
English Lectures / lipids 2 ENG
.pdf
Fat sources
• On average, 70 g of animal and vegetable fats enters the body of an adult every day with food.
• The end result is the formation of triglycerides of adipose tissue.
• Insulin stimulates this synthesis because in its presence the permeability of the adipose tissue cell membranes to glucose
increases.
21
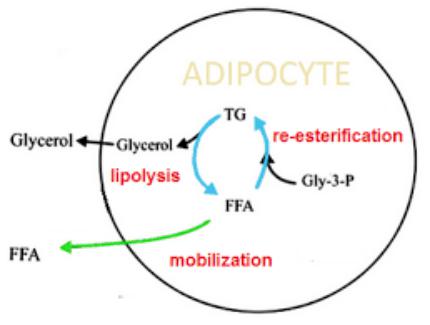
Fat Mobilization
•Most of the blood-transported lipids are deposited in fat depots, which include subcutaneous fat, large and small epiploons.
•Mobilization of deposited fats (lipolysis) is catalyzed by an enzyme called lipase. As a result, fats break down into glycerin and free fatty acids, which from the adipose tissue enter the bloodstream.
•During fasting, when the glucose content in adipose tissue is reduced, the released fatty acids cannot be used by adipose tissue for the resynthesis of triglycerides, and therefore they quickly leave this tissue.
•Glycerin is transported to the liver, where it is used in gluconeogenesis reactions.
•Fatty acids are transported by blood to various organs and tissues, where they are included in the oxidation process22.

Fat mobilization regulation
Mobilization of deposited fats is stimulated by glucagon and adrenaline and, to a lesser extent, by some other hormones (somatotropic, cortisol).
•When fasting, glucagon, acting on adipocytes through the adenylate cyclase system, activates protein kinase A, which phosphorylates and thus activates hormone-sensitive lipase, which initiates lipolysis and the release of fatty acids and glycerol into the blood.
•With physical activity, the secretion of adrenaline increases, which acts through β-adrenergic adipocyte receptors that activate the adenylate cyclase system.
23
Obesity
• Obesity is considered a condition when body weight exceeds 20% of the "ideal" for a given individual.
• Obesity is associated with a decrease in the ability of insulin to stimulate the elimination of peripheral glucose and suppress the release of glucose by the liver. To compensate, the body then increases glucose secretion.
• This insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia can be caused by the flow of free fatty acids to the liver from adipose tissue in the abdominal cavity. Perhaps that is why abdominal obesity is associated with a large number of metabolic complications (impaired lipid metabolism, changes in the level of sex
hormones)
24

Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins (LPs) are the main transport form of lipids. LP differs in density:
-very low density (VLDL);
-low-density (LDL);
-high-density (HDL);
-intermediate density (IDL);
-very high density.

The structure of lipoproteins
•There are several types of ApoPt: A, B, C, E. They form the structure of lipoprotein particles, interact with tissue receptors for LP, and they act as activators of the LP metabolism enzymes.
•All LPs are built on a general principle: in the center of the particle is a hydrophobic core, which includes TAG and cholesterol esters (CE), a hydrophilic shell is formed around it, which includes phospholipids (PL), cholesterol. On the surface are proteins – apoproteins (ApoPt).
26
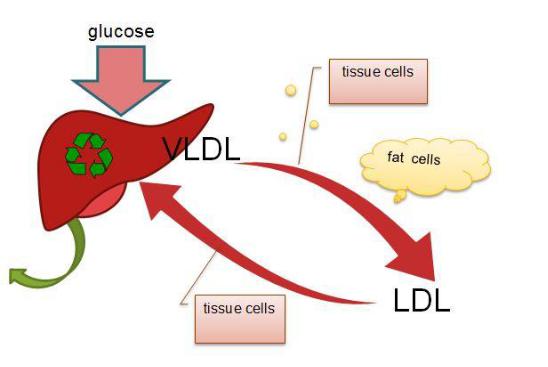
VLDL
VLDL is synthesized in the liver, are considered the main transport form of endogenous lipids. In the vascular endothelium, VLDLP and chylomicrons are exposed to the enzyme lipoprotein lipase, which breaks down TAG in their composition. As a result, the portion of cholesterol in the composition of LP increases, and VLDL are converted into LDL.
27
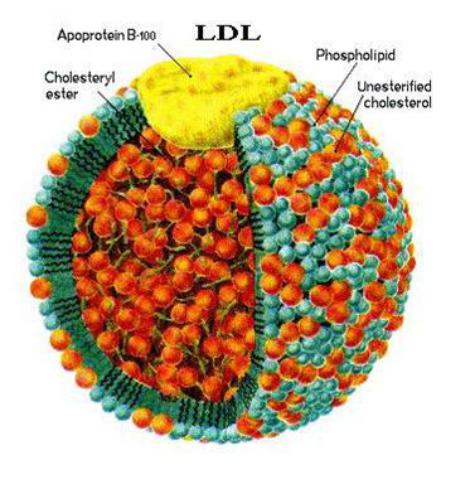
LDL
LDL is considered a transport form of cholesterol from the liver to organs and tissues. There are LDL receptors in the tissues, with the participation of which cholesterol is absorbed and then used to build membranes, synthesize steroids, and deposit it in the form of esters.
28
HDL
HDL is synthesized in the liver as disc-shaped structures. They are considered a transport form of cholesterol from tissues to the liver. In the bloodstream, upon contact with endothelium, cholesterol is absorbed from the tissues and transferred to HDL. They gradually turn into spherical structures and transfer cholesterol to the liver. In the absorption of cholesterol by HDL particles, the enzyme LHAT (lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase) is involved, which, as part of HDL, transfers fatty acid residues from phospholipids to cholesterol to form cholesterol esters. Cholesterol esters are more hydrophobic in comparison with free cholesterol and, due to this, they are immersed inside the LP particles.
29

Lipolysis
Lipids deposited in fat depots, as necessary, can again transfer to blood plasma (the so-called mobilization of fat), after which they are used by tissues as energy or plastic (building) material. The main endogenous source of lipids used as a metabolic “fuel” is reserve fat (mainly triacylglycerols), which is contained in the cytoplasm of cells in the form of droplets. Another source is membrane phosphatides undergoing continuous renewal.
30
