
polunina_ln_bobrovskaia_im_priroda_nauka_tekhnologii
.pdfWRITING
12. Put the words in the box into the correct category below. Can you name any more words?
athlete |
helmet |
ring |
umpire |
field |
|
gym |
referee |
team |
court |
players |
|
racket |
squad |
club |
pitch |
skis |
|
spectator |
bat |
net |
saddle |
goggles |
|
ball |
kit |
rink |
venue |
pool |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
People |
|
Places |
|
|
Equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. Complete the sentences with the words in the box.
supporters |
whistle |
stadium |
football |
referee |
goalkeeper |
players |
|
1.____________ is the most popular team sport in the world.
2.A ____________ tries to stop goals.
3.When the ____________ blows the ____________ the match is over.
4.A football team has eleven ____________ .
5.Football ____________ usually wear scarves and T-shirts of their teams.
6.You go to a football ____________ to see a football match.
14. Do the crossword puzzle.
91
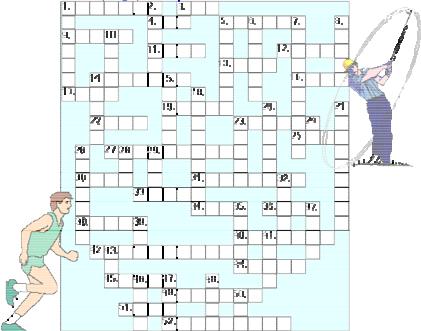
Across |
Down |
||||
1. |
Exercises before a game |
1. |
Opposite of losers |
||
3. |
Track ___ field |
2. Game played with a black & white |
|||
4. |
Three strikes and you are ___ |
ball |
|
||
5. |
Olympic water event |
3. |
Meet you ___ the ballpark |
||
9. |
Opposite of nephew |
5. |
Bounce the ball in basketball |
||
11. |
Umpires make this |
6. |
___ ball |
||
12. |
Playground equipment |
7. |
Where you play golf |
||
13. |
Let’s play ___ |
8. |
Track and ___ |
||
14. |
The best hit you can make in |
10. |
You paddle this |
||
baseball |
14. |
In basketball you shoot these |
|||
16. |
Opposite of hot |
15. |
Final decision maker in a game |
||
17. |
You wear this on your foot |
18. |
Bats and ___ |
||
19. |
Home ___ |
20. |
Game played on a court with |
||
22. |
Give the ball to someone else |
racquets |
|||
23. |
The crowd does this |
21. |
Game played with a ‘birdie’ |
||
25. |
The game was ___ out |
23. |
American spelling of colour |
||
|
|
|
92 |
|
|
27. |
A sport that involves dribbling |
24. |
I’m ___ happy! |
30. |
Relay ___ |
26. |
You need to do this to your |
31. |
A sport played on a field |
muscles before you play |
|
33. |
Athletes need this to be good at |
28. |
Highest card |
their sport |
29. |
Move the ball with your feet |
|
34. |
Give it a ___ (a try) |
32. |
Points for each side |
36. Tees, clubs and greens are part of |
35. |
Take ___ , share |
|
this sport |
37. |
Your shoes cover them |
|
38. |
A director of athletics |
39. |
___ , skip and jump |
40. |
Rule keeper of the game |
41. |
___ me to you |
42. |
Working together |
43. |
Belonging to us |
44. |
Hockey is a ___ |
46. |
Swimmers swim these |
45. |
All sports have these |
47. |
___ a song |
49. |
Baseball has nine of these |
48. |
To look for and get back |
51. |
Twirl |
50. |
A small space between the teeth |
52. |
Be a ___ ___ |
|
|
KEY WORDS
achievement, athletics, baseball, basketball, bodybuilding, capability, climbing, compete, competition, competitor, cricket, curling, cycle racing, diving, dressage, entertainment, equipment, exercise, figure skating, game, golf, gymnastics, hockey, horse racing, judo, jumping, karate, kung fu, leisure, lose, motor racing, opponent, participant, physical activity, physical condition, play, recreation, rowing, running, skiing, skill, soccer, sports, sportsman, swimming, Tai chi, take part in, tennis, volleyball, weightlifting, win, wrestling
SUPPLEMENTARY READING
Olympic Games
(1) Olympic Games, international sports competition, held every four years at a different site, in which athletes from different nations compete against each other in a variety of sports. There are two types of Olympics, the Summer Olympics and the Winter Olympics. Through 1992 they were held in the same year, but beginning in 1994 they were rescheduled so that they are held in alternate even-numbered years. For
93
example, the Winter Olympics were held in 1994 and the Summer Olympics in 1996.
