
- •II курс, семестр IV, лекция IV
- •Cardiac cycle
- •Phases of ventricular systole
- •Cardiac cycle
- •Ventricular diastole
- •Auscultation of the heart
- •Rules of auscultation
- •Additional maneuvers
- •Points of auscultation
- •Points for auscultation
- •Auscultation of the heart
- •Auscultation of the heart
- •Process of Auscultation
- •Process of Auscultation
- •S1 (systolic )
- •Factors that may influence the intensity of S1
- •S2 (diastolic)
- •Factors that may influence the intensity of S2
- •Differences between S1 and S2
- •Specific features of auscultation
- •I и II тоны
- •Changes of heart sounds
- •Physiological causes of cardiac sounds changes
- •Extracardiac causes of sound changes
- •Intensity of S1
- •Влияние длительности интервала PR на
- •Changes of S2
- •Decreased intensity of both sounds
- •Splitting of S1
- •Physiological split of S2
- •Physiological split of S2
- •Pathological split of S2
- •Paradoxical split of S2
- •Extra sounds
- •Добавочный IV тон
- •Summation gallop (triple rhythm)
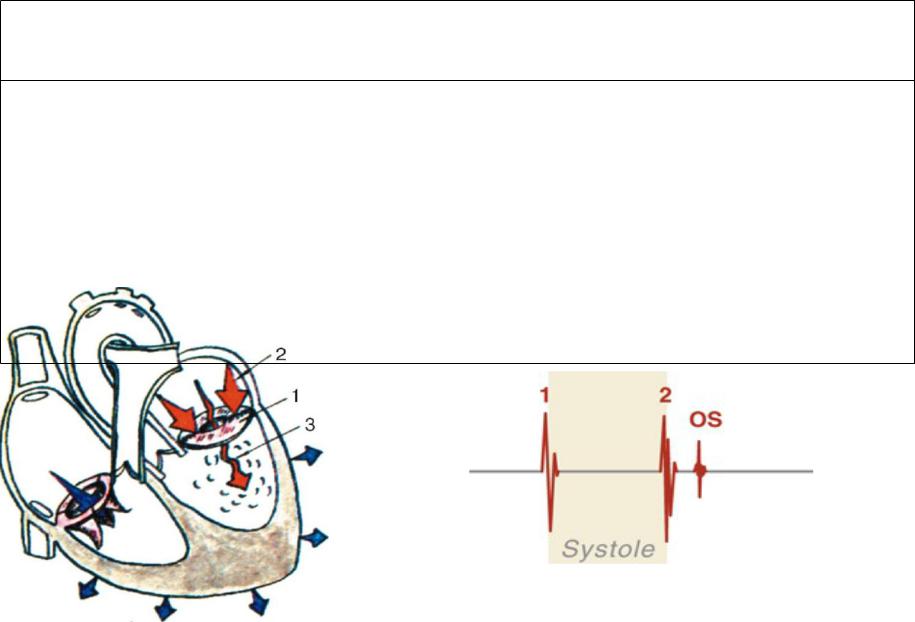
- •Opening snap of mitral stenosis
- •Opening snap of mitral stenosis
- •Triple rhythm in mitral stenosis
- •Opening snap of mitral valve
- •Heart murmurs
- •Mechanisms of murmurs
- •Classification of murmurs
- •Description of murmurs
- •Grading the intensity of murmurs
- •Functional (innocent) murmurs
- •Functional murmurs
- •Pathologic murmurs
- •Etiology of systolic murmurs
- •Types of systolic murmurs
- •Mitral valve insufficiency
- •Etiology of diastolic murmurs
- •Types of diastolic murmurs
- •Aortic insufficiency
- •Extracardiac murmurs
- •Pulse and blood pressure
- •Arterial pulse
- •Palpation of the pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Assessment of pulse
- •Assessment of pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Properties of arterial pulse
- •Assessment of the pulse on peripheral arteries
- •Assessment of the pulse on peripheral arteries
- •Auscultation of the arteries
- •Blood pressure measurement
- •Methods of BP measurement
- •Н.С.Коротков
- •The auscultatory method is commonly used in medical practice. The method was proposed
- •BP measurement
- •Rules of BP measurement
- •Rules of BP measurement
- •BP measurement
- •Classification of BP levels in adults
- •Arterial hypertension
- •Arterial hypotension
- •Methods of BP measurement
- •Diagnosis of arterial hypertension
- •Applanation tonometry
- •Applanation tonometry is a gold standard of central BP measurement
- •Methods of arterial compliance measurement
- •Спасибо за внимание
- •Выберите положение, верное в отношении I тона:
- •О чем свидетельствует выявляемый во время аускультации «ритм перепела»?
