
English Lectures / lipids 3 ENG
.pdfKUBAN STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
KUBAN MEDICAL INSTITUTE
DEPARTMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL AND
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
Lipids. Part 3
Krasnodar
2020
Ketone bodies
•During starvation, prolonged physical work, and in cases when cells do not receive enough glucose in the liver, part of the fatty acids turns into ketone bodies, which are oxidized by the brain, nerve tissue, and muscles, providing enough energy for ATP synthesis and reducing glucose consumption.
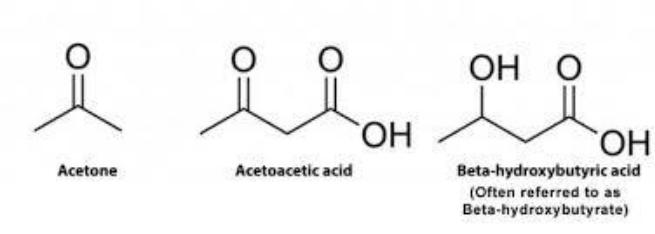
•Ketone bodies include β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone. The first two molecules can be oxidized in the tissues, providing the synthesis of ATP. Acetone is formed only at high concentrations of ketone bodies in the blood and, excreted in urine, exhaled air and then, allows the body to get rid of excess ketone bodies.
Synthesis of ketone bodies in the liver
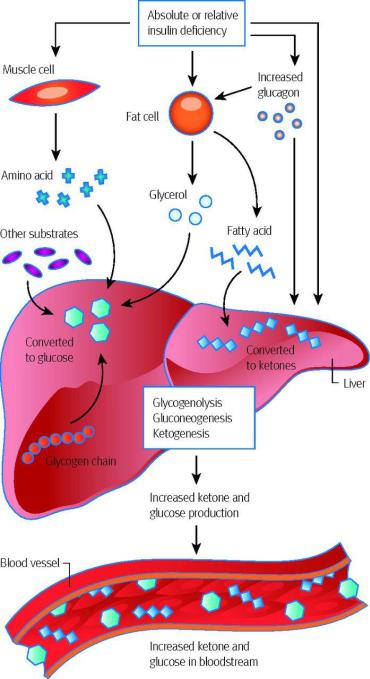
•With a low insulin / glucagon ratio in the blood, fat breakdown is activated in adipose tissue.
•Fatty acids enter the liver in a larger amount than normal, therefore, the rate of β-oxidation increases.
•The rate of CTK reactions under these conditions is reduced, since oxaloacetate is used for gluconeogenesis.
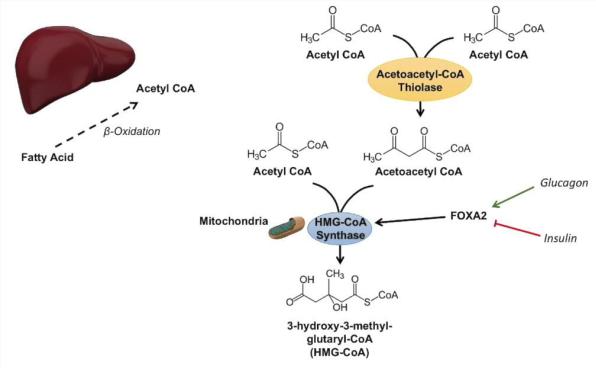
•As a result, the rate of formation of acetyl CoA exceeds the ability of CTK to oxidize it. Acetyl-CoA accumulates in the mitochondria of the liver and is used for the synthesis of ketone bodies.
•The synthesis of ketone bodies occurs only in the mitochondria of the liver.
The regulatory enzyme for the synthesis of ketone bodies (HMG-CoA synthase) is inhibited by free CoA - the reaction is non-enzymatic with a high concentration of ketone bodies in the blood.
Ketoacidosis
•Normally, the concentration of ketone bodies in the blood is 1-3 mg/dL (up to 0.2 mM/L), but with starvation it increases significantly.
•An increase in the concentration of ketone bodies in the blood is called ketonemia, and the secretion of ketone bodies in the urine is called ketonuria.
