
English Lectures / lipids 3 ENG
.pdf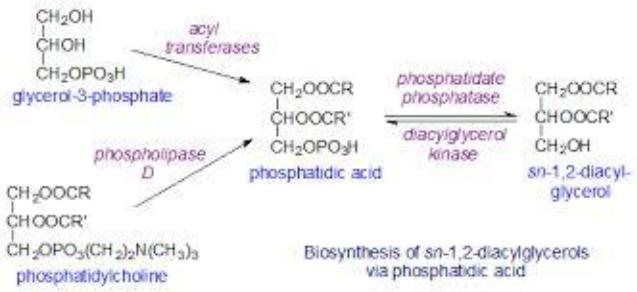
Phosphatidylserine biosynthesis
•There is a second way for the formation of phosphatidylserine, which is associated with the preliminary involvement of phosphatidic acid in the synthesis of phosphoglycerides
•Then, serine is transferred to the phosphatidyl residue to form phosphatidylserine
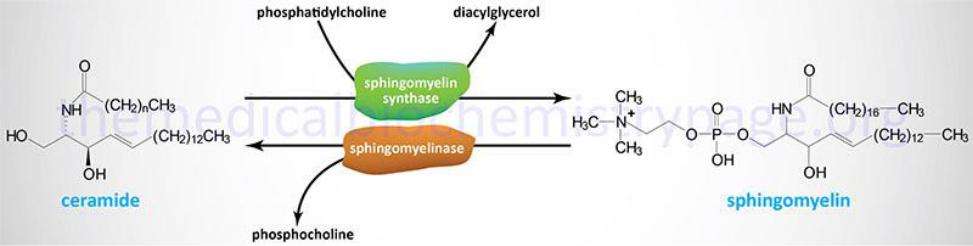
Sphingomyelin biosynthesis
The intermediate in the biosynthesis of sphingomyelin is ceramide (N- acylsphingosine), which is formed by the interaction of sphingosine with acyl-CoA. Sphingomyelin is synthesized as a result of the interaction (reaction) of ceramide with CDP-choline.

Cholesterol
•Cholesterol is a steroid specific to animal organisms. It is synthesized in many human tissues, but the main place of synthesis is the liver. In the liver, more than 50% of cholesterol is synthesized, in the small intestine - 1520%, the rest of the cholesterol is synthesized in the skin, adrenal cortex, and gonads. About 1 g of cholesterol is synthesized per day in the body; 300500 mg comes with food.
Cholesterol function
•it is a part of all cell membranes and affects their properties
•serves as an initial substrate in the synthesis of bile acids and steroid hormones
•precursors in the metabolic pathway of cholesterol synthesis also turn into ubiquinone - a component of the respiratory chain and dolichol involved in the synthesis of glycoproteins
•cholesterol due to its hydroxyl group can form esters with fatty acids
•esterified cholesterol predominates in the blood and is stored in small quantities in some types of cells that use it as a substrate for the synthesis of other substances
•cholesterol and its esters are hydrophobic molecules, so they are transported by blood only as part of different types of drugs.

Atherosclerosis
•Disorders of cholesterol metabolism lead to one of the most common diseases - atherosclerosis. Mortality from the effects of atherosclerosis leads in the overall structure of mortality. Atherosclerosis is a "polygenic disease", i.e. many factors participate in its development, the most important of which are hereditary. The accumulation of cholesterol in the body leads to the development of another common disease - gallstone disease.
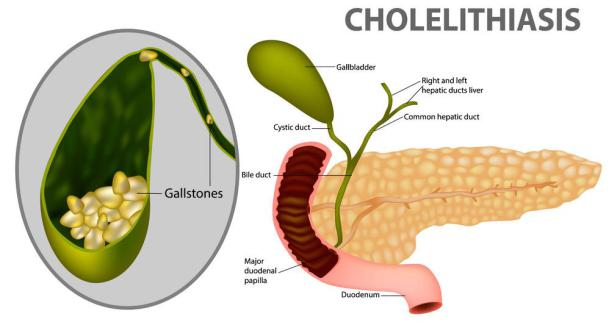
Cholelithiasis
Gallstones form in the gallbladder, less commonly in the bile ducts. The reasons for the formation of stones in the gallbladder are as follows:
•inflammatory changes in the mucosa
•stagnation of bile
•lipid metabolism disorders with an increase in cholesterol and a decrease in bile acids and lecithin in bile (increased lithogenicity of bile)

Cholelithiasis
•Inflammatory changes in the gallbladder mucosa lead to the appearance of microflora in bile, desquamation of epithelial cells, which are the primary nucleus of precipitation. Around these nuclei, cholesterol, salts, i.e. goes through the process of stone formation. Stagnation of bile enhances the precipitation of cholesterol and salts. An important role in stone formation is played by an increase in the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and in bile and a decrease in the content of bile acids in bile. With a decrease in the cholesterol-cholesterol ratio (coefficient), cholesterol precipitates, bile becomes lithogenic. The stones formed in such cases are called cholesterol. They are white or yellow in color, float in water, burn, are not contrast.

Cholesterol synthesis and its regulation
•Cholesterol synthesis reactions occur in the cytosol of cells. This is one of the longest metabolic pathways in the human body.
•All cholesterol carbon atoms come from acetyl-CoA. Squalene - a linear hydrocarbon structure - is converted by the enzyme cyclase into lanosterol containing 4 condensed rings and a hydroxyl group. Through a series of sequential reactions, lanosterol turns into cholesterol (I, II, III - synthesis steps).

Cholesterol esterification
•In some tissues, the hydroxyl group of cholesterol esterifies to form more hydrophobic molecules - cholesterol esters. The reaction is catalyzed by the intracellular enzyme AHAT (acylCoA: cholesterol and transferase).
•The esterification reaction also occurs in the blood in HDL, where the enzyme LHAT is located (lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase). Cholesterol esters are the form in which they are deposited in cells or transported by blood. In the blood, about 75% of cholesterol is in the form of esters.

Regulation of cholesterol synthesis
Regulation of the key enzyme for cholesterol synthesis (HMG-CoA reductase) occurs in different ways.
1) Phosphorylation / dephosphorylation of HMG-CoA reductase. With an increase in the inulin / glucagon ratio, this enzyme dephosphorylates and becomes active. The action of insulin is carried out through 2 enzymes:
•HMG-CoA reductase kinase phosphatase, which turns the kinase into an inactive dephosphorylated state
•HMG-CoA reductase phosphatase by converting it to a dephosphorylated active state. The result of these reactions is the formation of a dephosphorylated active form of HMG-CoA reductase
