
- •Icons in Body Text
- •Introduction to the Dictionary
- •Overview of the functions
- •Data objects in the ABAP Dictionary
- •Data types
- •Exercise 1: Basic Data Types
- •Exercise 2: Simple and Nested Structures
- •Exercise 4: Deep Structures
- •Tables
- •Summary
- •Exercise 5: Tables in the ABAP Dictionary
- •Pooled and cluster tables
- •Performance During Table Access
- •Improved Performance through Access per Index
- •Improving the Performance through Table Buffering
- •Exercise 6: Performance Aspects with Table Access
- •Task 1:
- •Input Checks
- •Input check via the technical domains
- •Object Dependencies
- •Activation and Where-Used List
- •Changes to Tables
- •Database Changes to Transparent Tables
- •Enhancement of SAP Standard Tables
- •Exercise 9: Changes to Database Tables
- •Views and Maintenance Views
- •Restricted or Enhanced Views on Database Tables
- •Exercise 11: Views
- •Creating Maintenance Views
- •Exercise 12: Maintenance Views
- •Search Helps
- •Input helps
- •Exercise 13: Search Helps
- •Table ZEMPLOY##
- •Table ZDEPMENT##
- •Table ZEMPLOY##
- •Table ZEMPLOY##
- •Table ZDEPMENT##
- •Table ZDEPMENT##
- •Check table T000
- •Check table SCARR
- •Check table ZDEPMENT##
- •Check table SCURX
- •Check table STRAVELAG
- •Check table ZDEPMENT##
- •Check table T002
BC430 |
Lesson: Changes to Tables |
Enhancement of SAP Standard Tables
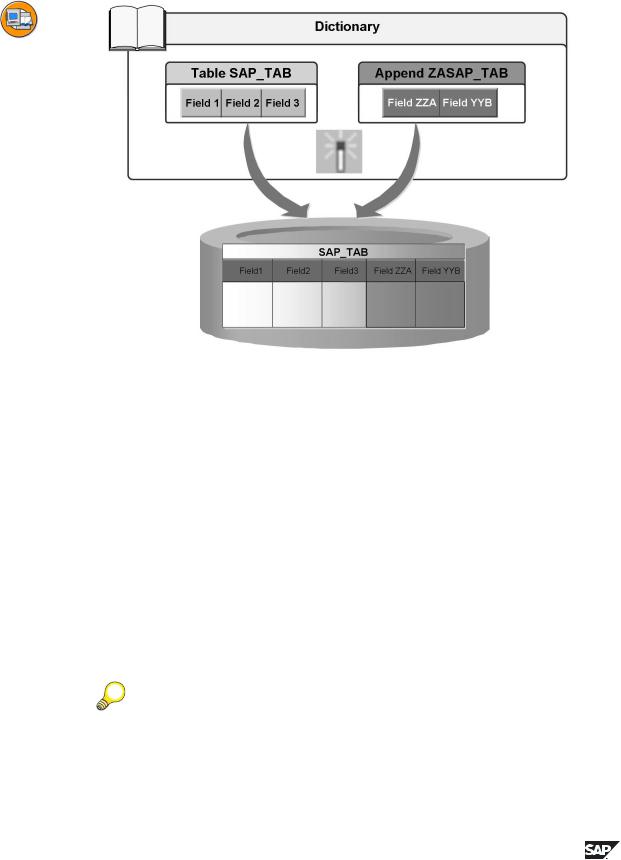
Figure 67: Append Structures 1
Append structures permit you to append fields to a SAP standard table and structures without having to modify the table definition.
An append structure is a structure which is assigned to exactly one table. There can be several append structures for a table.
When a table is activated, all the active append structures for the table are found and their fields are appended to the table. If an append structure is created or changed, the table to which it is assigned is also activated and the changes also take effect there when it is activated.
Like all structures, an append structure defines a type that can be used in ABAP programs.
With Release 4.6C you can define foreign keys for fields that already exist in the table using an append structure. Search helps can also be attached to fields that already exist in the table.
Hint: If you copy a transparent table in the Data Dictionary (DDIC) to which an append structure has been added, the fields of the append structure become normal fields in the target table.