•The accumulation of ketone bodies in the body leads to ketoacidosis: a decrease in alkaline reserve (compensated acidosis), and in severe cases, to a pH shift (uncompensated acidosis), since ketone bodies (except acetone) are water-soluble organic acids (pK ~ 3.5), capable of dissociation.
Ketoacidosis
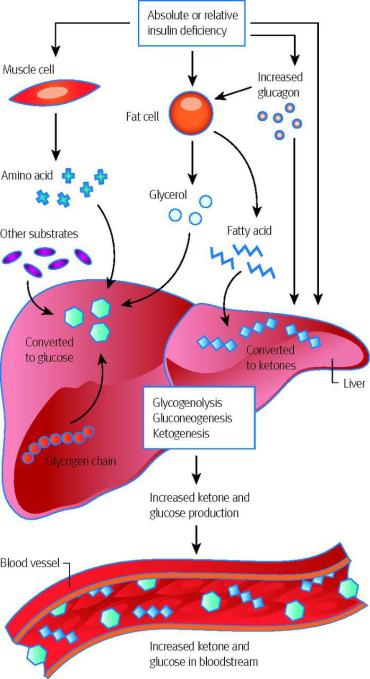
•Acidosis reaches dangerous values in diabetes mellitus, since the concentration of ketone bodies in this disease can reach 400-500 mg/dL.
•Severe acidosis is one of the leading causes of death in diabetes. The accumulation of protons in the blood disrupts the binding of oxygen by hemoglobin, affects the ionization of the functional groups of proteins, disrupting their conformation and function.
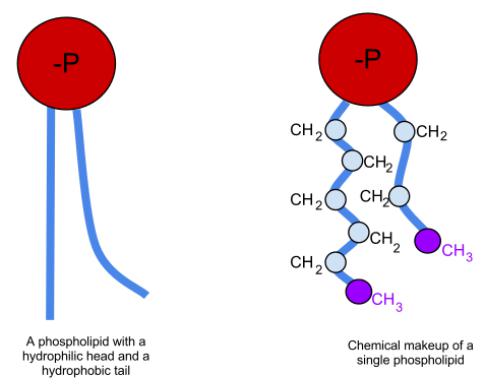
Metabolism of phospholipids
•Unlike triglycerides and fatty acids, phospholipids are not an essential energy material. Phospholipids play an important role in the structure and function of cell membranes, activation of membrane and lysosomal enzymes, in conducting nerve impulses, blood coagulation, immunological reactions, cell proliferation and tissue regeneration processes, in electron transfer to the chain of "respiratory" enzymes. A special role is given to phospholipids in the formation of lipoprotein complexes.
•The biosynthesis of phospholipids occurs intensively in the liver, intestinal wall, testes, ovaries, mammary gland and other tissues. The most important phospholipids are synthesized mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell.
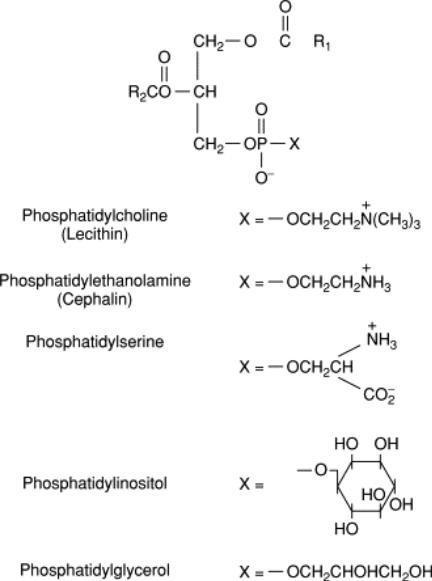
Metabolism of phospholipids
•The central role in the biosynthesis of phospholipids is played by 1,2-diglycerides (in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholines and phosphatidylethanolamines), phosphatidic acid (in the synthesis of phosphatidylinosites) and sphingosine (in the synthesis of sphinhomielins). Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is involved in the synthesis of almost all phospholipids. As an example, consider the synthesis of individual representatives of phospholipids.
