
Automatic welding
.docRole of automatic welding.
Automatic welding, by MIG, pulse and C02 processes, now plays an important part in welding fabrication practice. It enables welds of consistently high quality and accuracy to radiographic standard to be performed at high welding speeds because of the close degree of control over the rate of travel and nozzle-to-work distance. It is less tolerant than semi-automatic welding to variations of root gap and fit-up but reduces the number of start-stop breaks in long sequences.
Essence of automatic welding.
The choice between semiautomatic and automatic process becomes a question of economics, involving the length of runs, number involved, volume of deposited metal if the sections are thick, method of mechanization and set-up time. The torches are now usually air cooled even for currents up to 450 A and are carried on welding heads fitted with controls similar to those used for semiautomatic welding, and may be remote controlled (Fig, 2.20).
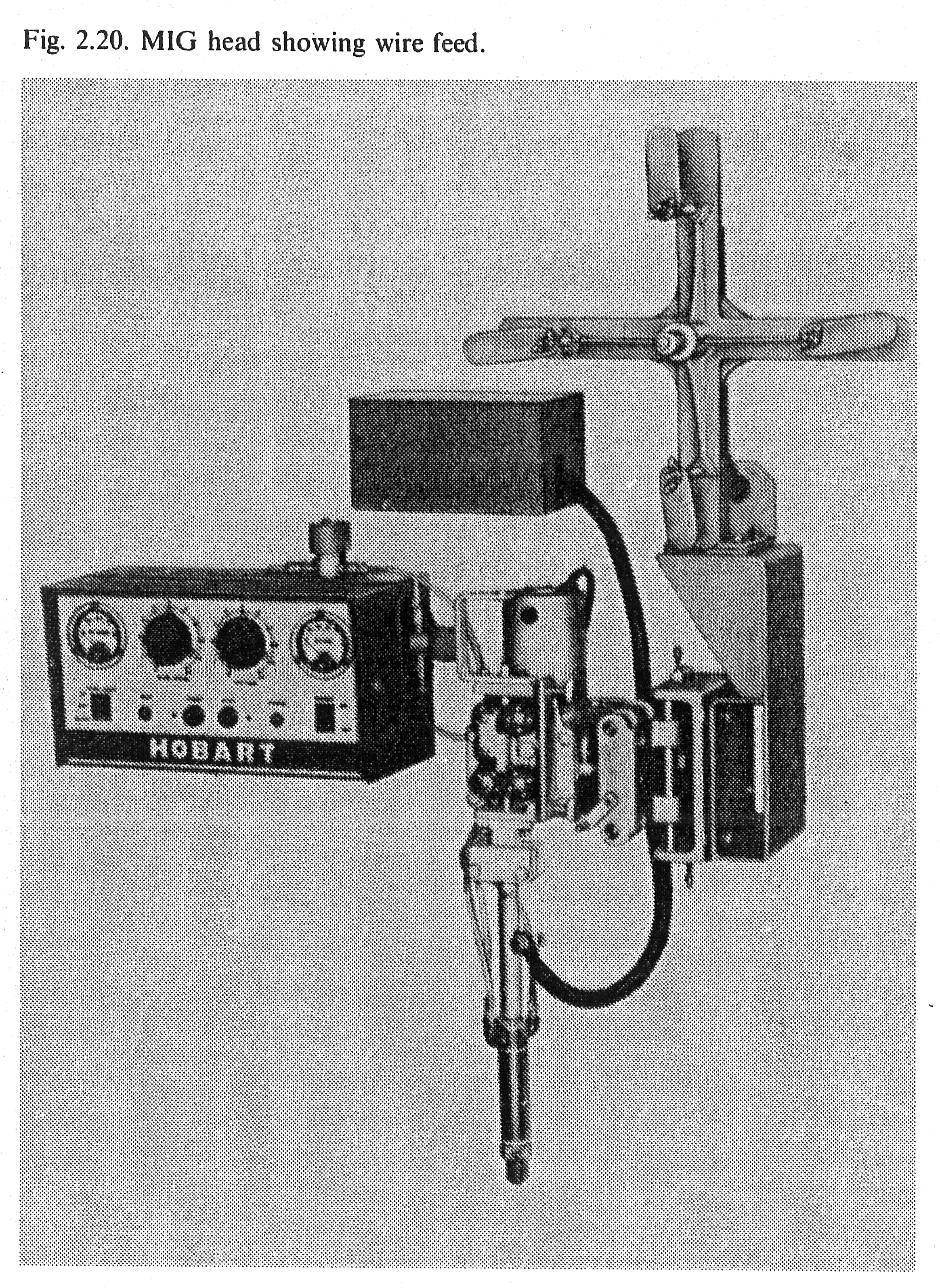
The head may be: (1) fixed, with the work arranged to move or be rotated beneath it, (2) mounted on a boom and column which can either be of the
Fig. 2.19. (a) Unprepared fillets, {b) multi-run prepared fillets in thick plate, (c) \ deep preparation fillets, (d) multi-run unprepared fillet. CO, welding.