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
155 |
Unit 6: Changes to Tables |
BC430 |
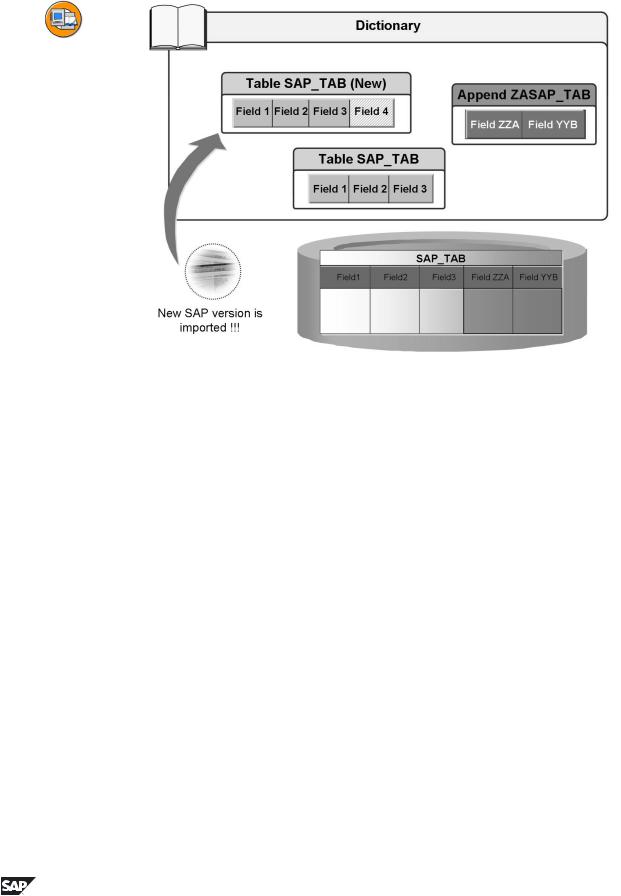
Figure 68: Append Structures 2
Customers create append structures in their namespace. The append structures are thus protected against overwriting during an upgrade.
The new versions of the standard tables are imported during the upgrade. When the standard tables are activated, the fields contained in the active append structures are appended to the new standard tables. When append structures are added to a table, you do not have to manually adjust the customer modifications to the new SAP version of the table (Transaction SPDD) during the upgrade.
Since the order of the fields in the ABAP Dictionary since Release 3.0 can differ from the order on the database, a conversion is not necessary when you add an append structure or insert fields in an existing append structure. The structure is adjusted when the database catalog is adjusted (ALTER TABLE). When activating in the ABAP Dictionary, the definition of the table is changed and the new field is appended to the database table.
156 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
BC430 |
Lesson: Changes to Tables |
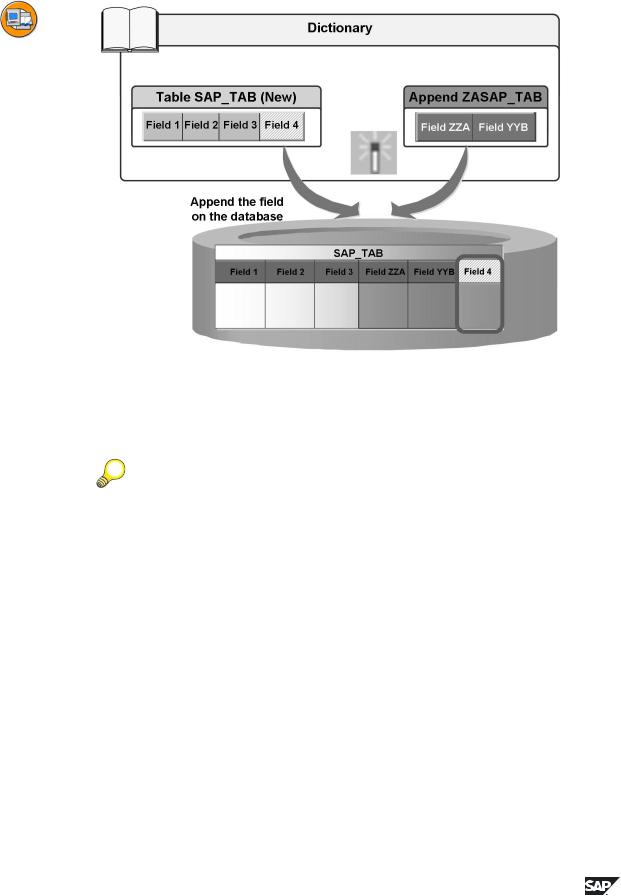
Figure 69: Append Structures 3
The new version of the SAP standard table is activated and the new field is appended to the database table.
Hint: Please note the following points about append structures:
•No append structures may be created for pooled and cluster tables.
•If a long field (data type LCHR or LRAW) occurs in a table, it cannot be extended with appends structures. This is because such long fields must always be in the last position of the field list (e.g. they must be the last field of the table).
•If you as a customer add an append structure to an SAP table, the fields in this append structure should be in the customer namespace for fields, that is they should begin with YY or ZZ. This prevents name collisions with new fields inserted in the standard table by SAP.