(2)The modern Olympic Games began in Athens, Greece, in 1896, two years after French educator Pierre de Coubertin proposed that the Olympic Games of ancient Greece be revived to promote a more peaceful world. The program for the 1896 Games, including only summer events (the Winter Olympics were not established until 1924), included about 300 athletes from fewer than 15 countries competing in 43 events in nine different sports.
(3)The Olympic Games are administered by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), which is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland. The IOC was created in 1894 in Paris, France, as an independent committee selecting its own members. Although the Olympic Charter, the official constitution of the Olympic movement, proclaims that the Olympics are contests among individuals and not among nations, the IOC assigns to the various NOCs (National Olympic Committees) the task of selecting national Olympic teams.
(4)Although Coubertin opposed the participation of women in the Olympics and no women competed in 1896, a few female golfers and tennis players were allowed to participate in the 1900 Games. Female swimming and diving were added to the 1912 Games, and female gymnastics and track-and-field events were first held at the 1928 Games. Women’s Olympic sports have grown significantly since then, and currently women account for approximately half of the members of teams, except in teams from Islamic nations, where the level of female participation is generally lower.
(Abridged from Microsoft Encarta, 2008)
1. Read the text and decide whether the following statements are TRUE, FALSE or there is NO such INFORMATION in the text.
1. |
In selecting the site of the Olympic Games, the IOC |
|
considers a number of factors. |
_______ |
|
2. |
The first modern Olympic Games included summer |
|
events only. |
_______ |
|
3. |
The Olympic Charter declares that the Olympics are |
|
competitions among nations and not among individuals. |
_______ |
|
|
94 |
|
4. The Summer Olympics and the Winter Olympics have |
|
always been held in odd-numbered years. |
_______ |
2. Decide which part of the text contains the following information.
1.Sportswomen account for almost half of the members of teams at the Olympics.
2.The National Olympic team is selected by the National Olympic Committee of a country.
3.Give the answer to the following question.
What did the program for the 1896 Games include?
1.The program for the 1896 Games, including only summer events, included about 300 athletes from more than 15 countries competing in 43 events in nine different sports.
2.The program for the 1896 Games, including only winter events, included about 300 athletes from fewer than 15 countries competing in 43 events in nine different sports.
3.The program for the 1896 Games, including only summer events, included about 300 athletes from less than 15 countries competing in 43 events in nine different sports.
4.The program for the 1896 Games, included about 300 athletes from less than 15 countries competing in 43 events in ten different sports.
4. What is the main idea of the text?
1.Many sportsmen around the world take part in the Olympic Games.
2.Olympic Games is an international sports competition.
3.The main aim of the modern Olympic Games is to promote a more peaceful world.
4.The main aim of the modern Olympic Games is to promote sports.
95
UNIT 8
MATHEMATICS
WARMING UP
1.What springs to mind when you hear the word ‘mathematics’?
2.What is maths useful for nowadays if we have computers and calculators?
3.How many different branches of mathematics do you know of?
4.Is it possible that two plus two equals five?
READING
Mathematics is the study of quantity, structure, space, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns, formulate new conjectures, and establish truth by rigorous deduction from appropriately chosen axioms and definitions.
Through the use of abstraction and logical reasoning, mathematics evolved from counting, calculation, measurement, and the systematic study of the shapes and motions of physical objects. Practical mathematics has been a human activity for as far back as written records exist.
Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind, although practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered.
Mathematics can, broadly speaking, be subdivided into the study of quantity, structure, space, and change (i.e. arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and analysis). In addition to these main concerns, there are
96
also subdivisions dedicated to exploring links from the heart of mathematics to other fields: to logic, to set theory (foundations), to the empirical mathematics of the various sciences (applied mathematics), and more recently to the rigorous study of uncertainty.
The study of quantity starts with numbers, first the familiar natural numbers and integers (‘whole numbers’) and arithmetical operations on them, which are characterized in arithmetic. The deeper properties of integers are studied in number theory, from which come such popular results as Fermat’s Last Theorem. Number theory also holds two problems widely considered to be unsolved: the twin prime conjecture and Goldbach’s conjecture. As the number system is further developed, the integers are recognized as a subset of the rational numbers (‘fractions’). These, in turn, are contained within the real numbers, which are used to represent continuous quantities. Real numbers are generalized to complex numbers.
