728 Project 6 CREATING A MOBILE APPLICATION
Over the years, the Internet has become more of a necessity than a luxury. In today’s scenario, the Internet is not restricted only to the business world but
has become an essential part of our day-to-day activities. For example, you can
Y L Moreover, with the increasing popularityFof the Internet, people worldwide want
search for information on the Internet, shop on the Internet, pay your bills on the Internet, and so on.
make this possible, software developersMaround the world are developing applica-
to access the Internet from anywhere and anytime. People no longer want to restrict themselves to accessing the World Wide Web from their personal computers at home or in their offices. Instead, they want to access the Internet from
any mobile device, such as Pocket PC handhelds, mobile phones, and so on. To
|
tions that can be accessed from mobile devices. Such applications are called mobile |
|
applications. |
A |
|
E |
|
|
|
|
T |
In this chapter, I will discuss the basics of mobile applications. In addition, you will learn about the Mobile Internet Toolkit and the basics of the WAP (Wireless Application Protocol ) and WML (Wireless Markup Language) technologies. Finally, you will learn to create a simple mobile Web application that can be accessed from a mobile phone in Visual Studio .NET.
Overview of Mobile Applications
Mobile applications are the applications that are accessible from various mobile devices. In addition, mobile applications allow you to access a Web site from the mobile devices. Until now, users have not been extensively using the mobile applications, because of the following limitations of the mobile applications:
Mobile applications running on a mobile device, such as a mobile phone, require higher bandwidths. This adds to the overall cost of running a mobile application.
Mobile devices have a limited memory and battery life. Therefore, it becomes difficult to run the application for a long time.
BASICS OF MOBILE APPLICATIONS |
Chapter 32 |
729 |
|
|
|
|
It is difficult for a user to access information from the applications on the Internet, which are designed to be accessed from a personal computer, by using a mobile application. A Web page does not exactly fit the small screen of a mobile device. This makes it difficult for the user to navigate through the Web pages on a small screen.
As a solution to the previously mentioned problems, Visual Studio .NET provides you with the mobile technology that you can use to create applications that can be accessed from mobile devices. These applications contain mobile Web forms that can easily fit to the small screen of the mobile device, making navigation of Web pages possible. In addition, these mobile Web forms can adapt to the memory and bandwidth requirements of various mobile devices from which the Web form is accessed. I will discuss mobile Web forms in detail later in this chapter.
To be able to create mobile applications by using the Visual Studio .NET mobile technology, you need to use the Microsoft Mobile Internet Toolkit. The following section discusses the Mobile Internet Toolkit.
The Microsoft Mobile Internet Toolkit
The Microsoft Mobile Internet Toolkit provides you with the essential tools for creating, testing, and deploying a mobile application. These tools include the mobile Web forms, components, and controls. These tools provide you with a user-friendly interface for creating mobile applications. Creating a mobile application by using the Mobile Internet Toolkit becomes as simple as creating an ASP.NET Web application in the .NET Framework. You have learned to create an ASP.NET Web application in the .NET Framework in Project 5, “Creating a Web Portal for a Bookstore.”
The following list looks at some of the features of the Mobile Internet Toolkit that make it an easy-to-use tool for developing mobile applications.
The Mobile Internet Toolkit is based on the .NET Framework and, therefore, provides you with all the features of the .NET Framework, such as the toolbox that contains mobile Web controls. You can drag these controls to the form to use them. In addition, the Mobile Internet Toolkit has the Mobile Internet Designer. The Mobile Internet Designer is a visual tool that works as a part of the existing Visual Studio .NET

730 Project 6 CREATING A MOBILE APPLICATION
IDE (interactive development environment) and provides you with a visual interface for creating the mobile Web forms. Figure 32-1 shows the Mobile Internet Designer with a blank mobile Web form created by the Mobile Internet Toolkit.
The Mobile Internet Toolkit creates managed code that can be accessed from various mobile devices.
The Mobile Internet Toolkit enables you to debug and deploy the mobile Web application on various devices, such as mobile phones, pagers, and PDAs (personal digital assistants). In addition, the Mobile Internet Toolkit extends the functionality of the .NET Framework to allow you to create applications that can be accessed from any supporting device.
In addition to allowing you to test your mobile application on a built-in browser, the Mobile Internet Toolkit allows you to test your application on an emulator by using emulator software. However, to do this, you need to install the emulator and the emulator software. Testing the application on an emulator provides you with a fair idea of how your application will appear on the actual mobile device. An emulator simulates the mobile device environment for you so that you can test your application before deploying it on the actual mobile device.
FIGURE 32-1 Mobile Internet Designer with a blank mobile Web form

BASICS OF MOBILE APPLICATIONS |
Chapter 32 |
731 |
|
|
|
|
The Mobile Internet Toolkit is not packaged as a part of Visual Studio .NET. Therefore, to create mobile applications, you need to install the Mobile Internet Toolkit. Microsoft provides a freely downloadable version of the Mobile Internet Toolkit on its site. You can download the Mobile Internet Toolkit from the following link: http://msdn.microsoft.com/subscriptions/resources/subdwnld.asp. This link connects you to the MSDN Subscriber Downloads page on the Microsoft Web site. You can then search for the Mobile Internet Toolkit on the page.
