
FinMarkets_BA14-2_03_mail
.pdf
«Financial Markets.
Interest rates»
Sergey Zaverskiy
February, 18, 2013
Moscow State University Business School
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets

Issues for today
•Types of credit instruments
–Fixed-payment loans
–Discount bonds
–Coupon bonds
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets
Fixed-payment loans
•Simple Loans require payment of one amount which equals the loan principal plus the interest
•Fixed-Payment Loans are loans where the loan principal and interest are repaid in several payments, often monthly, in equal ruble or dollar amounts over the loan term
–Installment Loans, such as auto loans and
home mortgages are frequently of the fixed-payment type
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets
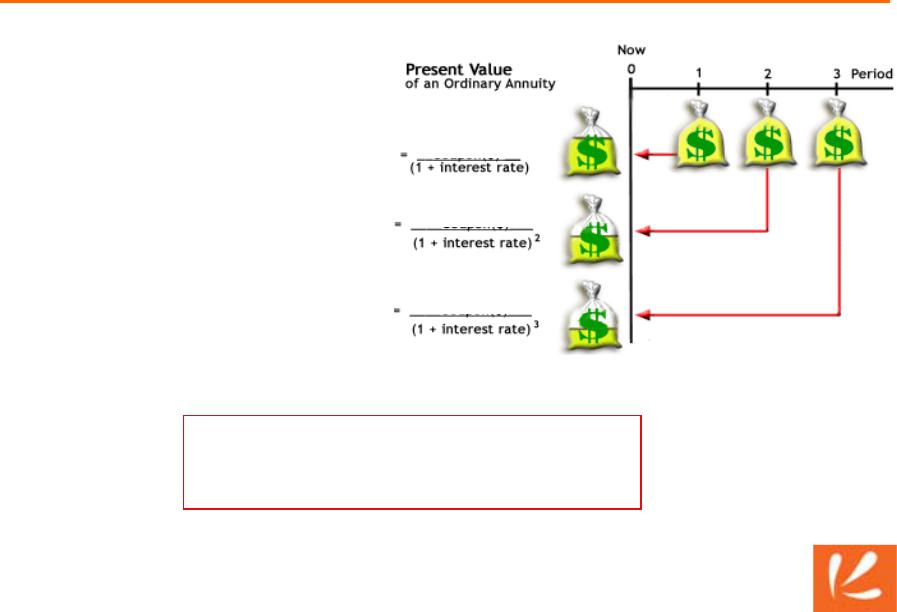
Fixed-payment loans
•Each bag = payment
•Each payment consist of interest payment and principal payment
•PV decreases further in future because future money worth less
PV1 Payment
PV2 Payment
PV3 Payment
|
PV |
PMT |
|
PMT |
... |
PMT |
|
|
|
1 i 1 |
1 i 2 |
1 i n |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets

Fixed-payment loan
•You have borrowed RUR 10,000 with the annual interest rate of 12% (monthly interest rate is 1%) and you have to make the repayment by two equal monthly payments
–Calculate the monthly payment
–What is the sum of your interest payments?
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets
Fixed-payment loans
•Fixed payment loan parameters usually are calculated using financial calculators and computer programs
•Helpful soft – MS Excel (functions):
–PMT (ПЛТ) – sum of payment
–RATE (СТАВКА) – interest rate
–NPER (КПЕР) – number of payments
–PV (ПС) – present value (loan principal)
|
|
(1 i) |
n |
|
||
• For manual calculations: |
PV PMT |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
i |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets

Quantitative problem (11)
•You are taking out a RUR 7 500 000 mortgage loan to be repaid over 20 years in monthly payments.
–If the interest rate is 15% per year what is the amount of the monthly payment?
–If you can only afford to pay RUR 70 000 per month, how large a loan could you take?
–If you can afford to pay RUR 150 000 per month and need to borrow 7 500 000, how many months would it take to pay off the mortgage?
–If you can pay RUR 150 000 per month, need to borrow
RUR 7 500 000, and want a 20 year mortgage, what is the highest interest rate you can pay?
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets

Discount bonds
•A discount bond (also called a zero-coupon bond) is bought at a price below its face value (at a discount), and the face value is repaid at the maturity date
•A discount bond does not make any interest payments; it just pays off the face value
•Discount bonds are convenient because they only involve one payment
•Well-known examples:
–TB, treasury bills (US)
–GKO, government short-term obligations (Russia)
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets

Discount bonds
•A 90 Day T-Bill is currently selling for $99,70. Calculate its yield to maturity.
i YTM |
100 99,70 |
0,003 0,3% |
||
|
99,70 |
|||
|
|
|||
Annualized YTM 0,3% 4 1,2%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i |
YTM |
F P |
|
|
Annualized YTM |
F P |
|
365 |
|
|
P |
P |
n |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets

Discount bonds
Consider a 1-year, $100 discount bond with a price of $98.00
YTM 100 98,00 100% 2,0% 98,00
Now, consider the same 1-year, $100 discount bond with a price of $94.00
YTM 100 94,00 100% 6,4% 94,00
Higher bond prices are associated with lower YTM!!
Moscow State University Business School
Financial Markets