- •Физиологическое ослабление обоих тонов сердца наблюдается при ожирении
- •Для парадоксального расщепления II тона НЕ верно
- •Какие ошибки в измерении клинического АД
Opening snap of mitral stenosis
Phase |
Mechanism |
Causes |
Opening of mitral valve |
Commissures |
between |
Mitral stenosis |
|
|
mitral valve leaflets |
|
||
|
Blood |
portion |
Порция |
|
|
крови |
из ЛП с большой |
||
|
силой |
ударяет |
в |
|
|
сросшиеся |
створки |
||
|
клапана |
|
|
|
At the apex
Triple rhythm in mitral stenosis
1.Loud S1 2.Normal S2
3.Opening snap of mitral stenosis
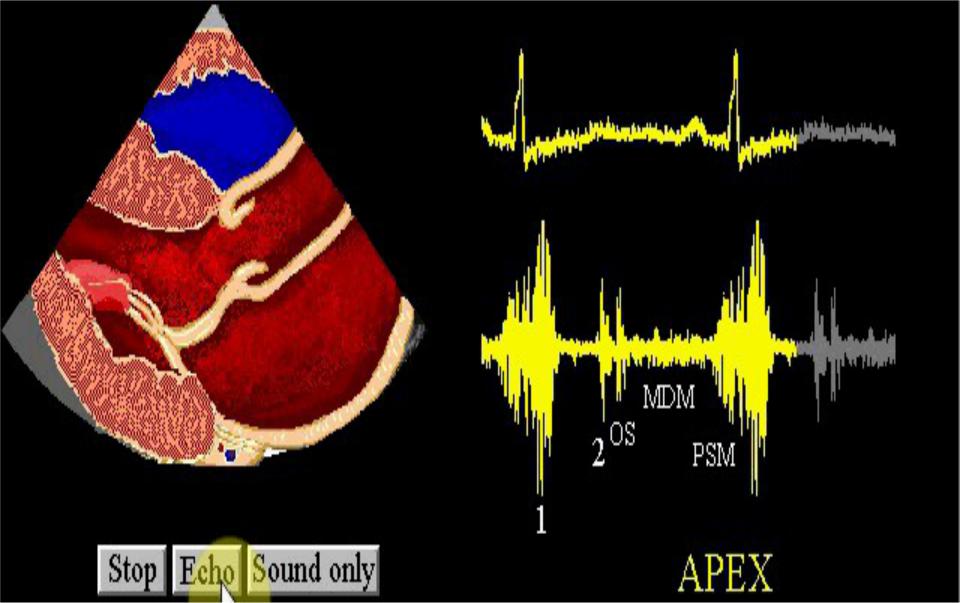
Opening snap of mitral valve
Heart murmurs
Mechanism: turbulent blood flow in the heart
Causes:
•Valve abnormalities
•Rapid blood flow
•Low blood viscosity
Mechanisms of murmurs
Comissures between valvular leaflets => incomplete opening of the valves
area or enlargement of valvular orifice => blood regurgitation
Septal defects
blood velocity
blood viscosity
Classification of murmurs
Cardiac
Pathologic |
Functional |
|
Valve |
(innocent) |
|
Anemic |
||
diseases |
||
Atrial and |
Thyrotoxicosis |
|
ventricular septal |
Fever |
|
defects |
Extra cardiac
Pericardial friction rub
Pleuropericardial rub
Vascular diseases (aneurisms, stenosis)
Description of murmurs
•Timing in the cardiac cycle (systolic, diastolic)
•Location
•Radiation
•Duration
•Intensity
•Pitch
•Quality (soft, rude)
•Relationship to respiration
•Relationship to body position
Grading the intensity of murmurs
•Grade 1 just audible with a good stethoscope in a quiet room
•Grade 2 quiet but readily audible with a stethoscope
•Grade 3 easily heard with a stethoscope
•Grade 4 a loud, obvious murmur with chest vibration
•Grade 5 very loud, heard not only over the precordium but elsewhere in the chest
•Grade 6: very loud, heard not only over the precordium but elsewhere in the body
Functional (innocent) murmurs
•Normal structure of the heart (valves)
•Only systolic
•Usually midsystolic
•Without radiation
•Quiet, soft
•Variable, short
Causes
•Fast blood flow o Fever
o Thyrotoxicosis
•Low viscosity
o Anemia

Functional murmurs
Dynamic |
Anemic |
Relative valvular |
Relative valvular |
|
|
insufficiency |
stenosis |
|
blood |
|
blood |
|
Enlargement of |
Coombs |
murmur |
|
|
velocity |
|
viscosity |
|
fibrous annulus |
|||
|
|
|
(relative stenosis of |
|||||
|
thyrotoxicosis |
|
Rapid |
|
Ventricular |
|||
left atrio-ventricular |
||||||||
|
fever |
|
bloodflow |
|
dilation |
|||
|
|
valve) |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