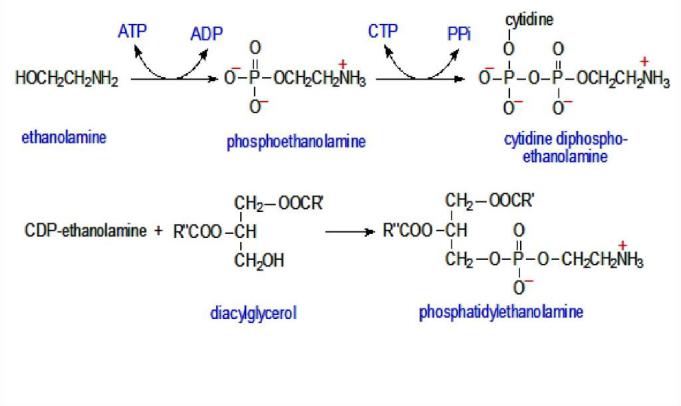
Phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis
1) Ethanolamine is initially phosphorylated with the participation of the corresponding kinase to form phosphoethanolamine.
2) Then phosphoethanolamine interacts with CTP, resulting in the formation of cytidine diphosphate ethanolamine (CDP-ethanolamine) and pyrophosphate (PPi).
3) In the following reaction, CDPethanolamine, reacting with 1,2- diglyceride formed during dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acid, is converted to phosphatidylethanolamine. The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme ethanolamine phosphotransferase.
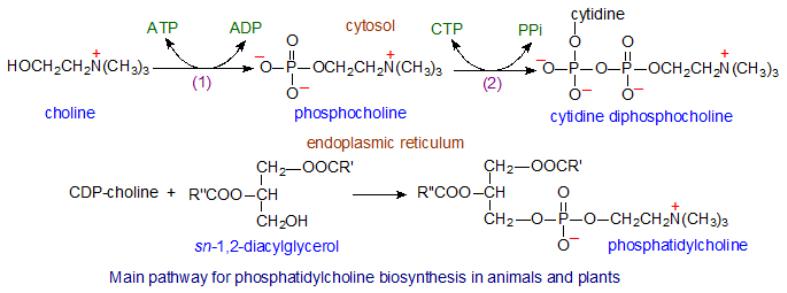
The biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine (lecithin)
• |
Phosphatidylethanolamine is a precursor of |
There is another way of synthesizing phosphatidylcholine in |
|
phosphatidylcholine. As a result of the sequential transfer of animal cells. In this case, as in the synthesis of
three methyl groups from three S-adenosylmethionine molecules to the amino group of the ethanolamine residue, phosphatidylcholine is formed.
phosphatidylethanolamine, CTP is used as a carrier, but not phosphoethanolamine, but phosphocholine.
•At the first stage of synthesis, free choline is activated by choline kinase with the formation of phosphocholine.
•Then phosphocholine reacts with CTP to form cytidine diphosphatecholine (CDP-choline).
•Subsequently, CDP-choline interacts with 1,2-diglyceride, resulting in the formation of phosphatidylcholine.
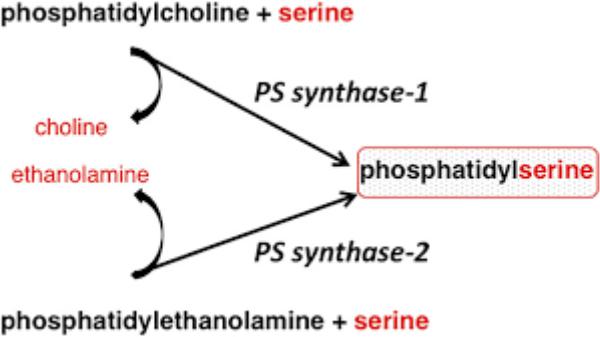
Phosphatidylserine biosynthesis
•In mammals, phosphatidylserine is formed in the reaction of the exchange of ethanolamine to serine in the following way:
