
English Lectures / lipids 2 ENG
.pdfKUBAN STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
KUBAN MEDICAL INSTITUTE
DEPARTMENT OF FUNDAMENTAL AND CLINICAL
BIOCHEMISTRY
Lipids. Part 2
Krasnodar, 2020
1
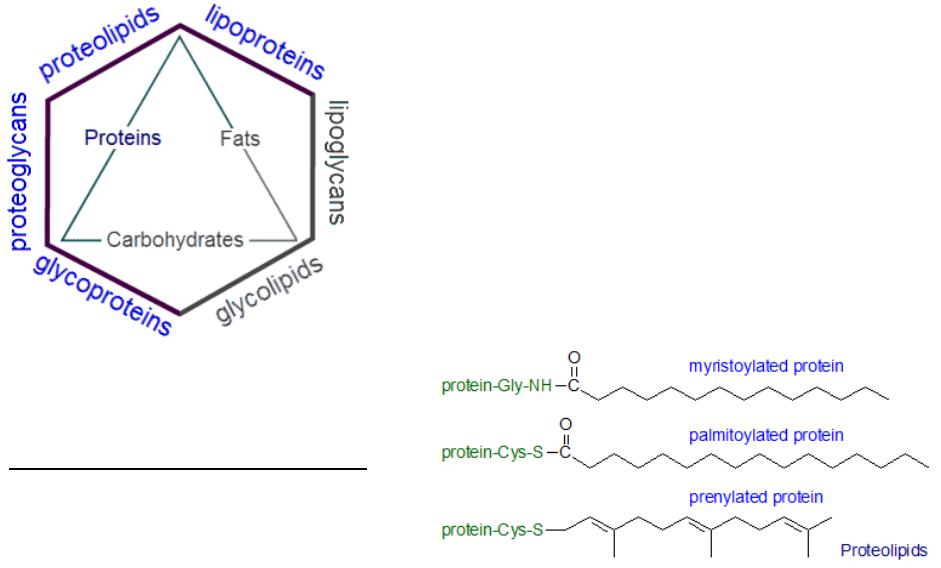
Complex lipids
•Complex lipids include those compounds that, in addition to the lipid component, also contain a non-lipid component — protein (proteolipids), carbohydrate (glycolipids) or phosphate (phospholipids).
•Complex lipids perform plastic functions and are mainly used as structural components of biological membranes.
For example, proteolipids are structural components in the myelin sheaths of nerve cells, in synaptic membranes and in the inner membranes of
mitochondria. |
2 |
|
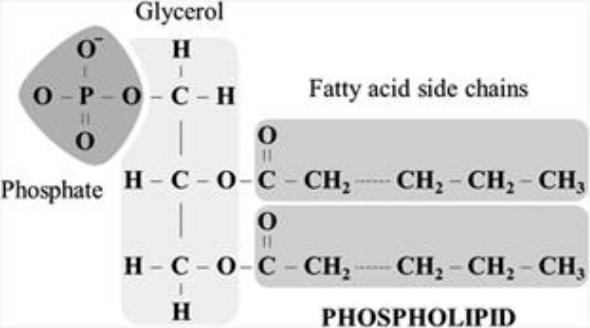
Phospholipids
Phospholipids (PLs) play an important role in the structure and functioning of cell membranes, the activation of membrane and lysosomal enzymes, in the conduct of nerve impulses, blood coagulation, immunological reactions, cell proliferation and tissue regeneration processes, and in electron transfer in cellular respiration .
3
Phospholipid catabolism
The decomposition of phospholipids can occur with the participation of several enzymes, each of which catalyzes the hydrolytic rupture of a strictly defined bond.
Phospholipases are involved in the catabolism of phospholipids, in changing the composition of fatty acids in
phospholipids and the formation of eicosanoids. |
4 |
|
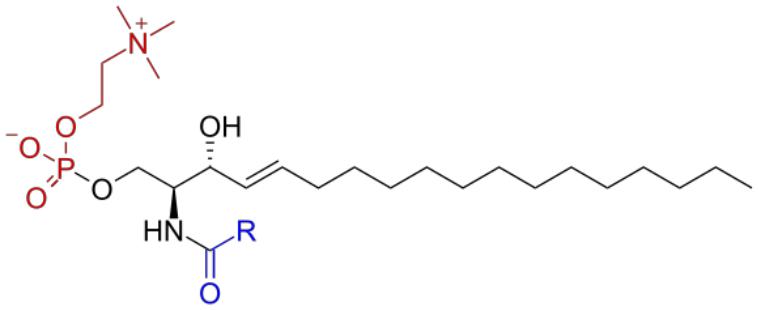
Sphingomyelin catabolism
•The catabolism of sphingomyelins and glycolipids occurs in lysosomes.
•In the breakdown of sphingomyelins, sphingomyelinase, which eliminates phosphocholine, is involved.
•The breakdown of ceramide to sphingosine and a fatty acid is carried out by ceramidase.
5
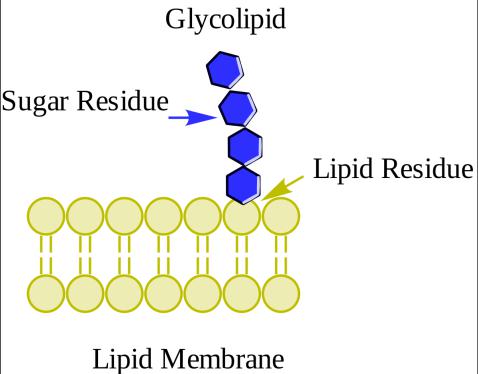
Glycolipids
Glycolipids are involved in the functioning of membranes: are involved in the processes of reception, are involved in the control and regulation of intercellular contacts. They have high tissue specificity and act as antigens of the cell surface.
6
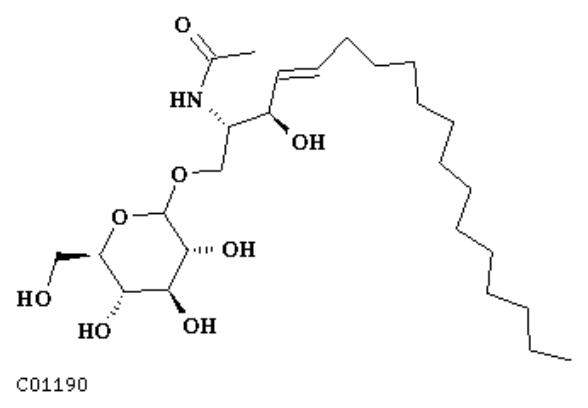
Glycolipid catabolism
Complex glycolipid molecules break down as a result of successive hydrolysis reactions to glucose, galactose, ceramide and other metabolites.
7
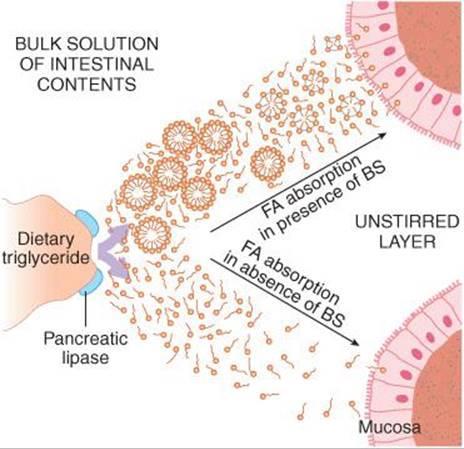
Absorption of lipid breakdown products
The absorption of lipid cleavage products occurs in the small intestine and is determined by the water solubility or water insolubility of the resulting products. Water-soluble substances (glycerin, choline, H3PO4) are easily absorbed by the concentration gradient.
8
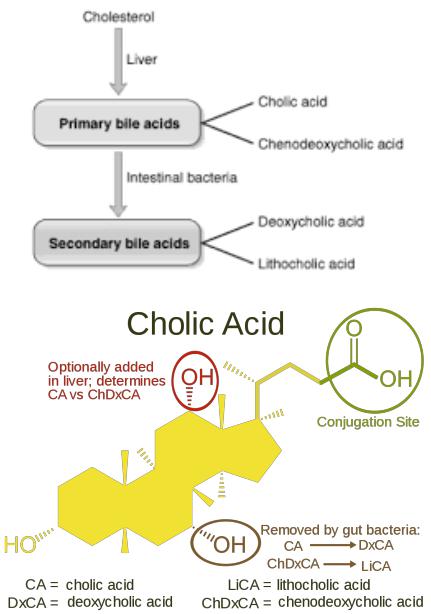
Bile acids
Water-insoluble substances
(cholesterol, long chain fatty acids) cannot be absorbed on their own. Bile acids are involved in their absorption – steroid compounds with 24 carbon atoms are derivatives of cholanic acid having one to three α-hydroxyl groups and a side chain of 5 carbon atoms with a carboxyl group at the end of the chain. In the human body, cholic acid is most important. In bile, at a slightly alkaline pH, it is present as a cholate anion.
9
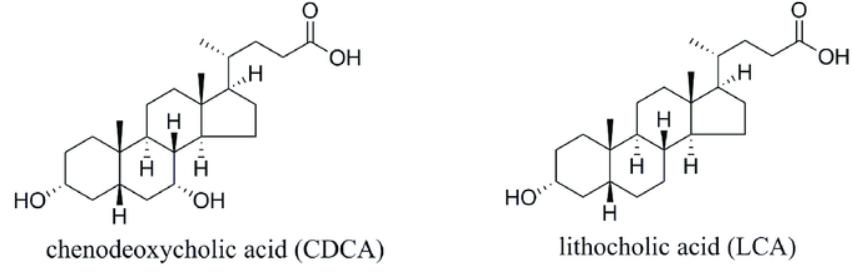
Bile acids
•In addition to cholic acid, bile also contains chenodeoxycholic acid. It differs from the cholic absence of a hydroxyl group at C- 12. Both compounds are called primary bile acids. Quantitatively, these are the most important end products of cholesterol
•The other two acids, deoxycholic and lithocholic, are called secondary bile acids, since they are formed by dehydroxylation of C-7 primary acids in the gastrointestinal tract.
10