•If you as a partner have your own reserved namespace for your developments, the fields you select in append structures should always lie in this namespace.
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
157 |
Unit 6: Changes to Tables |
BC430 |
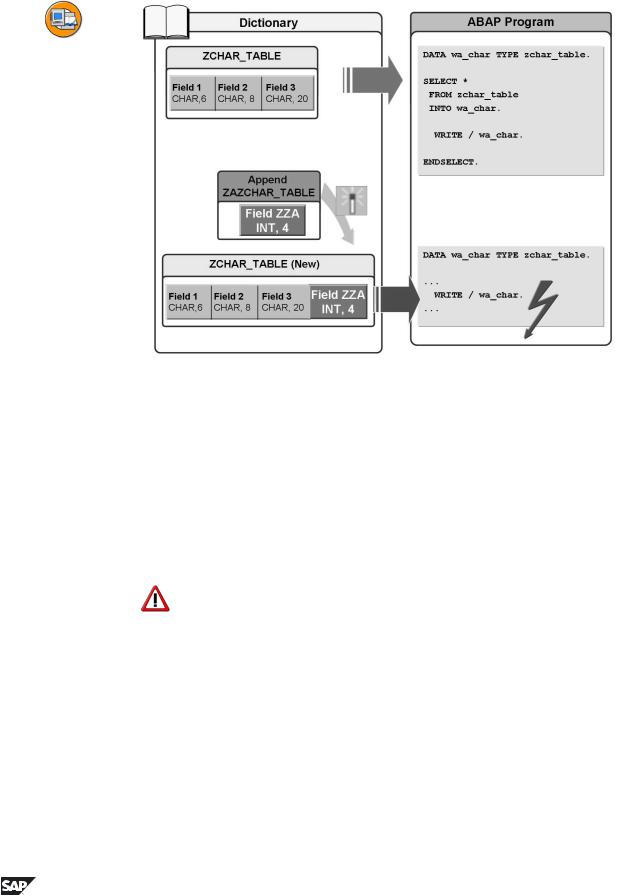
Figure 70: Enhancement of tables
Structures and tables that have been defined by SAP in the ABAP Dictionary can be subsequently enhanced by the customer in the following way:
Customizing includes
With this variant, certain places within a structure or tables for enhancements are already reserved. However, the associated Includes are first of all created by the customer.
Appends
With this variant, any fields without previous reservation are appended to the end of structures or tables.
Caution: Problems due to structure enhancements
Not only the enhanced structures and tables are affectted by enhancements of this kind, but also all dependent structures that the enhancement takes on as Include or substructure. For example, enhancements using appends, which only have an effect at the end of the initial structure, can, for dependent structures, also lead to adjustments within these structures.
In programs without active Unicode checking, structure enhancements can lead to syntax and runtime errors, especially in type checks and in connection with deep structures. In programs with active Unicode checking, assignments, operand checks and accesses with offset and length are also affected. Problematic here are changes if, for example, numerical or deep components are inserted into a purely character-like
158 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |

BC430 |
Lesson: Changes to Tables |
structure and this leads to the structure losing its character-like character. Enhancements are also therefore problematic, because the fragment view is changed and checks in assignments and comparisons which are based on this are influenced.
So that the effects pf structure enhancements are recognizable at all, structures and tables in the ABAB dictionary are classified under Extras -> Enhancement category according to the following procedure:
Level |
Category |
Meaning |
|
|
|
1 |
Not classified |
The structure does not have an enhancement |
|
|
category |
2 |
Not enhanceable |
The structure cannot be enhanced |
3 |
Enhanceable and |
All structure components and their |
|
character-like |
enhancements must be character-like |
4 |
Enhanceable and |
The structure and its enhancement cannot |
|
character-like or |
contain any deep data types |
|
numerical |
|
5 |
Freely extendable |
The structure and its enhancements may |
|
|
contain components whose data type is |
|
|
optional |
Here, the elementary types C, D, N and T are describes as character-like, the elemenatry types F, I, P and X as numerical. The deep types STRING and XSTRING are not supported.
With structures and tables with Includes or substructures, the enhancement categories of the Includes and substructures cannot be larger than those of the initial structure. For example, if the initial structure contains an Include of level 4, then levels 2 and 3 are not permitted for the initial structure.
Structure enhancements in Dictionary can also have an effect on internal structures in ABAP programs if Dictionary structures in the source text are used as Include or substructure. These dependencies are considered implicitly in the ABAP program check. This does not include classified structures that contain enhanceable Includes or substructures.
2006/Q2 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
159 |

Unit 6: Changes to Tables |
BC430 |
160 |
© 2007 SAP AG. All rights reserved. |
2006/Q2 |
