
- •Международных отношений (у) мид рф
- •Кафедра английского языка № 2
- •Основы политической системы сша The Way They Run America москва
- •Introduction
- •Checks and balances
- •In american government president Executive Branch
- •Supreme court and other federal courts
- •Congress Legislative Branch
- •Text 2 Congressional organization
- •Text 3 How a Bill becomes a Law
- •Text 4 What is the role of the lobbyist?
- •For your information… Growth of the United States original thirteen states
- •Read the text “The Constitution” on page __. Do the task which follows the text.
- •Read the extract from The Brethren by John Grisham on page __. Do the task which follows the text.
- •Read the article “The Human Side of Congress” on page __. Do the task which follows the text.
- •The executive
- •The Government of the United States
- •Text 1 The Administration
- •Impeachment
- •For your information…
- •Read the excerpt from “America and Americans” by j. Steinbeck on page __ and do the tasks which follow the text.
- •Read “The Full Text of President Clinton’s tv Address” on page ___ and answer the questions.
- •Read the excerpt from “The Moneychangers” by Arthur Hailey on page __ and answer the questions. Unit 3 the judiciary
- •Justice of the peace courts
- •Street Law. A Course in Practical Law The Adversary System
- •Judges and Juries
- •Lawyers
- •When Do You Need a Lawyer?
- •For your information…
- •Unit 4 the elections
- •The Announcement
- •(Spring) Nominating conventions
- •And primary elections
- •(Summer) National Conventions
- •The Campaign
- •(November) Election Day
- •(December / January) Electoral College Process
- •(January 20) Inauguration
- •What is the difference between popular vote and electoral vote?
- •Which type of vote elects a president?
- •College bound?
- •Everything you ever wanted to know about the Electoral College system - and now have to ask
- •By Matthew Cooper
- •Q. So these electors, who are they?
- •Q. When and how do they vote?
- •Q. Can electors vote how they please?
- •Q. We know it’s the new House that votes. But is it the new Senate?
- •Q. The President pro tempore of the Senate?
- •For your information… Televised Debates: How it All Started …
- •Reader the constitution a New Nation
- •The Constitution and the Bill of Rights
- •The brethren by j. Grisham (an extract)
- •The human side of congress Representative Jim Wright
- •The full text of president
- •How does Bill Clinton’s tv address correspond with John Steinbeck’s description of Americans’ attitude towards their Presidents?
- •By Arthur Hailey
- •By forum easters
- •Rage of angels
- •By Sidney Sheldon
- •By Mark Twain
- •Bibliography
Read the text “The Constitution” on page __. Do the task which follows the text.
Read the extract from The Brethren by John Grisham on page __. Do the task which follows the text.
Read the article “The Human Side of Congress” on page __. Do the task which follows the text.
UNIT 2
The executive
The Government of the United States
|
T |
|


|
LEGISLATIVE BRANCH |
|
EXECUTIVE BRANCH |
|
JUDICIAL BRANCH |
|
|
||||||
|
CONGRESS
the Senate the House of Representatives
|
|
THE PRESIDENT
Executive Office of the President The Vice President |
|
THE SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES United States Courts of Appeal United States District Courts
|
|
|||||||

