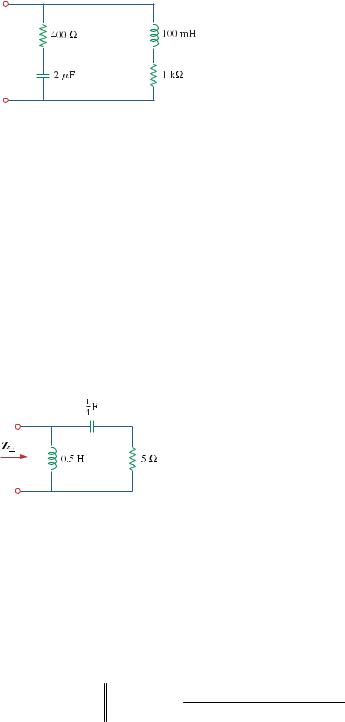
Chapter 9, Problem 58.
Find the equivalent impedance in Fig. 9.65 at ω = 10 krad/s.
Figure 9.65
For Prob. 9.58.
Chapter 9, Solution 58. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2µF |
→ |
|
1 |
|
= |
1 |
|
= − j50 |
|
|
jωC |
j104 x2x10−6 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
100mH |
→ |
|
jωL = j104 x100x10−3 = j1000 |
|
|||||
Zin = (400 − j50) //(1000 + j1000) = (400 − j50)(1000 + j1000) |
=336.24 + j21.83 Ω |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1400 + j950 |
|
|
Chapter 9, Problem 59.
For the network in Fig. 9.66, find Z in . Let ω = 10 rad/s.
Figure 9.66
For Prob. 9.59.
Chapter 9, Solution 59. |
1 |
|
1 |
|
|||
0.25F |
→ |
= |
= − j0.4 |
||||
|
jωC |
j10x0.25 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
0.5H |
→ |
jωL = j10x0.5 = j5 |
|||||
Zin = j5 (5 − j0.4) = (5 90°)(5.016 −4.57°) = 3.691 42.82°
6.794 42.61°
= 2.707+j2.509 Ω.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 60.
Obtain Z in for the circuit in Fig. 9.67.
Figure 9.67
For Prob. 9.60.
Chapter 9, Solution 60.
Z = (25 + j15) +(20 − j50) //(30 + j10) = 25 + j15 + 26.097 − j5.122 = 51.1+ j9.878Ω
Chapter 9, Problem 61.
Find Z eq in the circuit of Fig. 9.68.
Figure 9.68
For Prob. 9.61.
Chapter 9, Solution 61.
All of the impedances are in parallel.
1 |
= |
|
|
1 |
|
+ |
|
1 |
+ |
1 |
+ |
|
1 |
|
|
Zeq |
1 |
− j |
1+ j2 |
j5 |
1+ j3 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
1 |
= (0.5 + j0.5) +(0.2 − j0.4) +(-j0.2) +(0.1− j0.3) = 0.8 − j0.4 |
||||||||||||||
Zeq |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
1
Zeq = 0.8 − j0.4 = 1 + j0.5 Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 62.
For the circuit in Fig. 9.69, find the input impedance Z in at 10 krad/s.
Figure 9.69
For Prob. 9.62.
Chapter 9, Solution 62.
2 mH |
→ |
jωL = j(10 ×103 )(2 ×10-3 ) = j20 |
|||
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 µF |
→ |
jωC |
= j(10 ×103 )(1×10-6 ) |
= -j100 |
|
|
|
|
50 Ω |
j20 Ω |
|
|
|
+ + |
V |
− |
|
1 0° A |
Vin |
|
+ |
2V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
− |
|
|
|
-j100 Ω
V = (1 0°)(50) = 50
Vin = (1 0°)(50 + j20 − j100) +(2)(50)
Vin = 50 − j80 +100 =150 − j80
Zin = 1Vin0° = 150 – j80 Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 63.
For the circuit in Fig. 9.70, find the value of Z T .
Figure 9.70
For Prob. 9.63.
Chapter 9, Solution 63.
First, replace the wye composed of the 20-ohm, 10-ohm, and j15-ohm impedances with the corresponding delta.
z |
= |
200 + j150 + j300 |
= 20 + j45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
1 |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
z2 |
= |
|
200 + j450 |
|
= 30 − j13.333, z3 = |
200 + j450 |
=10 + j22.5 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
j15 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 Ω |
–j12 Ω |
|
–j16 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z2 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
Ω |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
ZT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
z3 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
Ω |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
–j16 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Now all we need to do is to combine impedances.
z2 |
|
|
|
(10 − j16) = |
(30 − j13.333)(10 − j16) |
= 8.721− j8.938 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
40 − j29.33 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
z3 
 (10 − j16) = 21.70 − j3.821
(10 − j16) = 21.70 − j3.821
ZT = 8 − j12 + z1
 (8.721− j8.938 + 21.7 − j3.821) = 34.69 − j6.93Ω
(8.721− j8.938 + 21.7 − j3.821) = 34.69 − j6.93Ω
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
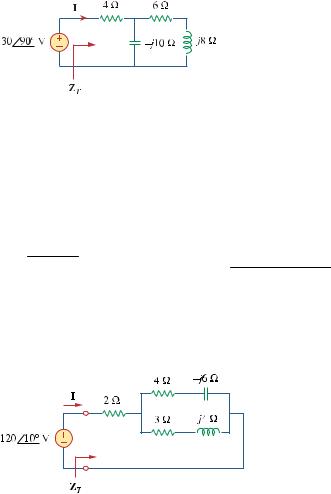
Chapter 9, Problem 64.
