
- •Form of government in the UK
- •FORM OF GOVERNMENT
- •THEFORMOFTHESTATE
- •Three branches of government
- •The legislative branch
- •The executive branch
- •The judicial branch
- •Political parties
- •Conservative Party
- •Labour party
- •Liberal Democrats
- •Electoral System of the UK
- •Government and personality
- •Thank you for attention

Form of government in the UK
Подготовили Мария Бару, Левина Софья, Ксения Федорченко, Полина Штерн

FORM OF GOVERNMENT
IN THE UK
The United Kingdom is a democratic constitutional monarchy. The monarch is Head of State and the Prime Minister is the head of Government.
The constitution is uncodified, being made up of constitutional conventions and various elements of statutory law.
The Sovereign formally appoints the Prime Minister, who, by convention, is the leader of the majority party in the House of Commons. Other ministers are appointed by the Sovereign on the advice of the Prime Minister. They make up the Government and act as political heads of the various Government Departments.

THEFORMOFTHESTATE
STRUCTURE
The form of the state structure of The United Kingdom is a quasi-unitary state, where three of the four constituent countries (Scotland, Northern Ireland, Wales) have the rights of limited autonomy since the end of the XX century.
A quasi-unitary state is characterized by the following features :
1) All power belongs to the Parliament.
2) There is no formally adopted constitution and no constitutional separation of powers.
3) It is considered unitary, since the Westminster Parliament is considered the only source of power.
4) The Kingdom is considered a legislative union (England, Scotland and Ireland).
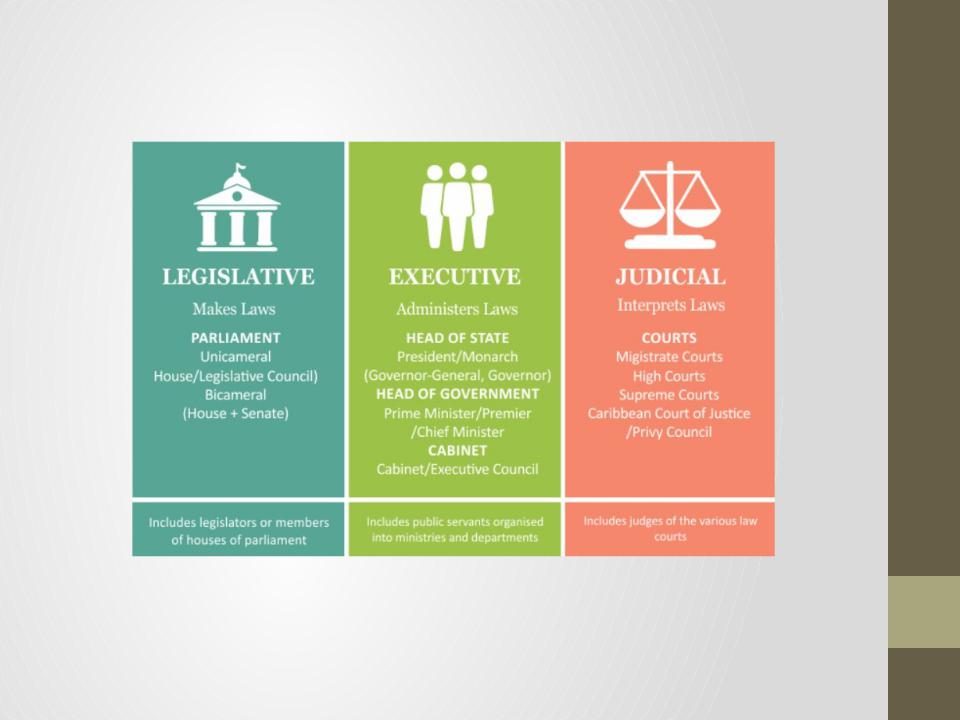
Three branches of government
In the UK , as in Russia, there are three branches of government : legislative executive and judicial.

The legislative branch
The legislative power of Great Britain is represented by the Parliament, which includes the House of Commons and the House of Lords.
Members of the House of Commons are elected by the districts into which the UK is divided.
The House of Lords consists of hereditary members, bishops of the Anglican Church, and appointed life members.
The UK’s legislative system includes the Scottish Parliament, the Northern Ireland Assembly and the National Assembly for Wales.
The House of Lords
The House of Commons

The executive branch
The executive branch in Britain is represented by the Government and ministries, which are called "government departments".
Currently, there are about 25 departments in the UK Government with the status of ministries. As a rule, they are headed by ministers whose positions are referred to as "Secretary of State". Administrative work within each ministry is headed by a "permanent secretary".

The judicial branch
The judicial system of Great Britain differs in that they turn not to the law, but to precedent, when considering cases.
Since the UK was formed on the basis of the union of several countries, there is no single judicial system. There are now three independent systems of law in the country: English law, Northern Ireland law and Scots law.

Political parties

Conservative Party
Members of the House of Commons: 365
Members of the House of Lords: 242
Scottish Parliament: 31
Welsh Assembly: 11
The Conservative Party, officially the "Conservative & Unionist Party", and commonly known as "The Tory Party" or "the Tories" is one of the two largest political parties in the United Kingdom. Generally standing for lower taxation, a smaller state and lower welfare, the Conservative Party is the traditional right-wing party in the UK. Notable figures include Winston Churchill, Margaret Thatcher, David Cameron, Theresa May, and Boris Johnson.
Immigration: Reduce immigration
Economy: Boost the economy by reducing taxes for all, including the wealthy. Reduce bureaucracy
Health: Provide an extra £20.5 bn a year for the health service.

Labour party
Members of the House of Commons: 202
Members of the House of Lords: 183
Scottish Parliament: 23
Welsh Assembly: 29
The Labour Party is the other main party. Founded as a socialist party, the Labour Party had a huge role in the creation of the Welfare State and the National Health Service. After nearly two decades of Conservative rule, the Labour Party moved much closer to the centre, stepping away from its socialist roots and becoming a "big tent" centrist party. Former leader Jeremy Corbyn, while restoring self- belief among the party faithful, appeared less popular among the general public - and they're the ones who decide elections. Notable Labour figures include Clement Attlee, Tony Blair, Gordon Brown, Jeremy Corbyn, Keir Starmer and a wealth of celebrity supporters.
Immigration: Keep the immigration that is vital for parts of the British economy
Economy: Reduce taxes for 95% of the population, but increase them for the top 5%. Renationalise parts of the economy, notably the railways. Abolish tuition fees for university students
Health: Provide an extra £26 bn a year for the health service
