
- •Icons in Body Text
- •Introduction to the Dictionary
- •Overview of the functions
- •Data objects in the ABAP Dictionary
- •Data types
- •Exercise 1: Basic Data Types
- •Exercise 2: Simple and Nested Structures
- •Exercise 4: Deep Structures
- •Tables
- •Summary
- •Exercise 5: Tables in the ABAP Dictionary
- •Pooled and cluster tables
- •Performance During Table Access
- •Improved Performance through Access per Index
- •Improving the Performance through Table Buffering
- •Exercise 6: Performance Aspects with Table Access
- •Task 1:
- •Input Checks
- •Input check via the technical domains
- •Object Dependencies
- •Activation and Where-Used List
- •Changes to Tables
- •Database Changes to Transparent Tables
- •Enhancement of SAP Standard Tables
- •Exercise 9: Changes to Database Tables
- •Views and Maintenance Views
- •Restricted or Enhanced Views on Database Tables
- •Exercise 11: Views
- •Creating Maintenance Views
- •Exercise 12: Maintenance Views
- •Search Helps
- •Input helps
- •Exercise 13: Search Helps
- •Table ZEMPLOY##
- •Table ZDEPMENT##
- •Table ZEMPLOY##
- •Table ZEMPLOY##
- •Table ZDEPMENT##
- •Table ZDEPMENT##
- •Check table T000
- •Check table SCARR
- •Check table ZDEPMENT##
- •Check table SCURX
- •Check table STRAVELAG
- •Check table ZDEPMENT##
- •Check table T002
Unit 7: Views and Maintenance Views |
BC430 |
Lesson: Maintenance Views
Lesson Overview
In this lesson, you will become familiar with the possibility of generating maintenance views for customer or customizing tables.
Lesson Objectives
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
•Create a maintenance view
•Create simple maintenance views
•Create complex maintenance views
Business Example
You should create simple views for the new DB tables to generate test data quickly in your project.
Creating Maintenance Views
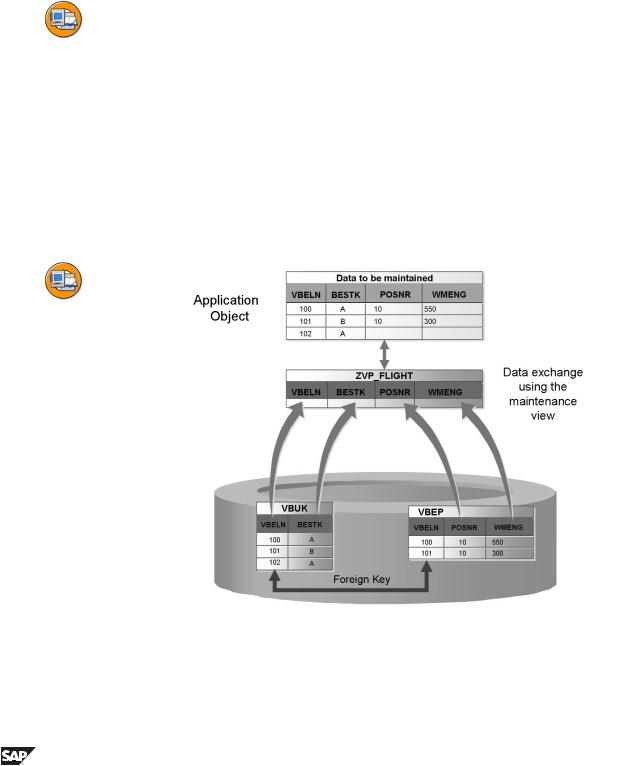
Figure 82: Collecting data with generated maintenance masks
190 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
BC430 |
Lesson: Maintenance Views |
Data that is distributed on more than one table often forms a logical unit, called an application object, for the user. You should be able to display, change and create the data of such an application object together. The user usually is not interested in the technical implementation of the application object, such as the distribution of the data on several tables.
You can maintain complex application objects in a simple way using a maintenance view. The data is automatically distributed on the underlying database tables.
