
Sentence analysis
T
 HE
NOUN
HE
NOUN
Common proper
Countable uncountable
in the singular in the plural
Ex. boy's - it is a common countable noun in the singular modified by the possessive
T
 HE
ADJECTIVE
HE
ADJECTIVE
In the positive degree In the superlative degree
In the comparative degree
T
 HE
VERB
HE
VERB
Finite Non-finite
Non-finite forms: infinitives, gerunds and participles
Finite forms differentiate:
1) the category of tense (past, present, future, future — in — the Past)
2) the category of aspect (continuous, non-continuous)
3) the category of voice (active, passive)
4) the category of perfect, non-perfect)
5) the category of mood.
The Infinitive has 6 forms. Gerund and participles — 4 forms.
THE PRONOUN
 in
the nominative case
in
the nominative case
1. Personal (I, you, he, she, it, we, they)
in the objective case
(me, you, him, her, it, us, them)
 In
the conjoint form (согласованная
форма)
In
the conjoint form (согласованная
форма)
2. Possessive (my, her, his, our, their, your)
In the absolute form (mine, yours, hers, his, ours)
3. Demonstrative - this, that, these, those
4. Indefinite - personal - somebody, some..., any, every..., either, each, all
5. Negative - no, no..., neither
6. Interrogative - who, whom, what, who
7. Relative - who, whom, whose, which
8. Reciprocal — each other, one another
9. Reflexive - myself, herself
The Numeral
Cardinal (one, two) Ordinal (first, second)
Sentence Analysis-2
S
 entence
entence
S
 imple Composite
imple Composite
Compound Complex
S
 entence
entence
Extended Unextended
S

 entence
entence
Definite-personal Indefinite-personal Impersonal
S
 entence
entence
One-member Two-member
S

 entence
entence
Declarative Interrogative Imperative Exclamatory
Sentence analysis. Complex sentence
T
 he
main clause
he
main clause

Subordinate clause1 Subordinate clause 2 Subordinate clause3
Subordination
Syntactical Asyntactical
(
 Conjunctions,
conjunctive words)
Conjunctions,
conjunctive words)
Conjunctive adverbs Relative pronouns
(Where, why, somewhere)
Conjunctions have no independent syntactic function in the sentence.
E.g.: He said that he would come. (A conjunction)
The building that is being built well will be a hotel. (A conjunctive word)
![]()
Subordination
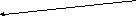

Parallel Consecutive (последовательное)


Homogenous Heterogeneous Main clause
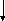
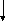
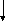
Main clause Main Clause Sub. Clause 1




S 1
S2 S3 S1 S2 S3 Sub. Clause 2
1
S2 S3 S1 S2 S3 Sub. Clause 2


Sub. Clause 3
Parallel homogenous and heterogeneous Ex. She said, she would come if subordination she had spare the time.
Main clause Main clause


 S1 S2
S1 S2
S
 1
1
S2 S3
S3 S4
![]()
Types of Subordinate Clause
Subject clauses
Ex. What is done cannot be undone.
Predicative clause
Ex. His proposal was that we should join the excursion.
Object clauses
Ex. He knows what should be done
Attributive clauses
Ex. He is a person, who always ready to help.
Adverbial clause
Of time;
Of place;
Of manner (образа действия);
Of cause;
Of condition;
Of concession;
Of purpose;
Of comparison
Samples of Analysis
During (be last year I had become absolutely interested in her private life.
The subject is “I”. It is expressed by a personal pronoun in the nominative case.
The predicate is “had become uninterested”. It's a compound nominal predicate in which the link-verb is expressed by the “become” in the Past Tense, Active Voice, and Indicative Mood, Perfect.
“During the last year” is an adverbial modifier of tense. The noun expresses it.
“Her” is a possessive pronoun in the conjoined form.
“Private” is an adjective.
![]()
