
The_Soviet_Army_troops_organization_and_equi
.pdf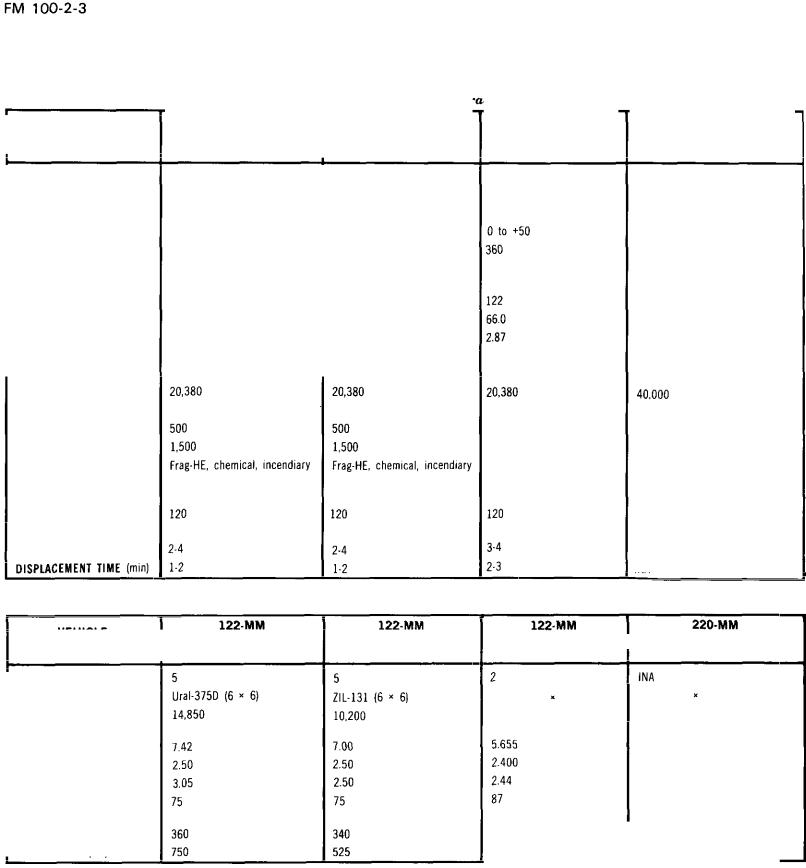
Rocket Launchers
|
|
|
|
Rocket launcher armament char |
cteristics |
|
|||
I |
A R M A M E N T |
122-MM |
1 2 2 - M M |
|
122-MM |
220-MM |
|||
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
||||||
CHARACTERISTICS |
|||||||||
(40-RD) B M - 2 1 |
(36-RD) B M - 2 1 - 1 |
(12-RD) B M - 2 1 V |
(16-RD) B M - 2 2 |
||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
DOI |
|
1964 |
1976 |
1975 |
|
1977 |
|
|
|
STATUS |
|
standard |
standard |
standard |
standard |
||
|
|
LAUNCHER |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Elevation (c) |
0 to +56.5 |
0 to +55 |
|
|
approximately 0 to +55 |
||
|
|
Traverse |
(c) |
168 |
270 |
|
|
240 (estimated) |
|
|
|
|
|
(100 left, 68 r i g h t ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ROUND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C a l i b e r(mm) |
122 |
122 |
|
|
220 |
||
|
|
Total w e i g h t(kg) |
66.0 |
66.0 |
|
|
approx~mately300 |
||
|
|
Length, |
overall (m) |
2.87 |
2 87 |
|
|
4.80 |
|
|
|
Type of |
stabilization |
fin and s p i n |
f i and spin |
f i n and spin |
fin and spin |
||
|
|
RANGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Maximum (m) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Minimum |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Direct f i r e(m) |
|
|
500 |
|
INA |
||
|
|
Indirect fire (m) |
|
|
1,500 |
|
approxlmately 5,000 |
||
|
|
WARHEAD (types) |
|
|
Frag-HE,chemical, |
Frag-HE,chemical,ICM |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
incendiary |
(scatterable AP and AT mines; |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
frag and i n c e n d i a rbomblets)y |
|
|
|
UNIT OF |
FIRE (rd) |
|
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
EMPLACEMENT TIME. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
launcher |
preloaded (min) |
|
|
|
|
INA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rocket launcher vehicle characteristic8
|
VEHICLE |
|
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
|
ROCKET LAUNCHE R |
||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|||||||||
|
(40 |
-RD) |
BM-21 |
(36 - RD ) B M - 2 1 - 1 |
(12-RD) B M - 2 1 V |
|
(16-RD) BM-22 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
CREW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MODEL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GAZ-66B(4 4) |
|
ZIL-135 (8 |
8) |
WEIGHT, |
with launcher |
|
|
|
|
|
6.000 |
|
approximately23,000 |
||
and rockets (kg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
LENGTH, travel position(m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
approxlmately |
9.30 |
||
WIDTH, |
travel |
position (m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
approximately |
2.80 |
HEIGHT, |
travel |
position (m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
approx~mately3.20 |
|
ROAD SPEED, |
maximum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
approxlmately |
65 |
|
(km/hr) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FUEL CAPACITY (liters) |
|
|
|
|
|
210 |
|
approximately |
770 |
||
ROAD RANGE (km) |
|
|
|
|
|
875 |
|
approximately |
520 |
||