TIP
You can download the Mobile Internet Toolkit on a computer running Windows NT or higher. In addition, you need to have either the .NET Framework or Visual Studio
.NET on your computer before installing the Mobile Internet Toolkit.
After you have downloaded and installed the Mobile Internet Toolkit on your computer, several new project types are added to the New Project dialog box. Figure 32-2 shows the New Project dialog box with the Mobile Web Application project type selected.
FIGURE 32-2 The New Project dialog box with the Mobile Web Application project type selected

732 Project 6 CREATING A MOBILE APPLICATION
I will discuss how to create a mobile Web application by using the Mobile Web Application project type later in this chapter. I will first discuss the transfer protocol used with the mobile applications that can be accessed from a mobile phone, WAP. However, when you access the mobile application from a PDA, the transfer protocol used will be TCP/IP.
Overview of WAP
I have already discussed the limitations of the earlier mobile Web applications, such as low memory and CPU capacity and higher bandwidth requirements. As a solution to these problems, a new protocol was developed. This protocol enables a wireless device, such as a mobile phone or a two-way pager, to access a Web site on the Internet. Therefore, this protocol was named WAP. WAP is a communication protocol, or a set of rules, that allows a wireless device to access a mobile application. To enable a user to access a mobile application, the user needs to have a WAP-enabled mobile device, such as a WAP-enabled mobile phone.
WAP is an industry standard developed by the WAP Forum that provides a set of rules for communication between the wireless devices and the world of the Internet. In addition, it provides telephony services for several wireless devices. WAP extends support to several advanced Internet technologies, such as IP (Internet Protocol ), TCP (Transmission Control Protocol ), and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol ).This makes it possible for a wireless device to utilize the functionality of these Internet technologies.
In addition, the wireless devices have hardware factors suitable for accessing an Internet site from the device. These hardware factors include a small screen, limited RAM, ROM, and a battery. These devices also allow users to navigate through the site by using the one-finger navigation feature, which makes navigation fun for the users.The wireless devices are capable of using the maximum
THE WAP FORUM
WAP is a protocol developed by the WAP Forum. The WAP Forum works in coordination with several organizations, such as W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), to provide the wireless industry with a global specification for all wireless networks. In this context, the WAP Forum released its first specification, WAP 1.0, in 1998.The WAP Forum has also released its second specification, WAP 2.0. The WAP Forum includes the major wireless technology companies, such as Nokia, Ericsson, Oracle Corporation, and so on.

BASICS OF MOBILE APPLICATIONS |
Chapter 32 |
733 |
|
|
|
|
power of processors, which reduces the overall cost of accessing the application from a wireless device.
To access an Internet site from a mobile device, your mobile device needs to be WAP-enabled. A WAP-enabled mobile device has microbrowser software installed on it.This software is used to send and receive a user’s request for accessing a Web site. For example, when a user tries to access a site from the WAPenabled device, the microbrowser sof tware sends a request to the server to allow the user to access the site. The following section discusses the WAP architecture in detail.
The WAP Architecture
To understand the concept of the WAP architecture, first have a look at the Web architecture.The Web architecture refers to the architecture involved when a user tries to access a Web site from a Web browser. When a user tries to access a Web site on a Web server, a request for the site is sent from the client to the server. In this case, the client is the Web browser that sends a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) request to the server, which is the Web server. Then, at the server site, the request is processed in the form of CGI (Common Gateway Interface) scripts, and the content of the site is returned to the client as a response to the user’s request. Figure 32-3 shows the Web architecture in detail.
FIGURE 32-3 The Web architecture
734 Project 6 CREATING A MOBILE APPLICATION
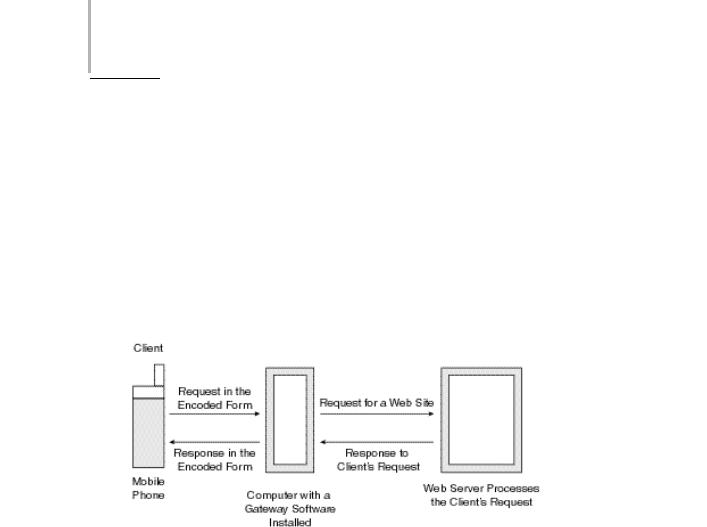
After learning about the Web architecture, you can easily understand the WAP architecture.The WAP architecture is similar to the Web architecture, except that the WAP architecture involves a WAP gateway that acts as an interface between the client and the server. A WAP gateway is software placed between the client and the ser ver that supports the WAP standards and the Internet protocols, such as HTTP and IP. In addition, the WAP gateway supports XML (Extensible Markup Language) and WML. A WAP gateway consists of encoders, decoders, and script compilers that are used for communication between the client and the server.