All the tables used in a maintenance view must be linked with a foreign key. This means that the join conditions are always derived from the foreign key in the maintenance view. You cannot enter the join conditions directly as in a database view.
A maintenance interface with which the data of the view can be displayed, changed and created must be generated from the definition of a maintenance view in the ABAP Dictionary.
When the maintenance interface is created, function modules that distribute the data maintained with the view on the underlying tables are automatically generated.
The maintenance interface is generated with the Transaction Generate Table View (Transaction SE54) or from the view maintenance screen with Utilities → Tab.maint.generator.
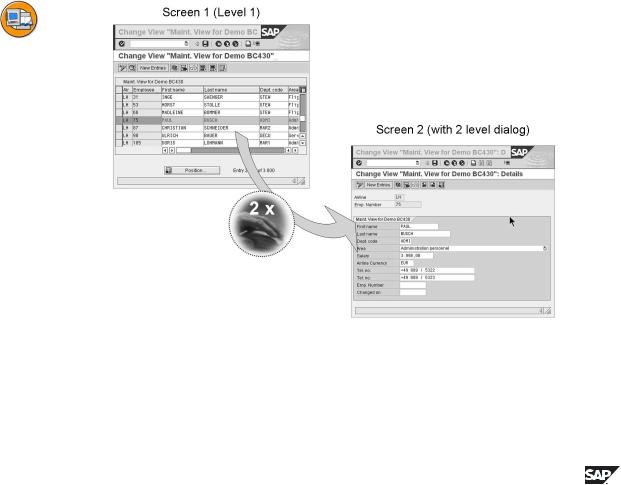
Figure 83: Maintenance view from a maintenance view
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
191 |
Unit 7: Views and Maintenance Views |
BC430 |
In a one-step maintenance view, the data of the table lines are represented as TableControl. The key fields have a gray background and are not intended for changes. The function fields have a white background and can be changed.
If you have created a two-step maintenance view, another screen can be opened by double-clicking a table line in which the selected data record is presented in a clear form.
Figure 84: Define maintenance view 1
When creating a maintenance view, you should note the following: In Views, select maintenance view as the view type.
All key fields of the primary table must be contained in the view definition.
The client field must be included for client-dependent tables/views. However, the field is not yet shown in the maintenance view.
For text tables as secondary tables, the language cannot be copied, as it is filled with the logon language automatically during maintenance.
The key fields must be defined before the function fields. Function fields and key fields cannot be mixed.
Using the maintenance status option, you can define the maintenance status for the entire table/view. You have the following possibilities:
read only
read, change, delete and insert (default setting) read and change
192 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
BC430 |
Lesson: Maintenance Views |
read and change (time-dependent views)
Figure 85: Define maintenance view 2
Enter an explanatory short text in the short description field. With the info system, for example, you can later search for the view via this short text.
Copy tables
Specifiy the primary table of the view on the tab page Tables/Join Conditions under Tables. Only those tables can be included in the maintenance view, which are connected to the primary table (indirectly) via the foreign key.
If necessary, include other tables in the view. You can only include tables in a maintenance view, which are connected to one another via foreign keys. Position the cursor on the primary table choose Relationships. All existing foreign key relationships of the primary table are displayed. Tick the desired foreign key and choose Copy. The secondary table involved in such a foreign key is copied in the view. The join conditions (foreign key relationship and join condition) derived from the foreign keys are displayed.
You can also include tables, which are connected to one of the previously copied secondary tables via a foreign key. Position the cursor on the secondary table and activate Relationships. Proceed as described above.
The foreign key relationships for which a maintenance view is not appropriate are displayed at the end of the list under the heading Relationships with unsuitable cardinality.
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
193 |

Unit 7: Views and Maintenance Views |
BC430 |
Copying the view fields
On the View field tab page, select the fields that you want to copy into the view.