Many mathematical objects, such as sets of numbers and functions, exhibit internal structure as a consequence of operations or relations that are defined on the set. Mathematics then studies properties of those sets that can be expressed in terms of that structure; for instance number theory studies properties of the set of integers that can be expressed in terms of arithmetic operations. Moreover, it frequently happens that different such structured sets (or structures) exhibit similar properties, which makes it possible, by a further step of abstraction, to state axioms for a class of structures, and then study at once the whole class of structures satisfying these axioms. Thus one can study groups, rings, fields and other abstract systems; together such studies (for structures defined by algebraic operations) constitute the domain of abstract algebra.
The study of space originates with geometry – in particular, Euclidean geometry. Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles and with the trigonometric functions; it combines space and numbers, and encompasses the well-known Pythagorean theorem. The modern study of space generalizes these ideas to include higher-dimensional geometry, non-Euclidean geometries (which play a central role in general relativity) and topology.
Understanding and describing change is a common theme in the
97
natural sciences, and calculus was developed as a powerful tool to investigate it. Functions arise here, as a central concept describing a changing quantity. The rigorous study of real numbers and functions of a real variable is known as real analysis, with complex analysis the equivalent field for the complex numbers. Functional analysis focuses attention on (typically infinite-dimensional) spaces of functions. One of many applications of functional analysis is quantum mechanics. Many problems lead naturally to relationships between a quantity and its rate of change, and these are studied as differential equations. Many phenomena in nature can be described by dynamical systems; chaos theory makes precise the ways in which many of these systems exhibit unpredictable yet still deterministic behavior.
(Abridged from Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia)
Expand your vocabulary
conjecture – гипотеза, догадка, предположение encompass – заключать (в себе)
inspire – способствовать, влиять infinite-dimensional – бесконечномерный
twin primes – простые числа, разность между которыми равна 2 rigorous – строгий (о доказательстве)
precise – точный; определенный
unpredictable – непредсказуемый; непрогнозируемый
POST-READING ACTIVITY
1. Answer the following questions.
What does mathematics study?
What is the difference between pure and applied mathematics?
Who formulated the most famous and mysterious theorem in the history of mathematics? Which field of maths does it belong to?
What mathematical objects are studied by abstract algebra?
What concepts are used to describe a relation between two sets? Why is the study of changing quantity so important nowadays?
98
2. English words often have silent consonants. Put the words below into the correct column according to whether or not they have silent consonants. Cross out the silent letters.
addition |
exhibit |
|
represent |
|
applied |
integer |
|
result |
|
chaos |
investigate |
|
science |
|
class |
measurement |
system |
||
contain |
mechanic |
|
term |
|
different |
operation |
|
through |
|
discovery |
powerful |
|
whole |
|
empirical |
property |
|
widely |
|
|
|
|
||
all consonants pronounced |
|
some consonants not |
||
|
|
pronounced |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.Match the words with their meanings.
1.conjecture a. an accepted statement regarded as being self-
evidently true
2.empirical b. a field or scope of knowledge or study
3.statistics c. based on practical experience
4.calculus d. the formation of an opinion on incomplete
information
5.axiom e. a general proposition proved by a chain of reasoning
6.domain f. the science of collecting and analysing numerical data
7.theorem g. a branch of advanced mathematics which deals with
variable quantities
99
4. Fill in the table with the missing degrees of comparison.
|
Comparative degree |
Superlative degree |
|
newer |
|
pure |
|
|
|
|
the most popular |
|
deeper |
|
modern |
|
|
|
|
the worst |
|
wider |
|
|
|
the easiest |
|
further |
|
rigorous |
|
|
5. Transform the following sentences using the Passive voice.
Ex.: Scientists use mathematics in many fields. – Mathematics is used by scientists in many fields.
1.Number theory studies the deeper properties of integers.
2.Mathematicians formulate new conjectures from appropriately chosen axioms and definitions.
3.Real numbers represent continuous quantities.
4.Groups, rings, fields and other abstract systems constitute the domain of abstract algebra.
5.Differential equations can describe the relationships between a quantity and its rate of change.
6.Put questions to the words or word expressions in the bold type.
Number theory also holds two problems widely considered to be unsolved.
The modern study of space includes higher-dimensional geometry, non-Euclidean geometries and topology.
Mathematics can be subdivided into the study of quantity, structure, space, and change.
Functional analysis focuses attention on spaces of functions.
100