In the case of a mobile device trying to access an Internet site, the mobile device becomes the client and the Web ser ver is the server from where the site is being accessed. Figure 32-4 shows the WAP architecture in detail.
FIGURE 32-4 The WAP architecture
As you can see in the figure, to access a Web site from a client (mobile device), the client first needs to send a request for the site. To do this, the client establishes a connection to the WAP gateway. Once a connection is established, the WAP gateway software uses an encoder to encode or convert the request to a form that is easily understood by the Internet server. This encoded form of the request is then forwarded to the server where the request is further processed.
BASICS OF MOBILE APPLICATIONS |
Chapter 32 |
735 |
|
|
|
|
TIP
WAP allows users to access only WAP-enabled sites, such as www.google.com and www.yahoo.com.
Then, as a response to the user’s request, the server sends the content of the site to the client. However, a user of a mobile device cannot read this content in the form returned by the server. Therefore, the WAP gateway transfers the content in the Internet language to a form supported by WAP devices, such as WML and WMLScript. WAP uses the WML and WMLScript languages to send and receive data on a wireless device. The data is then displayed to the user by using the microbrowser software on the mobile device.
Overview of WML
WML is a language based on XML. In addition to releasing specifications on WAP, the WAP Forum releases specifications on WML. Similar to XML, WML provides a standard for describing data.The standards defined for describing data are based on the W3C standards. You have learned about XML in detail in Chapter 17, “Interacting with a Microsoft Word Document and Event Viewer,” in the section “Overview of XML.”
The standards defined for describing data in WML are stored as rules in a document called DTD (Document Type Definition). This implies that the DTD document stores the syntax for describing data in a WML document. In addition, a DTD document can include the definition of the elements to be used in the WML document. The elements in a WML document are enclosed within tags. WML allows the users to define the tags to be used in the WML documents. While describing data in a WML document, you need to associate your WML document to a DTD document.
I have already discussed the use of the microbrowser software. A microbrowser understands and fully supports the syntax of a WML document.
After discussing the technology and the transfer protocol for a mobile Web application, I will discuss a simple mobile Web application. The following section discusses the mobile Web application that includes a mobile Web form.
736 Project 6 CREATING A MOBILE APPLICATION
Creating a Simple Mobile Web
Application by Using the Mobile
Internet Toolkit
As discussed earlier, when you install the Mobile Internet Toolkit on your computer, the Mobile Web Application project type is added to the New Project dialog box. You can use this project type option to create a sample mobile Web application. To access the mobile Web application project type, perform the following steps:
1.On the File menu, point to the New option.
2.In the displayed list, click on the Project option. The New Project dialog box is displayed.
3.In the Project Types: pane of the New Project dialog box, select the Visual C# option.
4.In the Templates: pane, select the Mobile Web Application option.
5.In the Location: text box, the localhost appears by default. Type the name of the application as MobileTimeRetriever.
Figure 32-5 shows the New Project dialog box.
6.Click on the OK button.
FIGURE 32-5 The New Project dialog box for the MobileTimeRetriever application
BASICS OF MOBILE APPLICATIONS |
Chapter 32 |
737 |
|
|
|
|
The MobileTimeRetriever application opens in the design view. Visual Studio
.NET creates a number of default files for the mobile Web application, as displayed in the Solution Explorer window. The MobileWebForm1.aspx file is selected by default. In addition to the default files, Visual Studio .NET creates a blank mobile Web form, Form1, in the design view. Figure 32-6 shows the default files and the mobile Web form.
FIGURE 32-6 The default files and a blank mobile Web form for the MobileTimeRetriever application
The following section discusses the mobile Web form in detail.
The Mobile Web Form
A mobile Web application contains a mobile Web form by default. However, you can add multiple mobile Web forms to the application. All the mobile Web forms that you add to your application appear on a single mobile Web form page in the design view. However, at run time, only one mobile Web form appears to a user at a time. The mobile Web form has an extension .aspx and appears as a control in the mobile Web forms toolbox. When you install the Mobile Internet Toolkit on your computer, the mobile Web forms toolbox is added to the toolbox of Visual Studio .NET. Figure 32-7 shows the mobile Web forms toolbox.