Activate Table fields. All tables contained in the view are displayed in a dialog box. Select a table. The fields of the table are now displayed in a dialog box. You can remove fields form here by highlighting these in the first column and choosing Copy.
All key fields of the primary table must be included in a maintenance view. In addition, all key fields of seconbary tables that are not involved in the foreign key (i.e. are not connected via a join condition to a key field already included in the view) must be included in the view.
This ensures that the records inserted via a maintenance view can be written correctly in the tables contained in the view.
Selection conditions
On the Selection conditions tab page, formulate (optional) restrictions to the data records, which can be displayed via the view (see Maintain selection condition of the view). The selection conditions define which data records can be selected via the view.
Maintenance status
On the Maintenance status tab page, define the maintenance status of the view. The maintenance status determines how you can access the view data via the standard view maintenance (SM30).
Activate
A log is written during activation, which you can display via Utilities -> Activation log. If errors or warnings occurred during the activation of the view, the activation log is automatically displayed.
Generate maintenance interfaces.
Via Environment -> Tab.maint.generator, go to the transaction SE54. There you can generate maintenance modules and maintenance interfaces from the view definition, which copy the distribution of the data entered via the view onto the basis tables of the view.
194 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
BC430 |
Lesson: Maintenance Views |
Figure 86: Define maintenance view
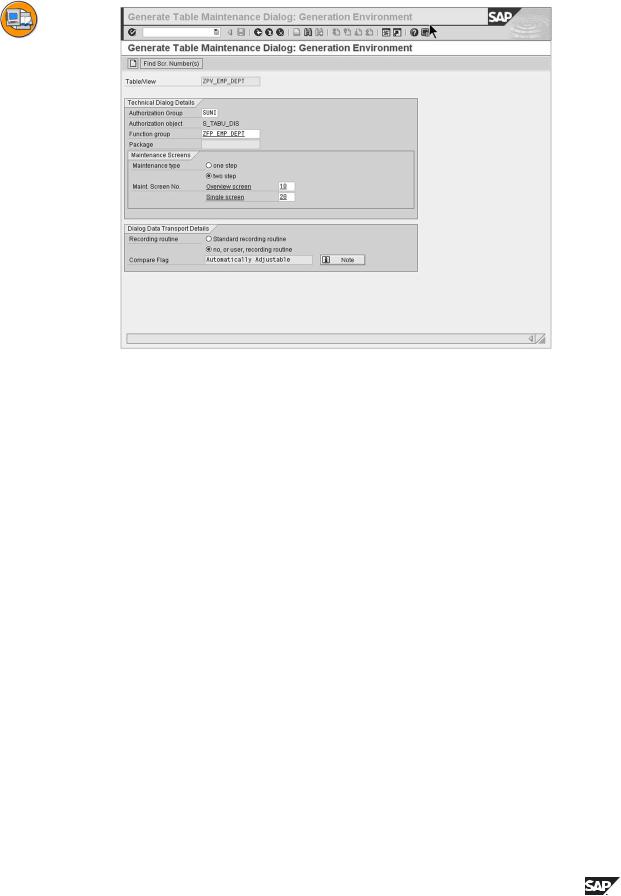
You reach the generation environment for maintenance views as follows:
•from the SE11 in the view for Tables/Views via the menu Utilities -> Table maintenance generator
•via the transaction SE54:
1.Choose Development -> Other tools -> Table maint. view. You are now in the initial screen of the maintenance transaction.
2.Enter the name of the table or the view
3.Select Generated objects
4.Choose Create/Change.
5.Confirm in the window after that, that the maintenance modules should be created
In the definition of the maintenance view, you must specify the following parameters:
Function group
Here, you define in which function group the tables/individual view maintenance view components are generated. If necessary, the function group is created anew.
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
195 |

Unit 7: Views and Maintenance Views |
BC430 |
Authorization group
Here, you specify which users are authorized to maintain the tables/view contents
Maintenance type
Here, you define whether the dialog should be integrated in one or two steps. One-step dialogs consist only of one overview screen which contains all fields. With two-step dialogs, only the key fields and text fields with a length of more than 20 characters are displayed in the overview screen. All fields are offered in the detailed screen.
