
English Lectures / lipids 1 ENG
.pdf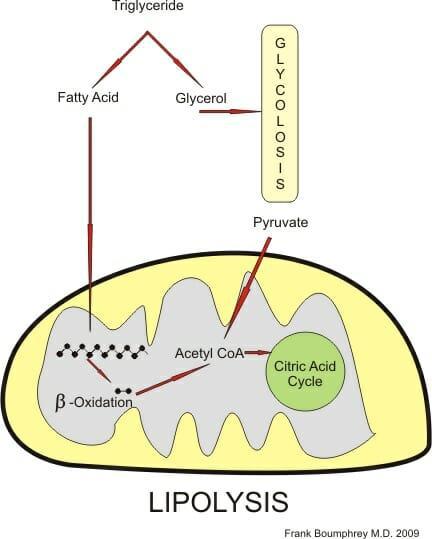
Lipolysis
•Lipolysis is the hydrolysis of lipids. Lipolytic enzymes are hydrolases that catalyze lipid hydrolysis. Lipases break down triacylglycerides (fats), phospholipases – phospholipids, cholesterases - cholesterol esters.
•Lipolytic enzymes exhibit maximum activity at pH = 7.8-8.2. In the oral cavity, fats do not undergo chemical changes due to the absence of lipolytic enzymes.
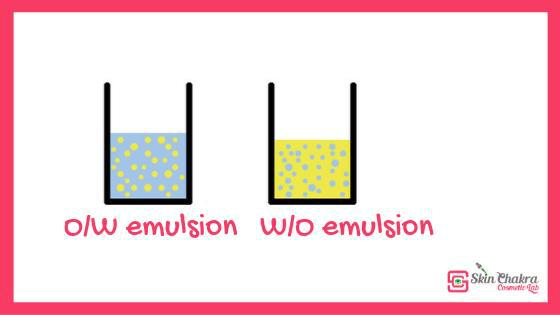
Emulsions
•The effect on fats of lipases becomes possible after emulsification of fats, because lipids are insoluble in water and they are exposed to lipolytic enzymes only at the phase boundary and, therefore, the rate of digestion depends on the surface area.
•An emulsion is a dispersed system of two immiscible liquids, of which one is in a fragmented state (in the form of droplets) in the mass of the other. When emulsifying fats, their total surface increases, which improves the contact of fat with lipase and accelerates its hydrolysis. In the body, the main emulsifiers are bile salts.
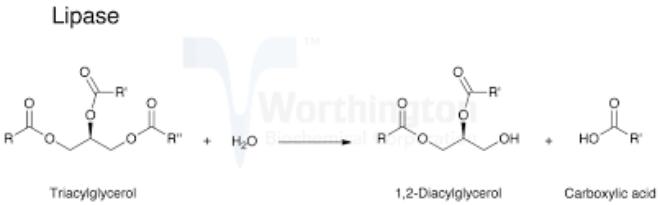
Lipases
In the stomach, the lipase content is extremely low, in addition, the pH of the gastric juice (1.0-1.5) does not correspond to the optimum pH of the lipase (5.5-7.5), and there are no fat emulsifiers in the stomach, so gastric lipase can only break down pre-emulsified fats (milk or egg yolk fats).

Lipases
•The department in which the bulk of the lipids is digested is the small intestine, where there is a slightly alkaline environment that is optimal for lipase activity. The neutralization of hydrochloric acid from food is carried out by bicarbonates contained in pancreatic and intestinal juices.
•The pancreas and cells of the intestinal mucosa secrete lipolytic enzymes. Bile entering the intestine contains bile salts that emulsify fat and increase lipase activity 10-15 times.
•The bulk of food lipids is represented by triacylglycerols (fats). Fats are hydrolyzed by lipase by 90-97%, of which 40% is broken down into glycerol and fatty acids, the rest to b (2) monoglycerides.
Lipases
•Pancreatic lipase catalyzes the hydrolysis of ether bonds only in a (1), a ′ (3) positions.
•In addition to lipase, pancreatic juice contains monoglyceride isomerase, an enzyme that catalyzes the intramolecular transfer of acyl from the b (2) position of the monoglyceride to the a (1) position.
•During the digestion of edible fats with the participation of this enzyme, approximately a third of b
(2)-monoglycerides is converted to a-monoglycerides, which are further broken down by pancreatic lipase to glycerol and fatty acids. Complete hydrolysis of triacylglycerides occurs in stages.

Digestion of fats in the gastrointestinal tract
