
English Lectures / lipids 2 ENG
.pdf
Lipolysis
The first step in using fat in tissues as an energy material is to break it down to form glycerol and higher fatty acids. This process is catalyzed by tissue lipases.
•Phosphorylated (active) triglyceride lipase breaks down the triglyceride into diglyceride and fatty acid.
•Then, under the action of diand monoglyceride lipases, the final products of lipolysis are formed - glycerol and fatty acids.
•In the future, glycerol and fatty acids are oxidized in the
tissues to CO2 and H2O. The chemical energy released in this case is partly accumulated in the ATP anhydride phosphate bonds, and partly passes into heat.
31
Lipolysis
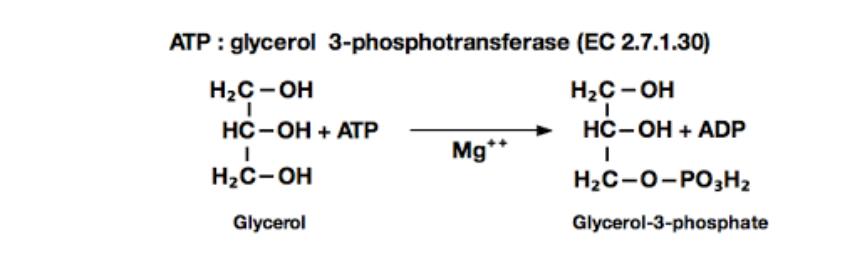
•Glycerin, regardless of whether it enters the resynthesis of fats or will undergo further decay, is primarily phosphorylated.
•The donor of the phosphoric acid residue in this reaction is ATP.
•The process is accelerated by the corresponding phosphotransferase, called glycerokinase.
•Phosphoglycerol (glycerophosphate) is oxidized in the tissues to phosphoglycerol aldehyde via phosphodioxiacetone.
Lipolysis
Pyruvic acid, by oxidative decarboxylation, is converted to acetyl-CoA, which is involved in the citric acid cycle coupled to the chain of respiratory enzymes and is oxidized to CO and H2O.
•When glycerol is oxidized to CO2 and H2O, three ATP molecules, one molecule, first appear during the oxidation of phosphoglycerol aldehyde ATP is synthesized during the oxidation of 1,3- diphosphoglyceric acid.
•One ATP molecule is formed during the oxidation of 2- phosphoenolpyruvic acid.
•Finally, 15 ATP molecules are formed during the oxidation of pyruvic acid slots in the citric acid cycle.
33

Lipolysis and beta oxidation
34
β-oxidation of fatty acids
β-oxidation reactions occur in the mitochondria of most body cells (except nerve cells). For oxidation, fatty acids are used, which enter the cytosol from the blood or appear during the lipolysis of intracellular TAGs.
β-oxidation consists in the gradual cleavage of two carbon atoms from fatty acid in the form of acetyl - CoA with the release of energy. The supply of fatty acids in cells is concentrated in the cytosol, where the activation of fatty acids with the formation of acyl-CoA
35
Fatty acid oxidation steps
1. Before entering the mitochondrial matrix and oxidizing, the fatty acid must be activated in the cytosol. This is accomplished by the addition of coenzyme A to it with the formation of acylScoA. Acyl-SCoA is a high-energy compound. The irreversibility of the reaction is achieved by hydrolysis of diphosphate into two phosphoric acid molecules.
36
Fatty acid oxidation steps
2. Acyl-SCoA is not able to pass through the mitochondrial membrane, therefore, there is a method of transferring fatty acids in combination with a vitamin-like substance carnitine (vitamin B11). On the outer membrane of mitochondria there is an enzyme carnitine acyltransferase I.
37
Fatty acid oxidation steps
3. After binding to carnitine, the fatty acid is transferred through the internal mitochondrial membrane by translocase. On the inner side of this membrane, the carnitine acyltransferase II enzyme again forms acyl-ScoA, which enters the β-oxidation pathway.
38
Fatty acid oxidation steps
4. The actual process of β-oxidation consists of 4 reactions that are repeated cyclically. Oxidation (acyl-ScoA-dehydrogenase), hydration (enoyl-ScoA- hydratase), and re-oxidation of the 3rd carbon atom (hydroxyacyl-ScoA-dehydrogenase) sequentially occur in them. In the last transferase reaction, acetyl-ScoA is cleaved from the fatty acid. HS-CoA is added to the remaining (shortened by two carbon) fatty acid, and it returns to the first reaction. Everything is repeated until two acetylScoA are formed in the last cycle.
39
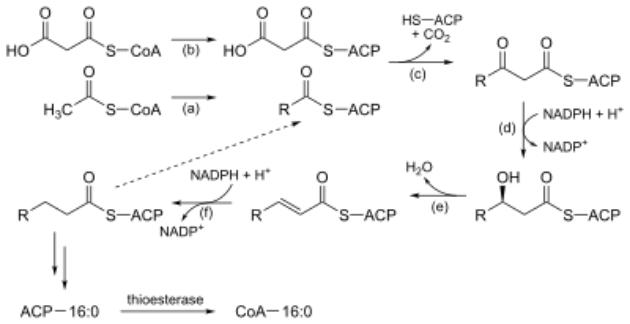
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
Stages of biosynthesis can be distinguished:
1.The formation of acetyl-ScoA from glucose, other monosugars or ketogenic amino acids.
2.Transfer of acetyl-ScoA from mitochondria to the cytosol:
-may be in complex with carnitine, similar to how higher fatty acids are transferred inside the mitochondria, but here transport goes in a different direction,
-usually in the composition of citric acid formed in the first reaction of CTK.
40
