
Lektsii (1) / Lecture 11
.pdf
ICEF, 2012/2013 STATISTICS 1 year LECTURES
Lecture 11 |
|
|
|
|
|
20.11.12 |
|
|
|
FUNCTION OF A RANDOM VARIABLE |
|||||
Let X be some (discrete) random variable |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
xn |
|
|
X |
x1 |
|
x2 |
… |
… |
||
P(X) |
p1 |
|
p2 |
… |
pn |
… |
|
We consider new random variable that is some function of an X, i.e. Y = g(X ) . For example X is the net family income and the food expenditure is cX α where α < 1.
Example. Let r.v. X has the following distribution:
X |
|
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
P(X) |
|
0.25 |
0.25 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
0.1 |
Let Y = X 2 . Then the distribution of Y is given by |
|
|||||
Y |
|
0 |
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
P(Y) |
|
0.2 |
0.45 |
0.35 |
|
|
and E(X 2 ) = E(Y ) = 0 0.2 +1 0.45 +4 0.35 =1.85 . Alternatively,
E(X 2 ) = (−2)2 0.25 +(−1)2 0.25 +02 0.2 +12 0.2 +22 0.1 =1.85
In order to calculate the expectation E(Y ) one should (according to definition) first construct the distribution (table) of Y:
Y |
y1 |
y2 |
… |
yn |
… |
P(Y) |
q1 |
q2 |
… |
qn |
… |
and then to calculate E(Y ) = ∑yi qi .
i
In fact it may be proved the following statement (that is quite clear intuitively):
E(Y ) = ∑g(xi ) pi .
i
In other words, in order to find the expectation E(Y ) one needs not to construct the distribution of the random variable Y.
Continuous random variables (distributions)
Continuous random variable X has strange and paradoxical property: for any possible value x0 we have Pr(X = x0 ) = 0 . Thus means that we cannot describe the distribution of such random variable via table of distribution similar to discrete r.v.
Alternative description of the distribution of a r.v. X is the probability density function (pdf).
Definition. The function |
fX (x), x R is called the pdf of X if |
Pr(X [a,b]) = ∫b |
fX (x) dx . |
a |
|
PROPERTIES |
|
1)f (x) ≥ 0 ;
2)+∞∫ f (x) dx =1 (the square under the curve is equal to 1).
−∞
To define the distribution of a continuous random variable X to define its density function fX (x) .
Definition. If X is a continuous r.v. with the pdf fX (x) then
+∞ +∞
µX = E(X ) = ∫ x fX (x) dx, σX2 =V (X ) = E((X −µX )2 ) = ∫(x −µX )2 fX (x) dx .
−∞ −∞
Standard normal r.v. (distribution)
Definition. Random variable Z is called a standard normal r.v. if
fZ (x) =ϕ(x) = |
1 |
e− |
x2 |
||
2 |
. |
||||
2π |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
Notation: Z N (0,1) .
It may be calculated that E(Z ) = 0, V (Z ) =1.
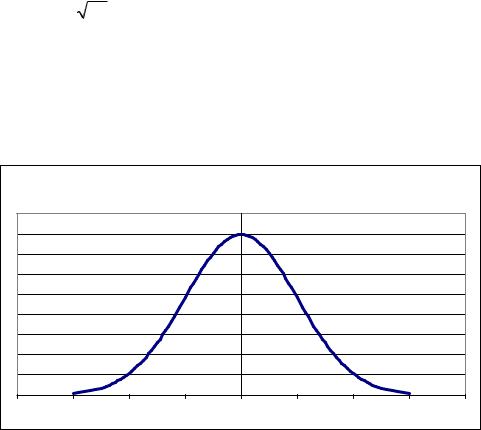
The graph of ϕ(x) is called standard normal curve. It is bell-shaped and symmetric with respect to oy axis.
|
|
|
|
phi(x) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.45 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
|
-4 |
-3 |
-2 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