Maintenance screens
Here, you specify the internal number of every maintenance screen. You can propose possible values using a search function.
Recording routine
Here, you specify whether and how tables/view contents maintained with a dialog can be included in a transport.
After entering all values, the generation of the maintenance view is started. If this process runs without error, the dialog can be used immediately to maintain the tables/view contents. To do this, start transaction SM30 and enter the table or view in the Table/View field for which you have generated the maintenance view. Activate the Maintenance button.
Figure 87: Advantages and disadvantages of a maintenance view
The maintenance view should not be used for the data maintenance in standard operation, as there is a risk of data inconsistencies.
It is intended much more for entering medium-sized amounts of data in customer tables or customizing tables, for which there can be no overlapping in the data entered.
196 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
BC430 |
Lesson: Maintenance Views |
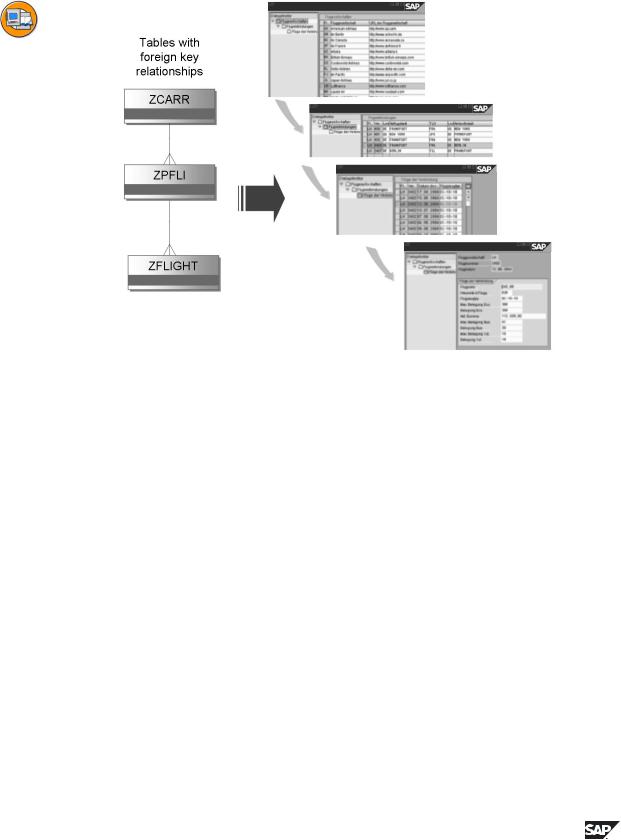
The secondary tables must stand in an N:1 dependency to primary tables or to transitively previous secondary tables (see above).
Figure 88: View Clusters and Maintenance Views
If you have generated maintenance views for tables/views, you can combine these to a view cluster.
As a view cluster, we understand a group of maintenance views, which have been combined in one maintenance unit for business or technical reasons.
View clusters thus offer the option of maintaining data that belong together from the point of view of content and which go beyond one table/one view.
While only 1:1 relationships can be processed in maintenance views (with the exception of language-dependent texts), with view clusters, key enhancements and relationships of the cardinality N:M can also be mapped. In addition, maintenance views can be combined into a view cluster without key or subkey dependency.
The navigation within the view cluster is generally oriented towards the hierarchy of the tables/views underlying the individual views. Master – Detail – Relationships, even those over several levels, are especially suitable for a view cluster.
Normally, a view cluster consists of one or more root views and the maximum 14 maintenance views dependent on it or on them. These maintenance views can be both one-step and two-step.
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
197 |

Unit 7: Views and Maintenance Views |
BC430 |
First of all, via SE54, you must generate a maintenance view for every table/view involved, in order to then combine these in SE54 in a view cluster.
You subsequently maintain the data with transaction SM34 and by specifying the cluster name.
Figure 89: Advantages
198 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