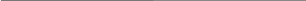
DEPARTMENT OF VETERANS' AFFAIRS 1989 министерство по делам ветеранов |
DEPART-MENT OF AGRI CULTURE 1889 министерство сельского хозяйства |
DEPART-MENT OF COMMERCE
1913 министерство торговли
|
DEPART- MENT OF DEFENSE
1949 министерство обороны |
DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION
1979 министерство образования |
DEPART- MENT OF ENERGY
1977 министерство энергетики |
DEPART- MENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES 1979 министерство здравоохра-нения и социальных служб |
DEPARTMENT OF HOUSING AND URBAN DEVELOPMENT 1965 министерство жилищного строительства и городского развития |
DEPART-MENT OF THE INTERIOR* 1849 министерство внутренних дел |
DEPART-MENT OF JUSTICE
1870 министерство юстиции |
DEPART- MENT OF LABOR
1913 министерство труда |
DEPART- MENT OF STATE
1789 государст-венный департамент (министерство иностранных дел) |
DEPART-MENT OF TRANSPOR-TATION 1965 министерство транспорта |
DEPART-MENT OF THE TREASURY 1789 министерство финансов |
Section 1. Read and Study.
Text 1 The Administration
Read the text and answer the following questions.
What are the responsibilities of the executive branch and its Chief Executive?
What do the newly elected president and the outgoing presidents do between the election and the inauguration?
Describe the forming of the cabinet.
What are the three main duties performed by the Secretaries?
What part of the US government deals with the US’s relations with other countries? Why does this department rank so high in the executive branch?
What are the duties of the Attorney General?
What do you know about the Federal Bureau of Investigation and its activities?
The presidency of the US is the highest governmental office.
The executive branch, which includes the President, the Chief Executive, Vice-President, and the President’s Cabinet, is responsible for administering and executing the laws.
The President must be a natural-born citizen, at least thirty five years old, and for at least fourteen years a resident of the United States.
A presidential term is four years. No person can be elected more than twice. Nor can a President be elected more than once if he has served more than half the term to which another President was elected. For instance, since Gerald Ford assumed office in only the second year of Richard Nixon’s four-year term, Ford could serve as President only one more term.
The President’s chief duties are to carry out the program of the government as directed in the Constitution and in laws made by Congress. In addition, however, he recommends to Congress much major legislation and the amounts of money which should be appropriated to carry out government functions. He also has the right to veto legislation passed by Congress, although Congress in turn may enact legislation over his veto by a two-thirds majority vote. The President is also commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
The newly elected president and vice president are inaugurated (formally sworn in) on January 20 following the election. The inauguration is nationally televised and is followed by a parade and many parties. The president then moves into the White House and appoints members of the Cabinet (the president’s closest advisers, who are also the heads of the various departments of the executive branch). Between the election and the inauguration, the outgoing president meets with the newly elected president and his staff to plan for a smooth transition from one administration to the next. Because the outgoing president is only awaiting the end of his term, he is often referred to as a “lame duck”. Sometimes the new president and the majority of the members of Congress belong to different parties. When this happens, it is more difficult for the president to keep promises made during the campaign.
Since the two major parties are not extremely different, there is seldom a sudden shift in national policy when a new president from a different party takes office. Change occurs only with the passage of time, as the new administration becomes accustomed to its powers.
Presidents are free to select the members of their Cabinets. They often appoint experienced national figures to serve in the Cabinet. Several Cabinet positions, however, are usually reserved for key political advisers.
Each nomination requires Senate approval before the new secretary can be sworn in. Almost all candidates are approved. If heavy opposition develops, the President is more likely to withdraw the nomination than to risk defeat on the Senate floor.
The heads of the executive departments, known as Secretaries perform three main duties:
They manage the affairs of their departments.
They represent their departments in public and before Congress by giving speeches, writing legislation, and testifying before committees.
They advise the President on matters that concern their departments.
When the President’s service ends, it is customary for the Cabinet to resign, so that the new President appoints new chiefs of executive departments.
The State Department. The fourth Act of Congress after adoption of the Constitution was a bill establishing a Department of Foreign Affairs, on July 27, 1789. That is, the State Department ranks ahead of other departments in prestige and seniority.
Among major activities of the State Department are: Embassies and Legations; European Affairs; Far Eastern Affairs; Near Eastern, South Asian and African Affairs; Inter-American Affairs; Bureau of Economic Affairs; International Trade and Resources; International Organizations Affairs; International Cooperation Administration; Mission to the United Nations; Passports and visas.
Political power of the Secretary of State is second only to that of the President. The Secretary of State has the duty of trying to maintain peace and to negotiate economic and political treaties.
An Ambassador is the highest ranking envoy. He is technically the representative of the chief executive. As such he has the right to audience with the head of the nation to which he is accredited. A minister must, on the other hand, deal through the head of the State Department or Foreign Ministry in the country to which he is sent. The minister is generally considered the highest ranking United States emissary in a small country.
The Head of the Department of Justice is the Attorney General who is the chief law-enforcement officer in the United States. He represents the United States in legal matters generally, and gives advice and opinion when requested by the President or by executive-departments heads.
While the President has a special counsel, the White House also calls on the Attorney General for legal advice, particularly on bills and resolutions passed in Congress and sent to the chief executive for his signature. The President also calls on the Attorney General for legal opinions concerning the exercising of special emergency powers.
The Attorney General has a wide discretion about what laws to enforce and about what actions he will regard as violations of the law.
The Solicitor General is the second ranking officer of the Department of Justice assuming the duties of the Attorney General in his absence.
The main unit of the Justice Department is the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). The Bureau is in effect an intelligence agency for the Justice Department, gathering information on criminal matters which come within the jurisdiction of Department. Functions of the FBI include the investigation of espionage, sabotage, and matters pertaining to the internal security of the United States as well as investigations of alleged violations of approximately 100 Federal statutes.
It does the field work of investigating the loyalty of Government employees. Other secret services located in the Treasury, pursue counterfeiters, smugglers, drug-traffickers, income-tax dodgers.
Task 1. Find in the text the English for:
исполнение законов;
вступать в должность;
приводить к присяге (президента);
президент, завершающий срок своих полномочий;
резкое изменение курса государственной политики;
срок полномочий президента;
главный дипломатический представитель (посланник);
иметь право на аудиенцию;
правовые вопросы;
иметь широкие полномочия в чем-либо.
Section 2. Glossary
the Administration |
исполнительная власть, правительство США |
Secretary of State |
государственный секретарь (министр иностранных дел США) |
Secretary of the Treasury |
министр финансов |
Secretary of Defense |
министр обороны |
Attorney General |
генеральный прокурор и министр юстиции |
law-enforcement officer |
представитель правоохранительных структур |
emergency powers |
чрезвычайные полномочия |
to enforce law |
проводить закон в жизнь |
Solicitor General |
заместитель министра юстиции |
Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) |
Федеральное бюро расследований (ФБР) |
to come within the jurisdiction |
подпадать под юрисдикцию |
income-tax dodger |
лицо, уклоняющееся от уплаты подоходного налога |
tax evasion |
уклонение от уплаты налогов |
Section 3. Texts to render and discuss.
Task 1. Read the text and answer the following questions.
What does the term “impeachment” legally apply to? What does it embrace in popular usage?
What is the only judicial power allotted to the US Congress? How do the two Houses divide their authority to bring impeachment charges and try impeached presidents?
Which of the US presidents faced impeachment? What impeachment charges were brought against them?

 HE
CONSTITUTION
HE
CONSTITUTION