Find ZT and I in the circuit of Fig. 9.71.
Figure 9.71
For Prob. 9.64.
Chapter 9, Solution 64.
ZT = 4 + |
− j10(6 + j8) |
=19 − j5Ω |
|
|
6 − j2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
I = 30 90° = −0.3866 + j1.4767 =1.527 104.7°A
ZT
Chapter 9, Problem 65.
Determine Z T and I for the circuit in Fig. 9.72.
Figure 9.72
For Prob. 9.65.
Chapter 9, Solution 65.
ZT |
= 2 +(4 − j6) || (3 + j4) |
|||||
ZT |
= 2 + |
(4 − j6)(3 + j4) |
|
|||
|
7 − j2 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
ZT |
= 6.83 + j1.094 Ω = 6.917 9.1° Ω |
|||||
|
V |
|
120 10° |
|||
I = |
|
= |
|
|
= 17.35 0.9° A |
|
ZT |
6.917 9.1° |
|||||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 66.
For the circuit in Fig. 9.73, calculate Z T and V ab .
Figure 9.73
For Prob. 9.66.
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
Chapter 9, Solution 66.
ZT |
= (20 |
− j5) || (40 + j10) = |
|
(20 − j5)(40 + j10) |
= |
170 |
(12 − j) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
145 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 + j5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
ZT |
= 14.069 – j1.172 Ω = |
14.118 -4.76° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
I = |
V |
|
60 90° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
= |
|
|
= 4.25 94.76° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
ZT |
14.118 - 4.76° |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I1 |
|
|
I2 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
20 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
j10 Ω |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ Vab −
I1 = 4060++j10j5 I = 128 ++j2j I
I2 = 6020 +− jj55 I = 124 −+jj I
Vab |
= -20I1 + j10I2 |
|
|
|
|
||||
V |
= |
- (160 + j40) |
I + |
10 + j40 |
I |
||||
ab |
|
12 + j |
|
12 + j |
|||||
|
|
|
|||||||
V |
= |
-150 |
I = |
(-12 + j)(150) |
I |
||||
ab |
12 + j |
145 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||||
Vab |
= (12.457 175.24°)(4.25 97.76°) |
||||||||
Vab |
= 52.94 273° V |
||||||||
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 67.
At ω = 10 3 rad/s find the input admittance of each of the circuits in Fig. 9.74.
Figure 9.74
For Prob. 9.67.
Chapter 9, Solution 67.
(a) |
20 mH |
→ |
jωL = j(103 )(20 ×10-3 ) = j20 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|||
|
12.5 µF |
→ |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
= -j80 |
|
|
|
jωC |
j(103 )(12.5 ×10-6 ) |
|||||||
|
Zin = 60 + j20 || (60 − j80) |
|
||||||||
|
Zin = 60 |
+ |
( j20)(60 − j80) |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
60 − j60 |
|
|
|
|
|||
Zin = 63.33 + j23.33 = 67.494 20.22°
1
Yin = Zin = 14.8 -20.22° mS
(b) 10 mH |
→ |
jωL = j(10 |
3 )(10 ×10-3 ) = j10 |
|||
20 µF |
→ |
1 |
= |
|
1 |
= -j50 |
jωC |
j(10 |
3 )(20 ×10-6 ) |
||||
30 || 60 = 20
Zin |
= -j50 + 20 || (40 + j10) |
|||
Zin |
= -j50 + |
(20)(40 + j10) |
|
|
60 + j10 |
||||
|
|
|||
Zin |
=13.5 − j48.92 = 50.75 - 74.56° |
|||
1
Yin = Zin = 19.7 74.56° mS = 5.24 + j18.99 mS
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.

Chapter 9, Problem 68.
Determine Y eq for the circuit in Fig. 9.75.
Figure 9.75
For Prob. 9.68.
Chapter 9, Solution 68.
Yeq = 5 −1 j2 + 3 1+ j + -1j4
Yeq = (0.1724 + j0.069) +(0.3 − j0.1) +( j0.25)
Yeq = 0.4724 + j0.219 S
PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this Manual may be displayed, reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, without the prior written permission of the publisher, or used beyond the limited distribution to teachers and educators permitted by McGraw-Hill for their individual course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.