positioning type in which the work moves, or the boom can traverse over the work (Figs. 2.2 la and b), (3) gantry mounted so as to traverse over the stationary work, (4) tractor mounted, running on guide rails to move over the fixed work, (5) mounted on a special machine or fixture designed for a specific production. A head may carry two torches arranged to weld simultaneously, thus greatly reducing the welding time.
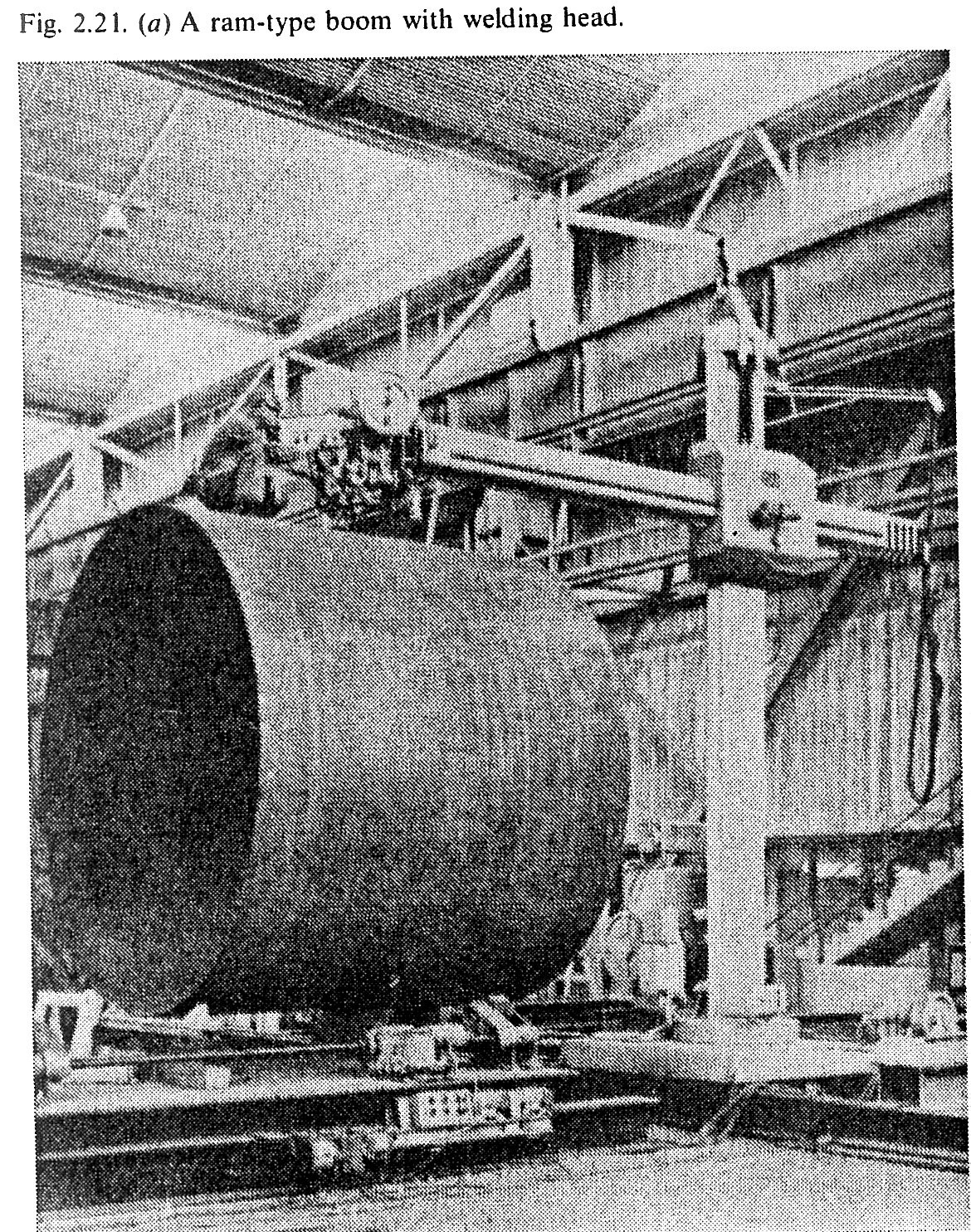
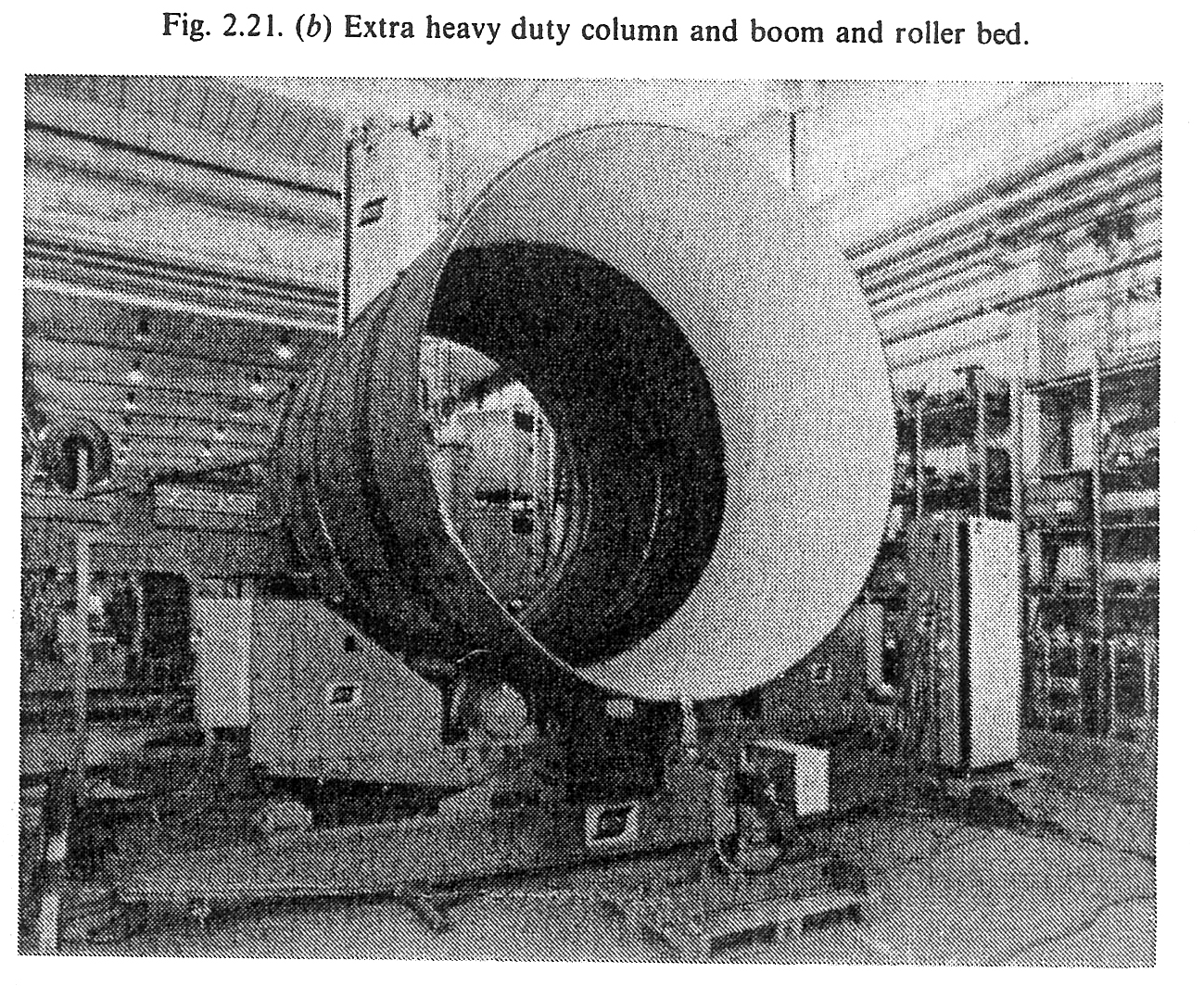
The description welding process.
For the C02 process in steel a typical example would be with wire of 1.2 mm diameter using 150-170 A on thinner sections and multiple passes up to 30 on thicknesses up to 75 mm with current in the 400-500 A range and 2.4 mm wire. With automatic surge (pulse) arc welding on stainless steel, accurate control of the underbead is achieved, obviating the necessity for back-chipping and sealing run. In the case of aluminium welding on plate above 10 mm thickness the accuracy of the underbead produced with the MIG automatic process results in more economical welding than by the double-operator vertical TIG method. In general the full automation of these processes results in greater productivity with high-quality welds.
Robot welding
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to: navigation, search

Spot welding: KUKA industrial robots welding a car body in the white section of a production line.[1]
Robot welding is the use of mechanized programmable tools (robots), which completely automate a welding process by both performing the weld and handling the part. Processes such as gas metal arc welding, while often automated, are not necessarily equivalent to robot welding, since a human operator sometimes prepares the materials to be welded. Robot welding is commonly used for resistance spot welding and arc welding in high production applications, such as the automotive industry.
Robot welding is a relatively new application of robotics, even though robots were first introduced into US industry during the 1960s. The use of robots in welding did not take off until the 1980s, when the automotive industry began using robots extensively for spot welding. Since then, both the number of robots used in industry and the number of their applications has grown greatly. Cary and Helzer suggest that, as of 2005, more than 120,000 robots are used in North American industry, about half of them pertaining to welding. Growth is primarily limited by high equipment costs, and the resulting restriction to high-production applications.
Robot arc welding has begun growing quickly just recently, and already it commands about 20% of industrial robot applications. The major components of arc welding robots are the manipulator or the mechanical unit and the controller, which acts as the robot's "brain". The manipulator is what makes the robot move, and the design of these systems can be categorized into several common types, such as the SCARA robot and cartesian coordinate robot, which use different coordinate systems to direct the arms of the machine.
The technology of signature image processing has been developed since the late 1990s for analyzing electrical data in real time collected from automated, robotic welding, thus enabling the optimization of welds.
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ АГЕНСТВО ПО ОБРАЗОВАНИЮ
Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования
«ТОМСКИЙ ПОЛИТЕХНИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
Реферат по английскому языку
Automatic welding.
Выполнил: студент гр. 4а76
Волошин И. В.
Проверил: преподаватель
Казарян А. Г.
Томск 2009
